- IRS forms
- Form 940-Schedule R
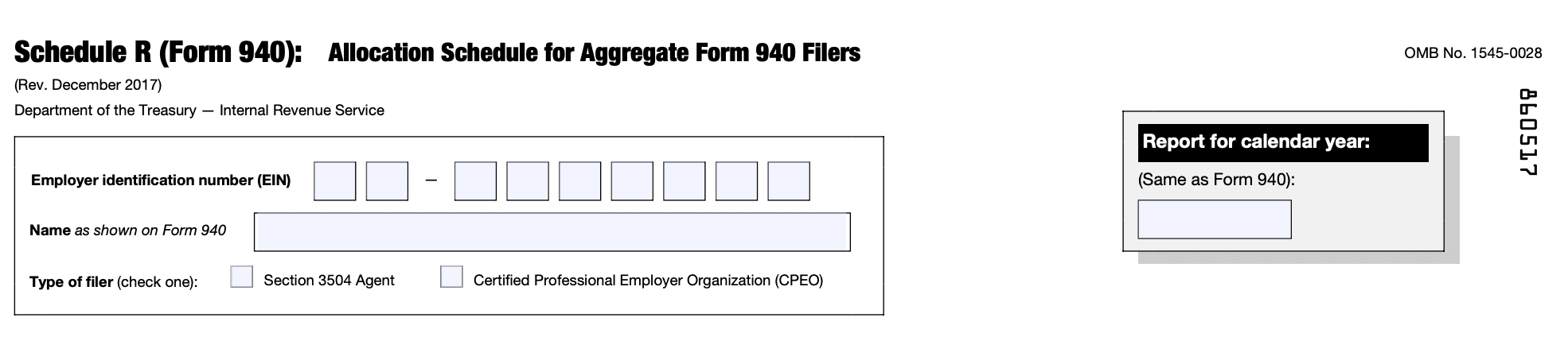
Form 940-Schedule R: Allocation Schedule for Aggregate Form 940 Filers
Download Form 940-Schedule RWhen it comes to payroll taxes, employers in the United States are required to file various forms to report their tax obligations accurately. One such form is Form 940, also known as the Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return. For employers who file Form 940 as part of an aggregated filing, they must also complete Schedule R: Allocation Schedule for Aggregate Form 940 Filers.
Before we dive into the details of Schedule R, it's important to understand what it means to be an aggregate Form 940 filer. When multiple entities are related or under common control, they may choose to file a consolidated Form 940 on behalf of all the related entities. This aggregated filing simplifies the reporting process and avoids the need for each entity to file separate forms. However, to ensure accurate reporting, Schedule R is utilized to allocate the FUTA tax liability among the related entities.
In this blog post, we will delve into the purpose of Form 940 Schedule R, its significance, and how employers can navigate this section effectively.
Purpose of Form 940: Schedule R
The purpose of Schedule R is to determine if an employer is eligible for the credit and to calculate the amount of credit they can claim.
The credit for employer social security taxes paid on tips is available to employers who operate establishments where tipping is customary, such as restaurants. This credit allows employers to claim a portion of the social security taxes they pay on employee tips as a credit against their federal tax liability.
To complete Schedule R, employers must gather information about the tips reported by their employees and the social security taxes they paid on those tips. They must also calculate the applicable credit rate based on the employer's type of business.
By completing Schedule R, employers can determine the amount of credit they are eligible for and report it on Form 940, which is the Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return. This credit reduces the overall tax liability for the employer, providing them with a potential tax savings.
Benefits of Form 940: Schedule R
Schedule R is an additional form that accompanies Form 940 and is used to calculate the FUTA tax credit for certain state unemployment taxes paid.
Here are some benefits of using Schedule R with Form 940:
-
FUTA tax credit: Schedule R allows employers to claim a credit for the state unemployment taxes they paid during the tax year. This credit helps offset the federal unemployment tax liability. The credit is available to employers who are subject to both federal and state unemployment taxes and have paid their state unemployment taxes in full and on time.
-
Reduced tax liability: By claiming the FUTA tax credit on Schedule R, employers can reduce their overall FUTA tax liability. The credit is calculated based on the amount of state unemployment tax paid, and it can significantly lower the amount owed in federal unemployment taxes.
-
Avoidance of double taxation: The FUTA tax credit helps prevent double taxation for employers who are subject to both federal and state unemployment taxes. It ensures that employers do not pay both state and federal unemployment taxes on the same wages.
-
Encouragement of state unemployment programs: The availability of the FUTA tax credit through Schedule R encourages employers to participate in state unemployment programs and contribute to the state's unemployment insurance fund. This helps support the state's unemployment benefits system, which provides financial assistance to eligible workers who are unemployed.
-
Compliance with federal reporting requirements: Schedule R ensures that employers accurately report their state unemployment tax payments and claim the appropriate FUTA tax credit on their Form 940. By providing a separate schedule for this purpose, it helps streamline the reporting process and ensures compliance with federal tax regulations.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 940: Schedule R?
Schedule R is used by employers who are required to file Form 940 but also have locations in multiple states with different unemployment tax rates.
The following employers are eligible to file Form 940: Schedule R:
Employers with multiple locations: If you are an employer with operations or locations in more than one state and the state unemployment tax rates vary, you may be required to file Schedule R. This form helps you allocate the FUTA tax liability among the different states based on the respective state unemployment tax rates.
Household employers: If you are a household employer and you have multiple household employees working in different states, you may also need to file Schedule R to allocate the FUTA tax liability appropriately.
It's important to note that not all employers are required to file Schedule R. If you are a single-state employer or your business operates in multiple states with the same unemployment tax rate, you may not need to file Schedule R.
How To Complete Form 940-Schedule R: A Step-by-Step Guide
Given below is a step-by-step guide to completing Form 940-Schedule R:
Step 1: Obtain the necessary forms
Download Form 940-Schedule R from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website or obtain a physical copy from an IRS office.
Step 2: Provide general information
At the top of the form, enter your business's name, address, and employer identification number (EIN). Make sure the information is accurate and up to date.
Step 3: Enter the total compensation subject to RRTA (Railroad Retirement Tax Act)
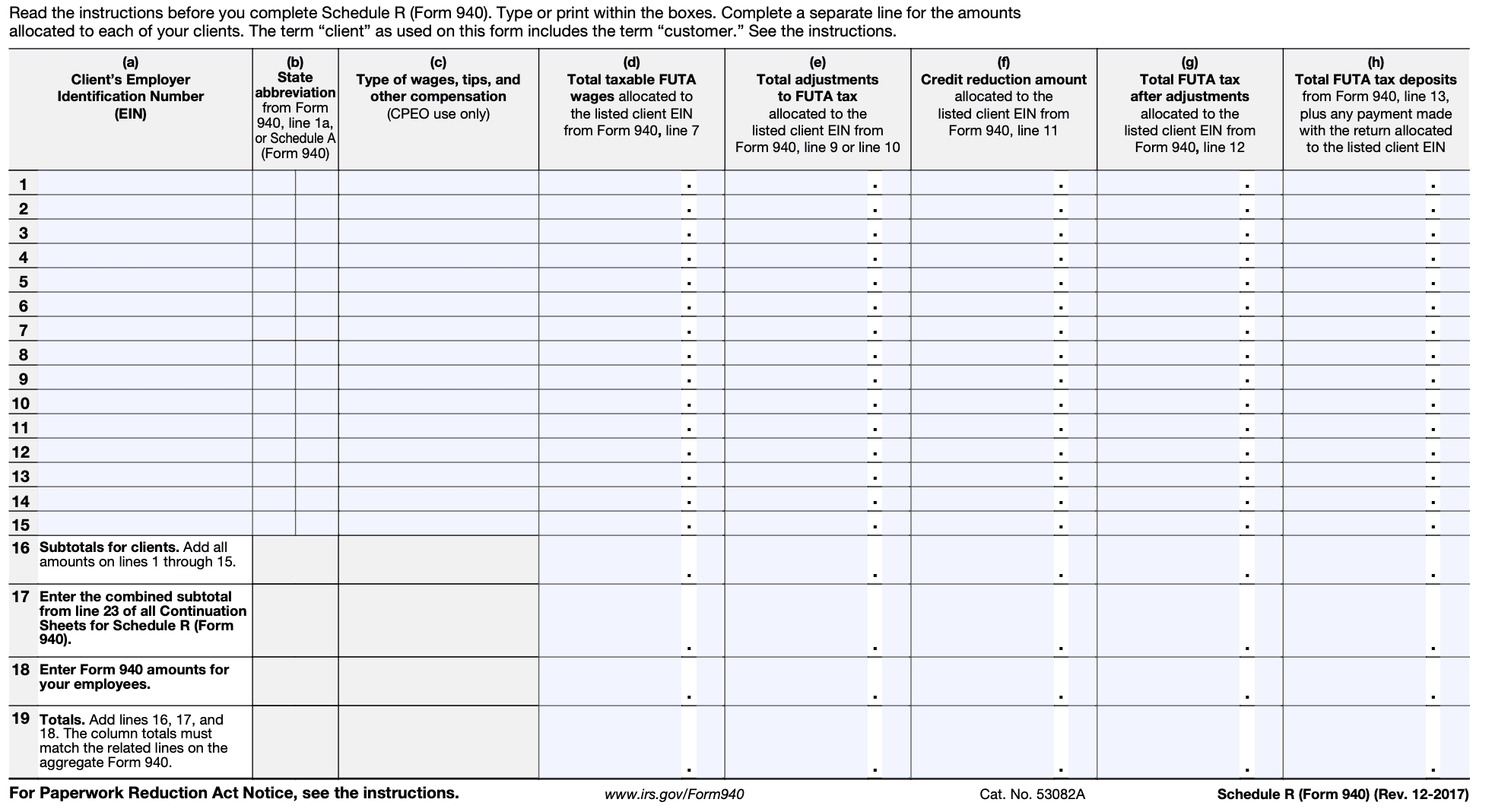
In Part I of Schedule R, you need to enter the total compensation subject to RRTA tax. This information is typically found on your payroll records. Report the total compensation for each employee who received compensation subject to RRTA tax during the year.
Step 4: Calculate the RRTA tax credit
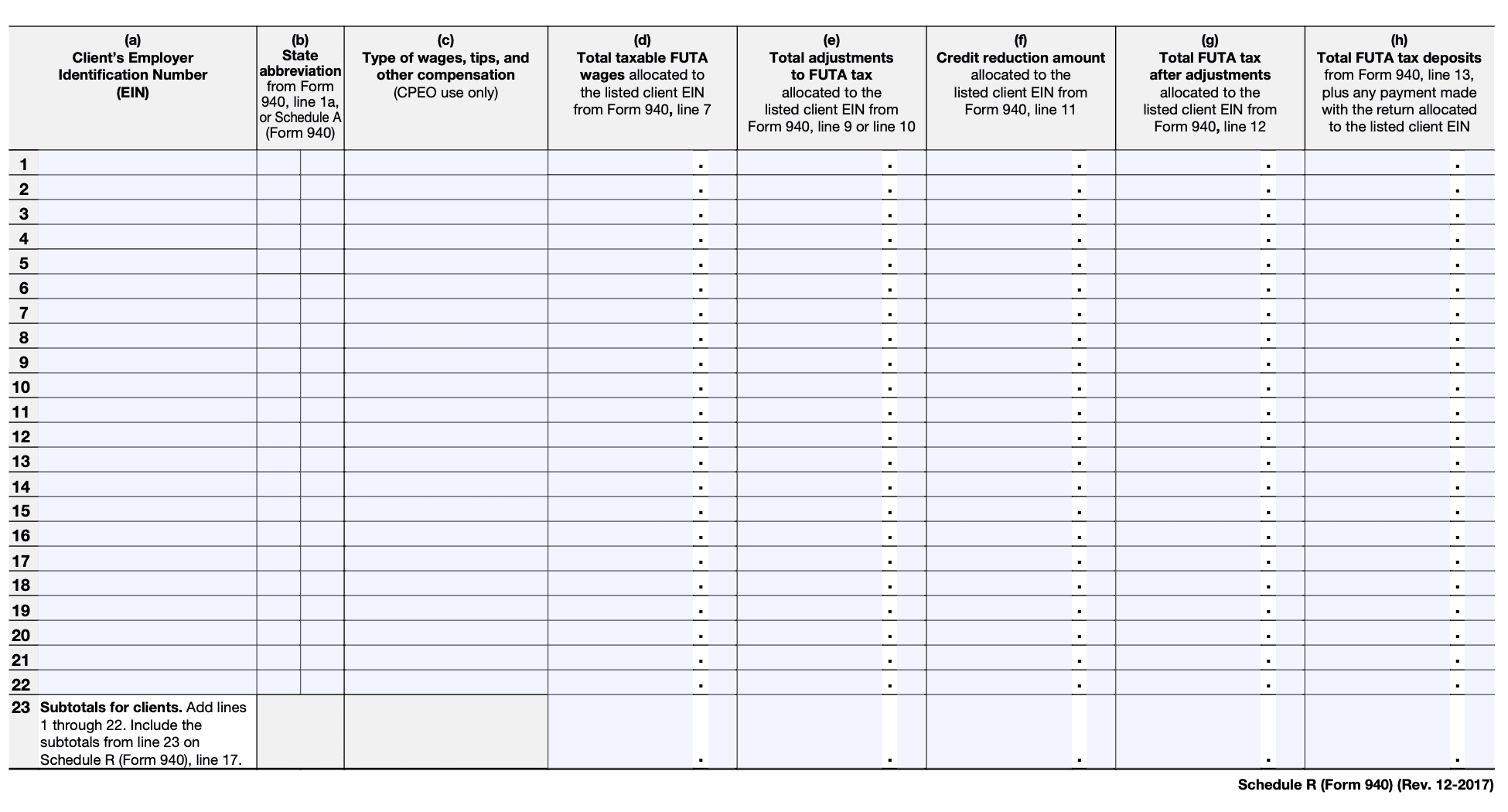
In Part II of Schedule R, you will calculate the credit for the portion of the RRTA tax that exceeds the unemployment tax. This calculation involves subtracting the unemployment tax from the RRTA tax. Refer to the instructions provided with the form for the specific calculation method.
Step 5: Determine the credit reduction
If you were subject to the credit reduction in a prior year, you need to determine if the reduction applies again. Follow the instructions provided with the form to determine if the credit reduction applies and calculate the amount accordingly.
Step 6: Calculate the allowable credit
In Part III of Schedule R, you will calculate the allowable credit. Subtract any credit reduction from the RRTA tax credit calculated in Part II. This will give you the allowable credit for the year.
Step 7: Report the credit on Form 940
Transfer the allowable credit amount from Part III of Schedule R to the appropriate line on Form 940. Make sure to accurately complete Form 940 in conjunction with Schedule R to ensure accurate reporting.
Step 8: Review and sign
Review all the information on Form 940-Schedule R for accuracy and completeness. Sign and date the form before submitting it to the IRS.
Step 9: Retain a copy
Make a copy of the completed Form 940-Schedule R for your records. It's important to keep a copy for your files in case of any future inquiries or audits.
Step 10: Submit the form
Send the original Form 940-Schedule R to the IRS along with your Form 940 and any other required tax documents by the due date specified by the IRS. It is recommended to use certified mail or a reliable delivery service to ensure proper delivery and to retain proof of submission.
It's worth noting that tax forms and instructions may change over time. Therefore, it's important to refer to the most recent version of Form 940-Schedule R and the corresponding IRS instructions when completing the form.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 940-Schedule R
Here are some special considerations when filing Form 940-Schedule R:
Multiple establishments: Schedule R is used when an employer has more than one establishment and wants to allocate the FUTA tax liability among those establishments. You'll need to provide the details of each establishment, such as name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN), along with the allocated wages and tax liabilities.
EIN and name control: Ensure that you enter the correct Employer Identification Number (EIN) and name control for each establishment. The EIN uniquely identifies each establishment, and the name control should match the name used on the respective establishment's tax return.
Allocated wages and tax liability: Schedule R requires you to allocate both the wages paid and the FUTA tax liability among the different establishments. You'll need to calculate the allocated wages based on the total wages paid by all establishments and the proportionate share of each establishment's wages.
Similarly, the allocated tax liability is calculated based on the total FUTA tax liability and the proportionate share for each establishment.
Signature and date: The Form 940-Schedule R should be signed and dated by an authorized person representing the employer. The signature affirms that the information provided is true, correct, and complete.
Attachments: If you're filing Form 940-Schedule R with Form 940, make sure to attach Schedule R to the Form 940 when submitting it to the IRS. Keep a copy of the complete filing for your records.
Timely filing: Ensure that you file Form 940-Schedule R and Form 940 by the due date. The due date for Form 940 is generally January 31 of the year following the tax year, unless it falls on a weekend or holiday.
Filing Deadlines & Extensions on Form 940-Schedule R
The filing deadlines and extensions for Form 940-Schedule R may vary depending on the tax year and any updates made by the IRS. It's important to consult the most recent IRS instructions or visit the official IRS website for the most up-to-date information.
Generally, Form 940-Schedule R is filed along with Form 940, which is the Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return. The standard due date for filing Form 940 is January 31 of the following year. However, if you timely deposit all the FUTA tax owed, you have an additional 10 calendar days to file, making the due date February 10.
In certain circumstances, you may be eligible for an extension of time to file Form 940. To request an extension, you can file Form 8809, Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns, with the IRS before the original due date of Form 940. This will grant you an additional 6 months to file, extending the due date to August 31.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 940-Schedule R
When filing Form 940-Schedule R, which is used to allocate the credit for employer-paid social security tax on qualified sick and family leave wages, it's important to be careful and avoid common mistakes. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Incorrect calculations: Double-check all calculations and ensure that the amounts entered on the form are accurate. Math errors can lead to discrepancies and potential penalties.
Incorrect identification numbers: Make sure to provide the correct Employer Identification Number (EIN) on the form. Using an incorrect or outdated EIN can cause delays in processing or result in incorrect allocation of credits.
**Failure to attach supporting documents: **Ensure that you attach all necessary supporting documentation, such as Form 941, Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return, and Form W-2 for each employee. These documents are required to substantiate the allocation of credits.
Missing or incomplete information: Fill out all the required fields on the form accurately and completely. Provide the necessary details about the employer, employee, and the wages subject to the credit. Omissions or incomplete information may lead to processing delays or the rejection of your form.
**Late filing: **Be mindful of the filing deadline for Form 940-Schedule R, which is generally the same as the deadline for Form 940. Failing to file the form on time can result in penalties and interest charges.
Failure to reconcile with other forms: Ensure that the information provided on Form 940-Schedule R aligns with other related forms, such as Form 941 and Form W-2. Inconsistencies or discrepancies between forms can raise red flags and may trigger further scrutiny.
Ignoring updates or changes: Stay informed about any updates or changes to the form instructions or requirements. The IRS may periodically update the form, so it's essential to use the most recent version and follow the latest instructions.
Conclusion
Form 940 Schedule R plays a crucial role in accurately allocating the FUTA tax liability among related entities filing an aggregated Form 940. By properly completing this allocation schedule, employers can ensure compliance with IRS regulations and maintain transparent reporting.
It is essential to gather all the necessary information and carefully follow the instructions to complete Schedule R accurately. In case of any doubts or complexities, consulting a tax professional or referring to the official IRS instructions can provide additional guidance.


