- IRS forms
- Form 1099-INT
Form 1099-INT: Interest Income
Download Form 1099-INTFor individuals who earn interest income, it is essential to be familiar with the various tax forms involved in reporting such earnings. One such form is the Form 1099-INT, which is used to report interest income received from various sources. Whether you're earning interest from a bank account, a certificate of deposit, or other financial instruments, understanding Form 1099-INT is crucial for accurate tax reporting.
Form 1099-INT, also known as the "Interest Income" form, is a tax document that financial institutions and other payers use to report interest income of $10 or more to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the recipient. The form serves as a record of the interest income earned by an individual during a tax year.
In this blog post, we will delve into the details of Form 1099-INT, its purpose, who receives it, and how to use it when filing your taxes.
Purpose of Form 1099-INT
Form 1099-INT is a tax form used in the United States to report interest income received by individuals or businesses. The purpose of Form 1099-INT is to provide information to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) about the amount of interest income that a taxpayer has earned during a tax year. The form is typically issued by banks, financial institutions, or other entities that pay interest to individuals or businesses.
The information reported on Form 1099-INT includes the total amount of interest income earned, any federal income tax withheld from the interest payments, and certain other details related to the interest-bearing account or investment. This form helps the IRS ensure that taxpayers accurately report their interest income and comply with their tax obligations.
Recipients of Form 1099-INT must include the information from the form when filing their federal income tax returns. The amounts reported on the form are generally taxable and should be included as part of the recipient's gross income. However, there may be some exceptions or special rules that apply to certain types of interest income, such as tax-exempt interest or interest earned on certain savings bonds.
Benefits of Form 1099-INT
Form 1099-INT is a tax form used to report interest income earned from various sources. There are several benefits associated with Form 1099-INT:
-
Accurate tax reporting: Form 1099-INT ensures accurate reporting of interest income received by taxpayers. It provides a clear breakdown of the interest earned from different sources, such as bank accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), bonds, and loans. This helps individuals and businesses accurately report their income on their tax returns.
-
Documentation for deductions: Form 1099-INT provides important documentation for taxpayers who want to claim deductions related to interest expenses. For example, if you have paid interest on student loans or mortgage loans, the form helps verify the deductible amount, enabling you to maximize your eligible deductions.
-
Compliance with tax laws: Form 1099-INT is required by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to ensure compliance with tax laws. Financial institutions and other entities that pay interest to individuals or businesses are required to report this income to the IRS using Form 1099-INT. By providing this information, taxpayers are able to fulfill their tax obligations and avoid potential penalties for underreporting income.
-
Enhanced financial record-keeping: Form 1099-INT serves as a useful financial record. It provides a summary of the interest income received during the tax year, making it easier to track and organize your finances. This documentation can be helpful for personal financial management, budgeting, and future tax planning.
-
Potential eligibility for tax credits: In some cases, interest income reported on Form 1099-INT may qualify for certain tax credits. For example, if you received tax-exempt interest from municipal bonds, you may be eligible for the federal tax exemption. By accurately reporting your interest income using Form 1099-INT, you can determine if you meet the criteria for any applicable tax credits.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 1099-INT?
The following individuals or entities are generally eligible to file Form 1099-INT:
**Individuals: **Any individual who has received interest income of $10 or more during the tax year must file Form 1099-INT. This includes individuals who earn interest on bank accounts, savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), or other interest-bearing accounts.
Partnerships: Partnerships must file Form 1099-INT to report interest income earned by the partnership.
Corporations: Corporations must file Form 1099-INT to report interest income received by the corporation.
Estates and trusts: Estates and trusts that have received interest income of $10 or more must file Form 1099-INT to report the income.
Financial institutions: Banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions are also required to file Form 1099-INT to report interest income paid to their customers.
How To Complete Form 1099-INT
Completing Form 1099-INT is relatively straightforward. Here are the general steps to complete the form:
Step 1: Obtain the necessary information
Gather all the required information for Form 1099-INT. This includes the payer's name, address, and tax identification number (TIN), as well as the recipient's name, address, and TIN.
Step 2: Identify reportable interest income
Determine the total amount of interest income you paid to the recipient during the tax year. This may include interest earned on savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), loans, or other financial instruments.
Step 3: Fill out recipient information
In the recipient's section, enter the recipient's name, address, and TIN. If the recipient doesn't provide their TIN, you may need to withhold backup withholding taxes.
Step 4: Complete the payer information
In the payer's section, enter your business or organization's name, address, and TIN.
Step 5: Report interest income
Box 1 of Form 1099-INT is used to report the total interest income paid to the recipient during the tax year. Enter the appropriate amount in this box.
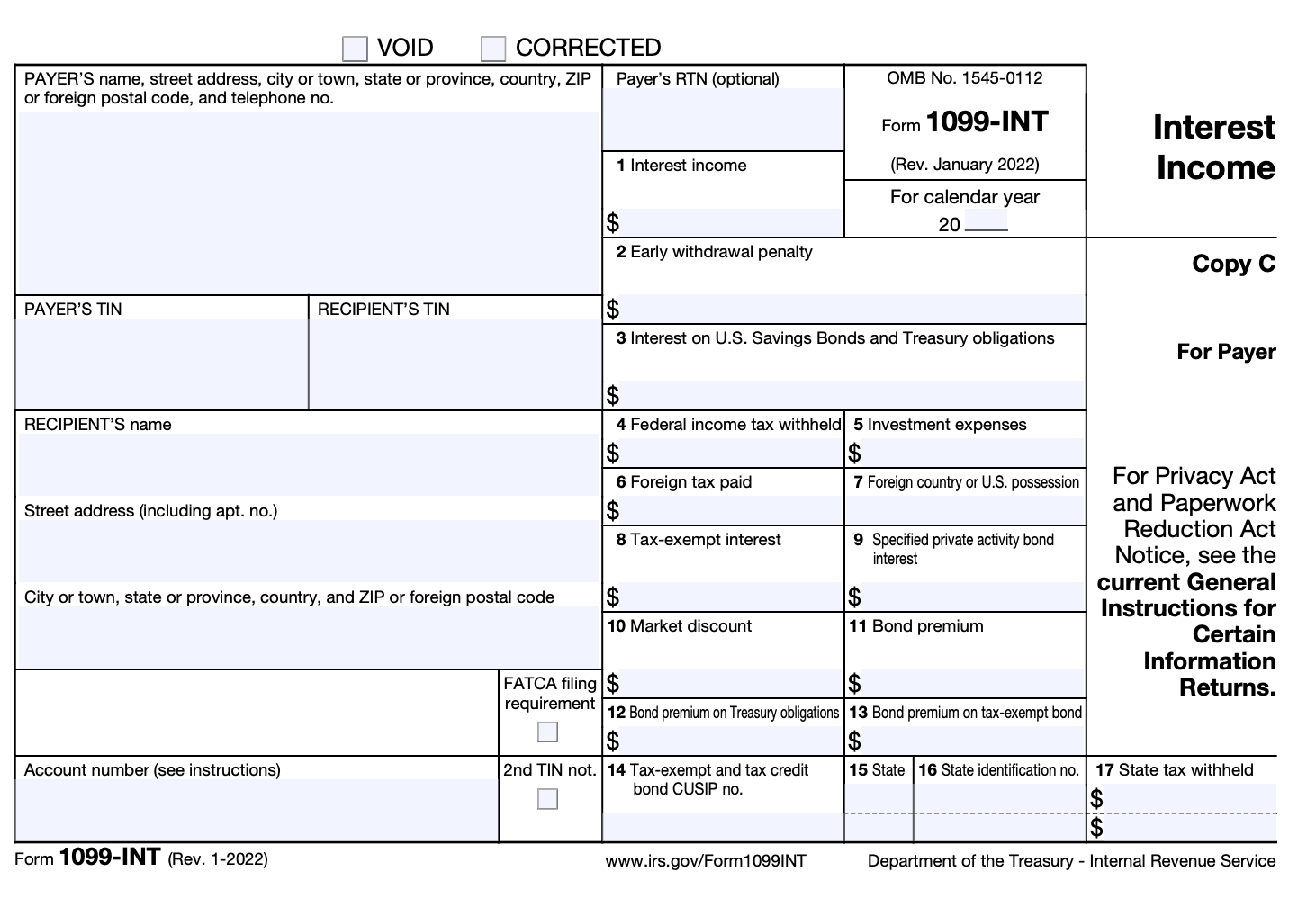
Step 6: Report early withdrawal penalties
If you withheld any early withdrawal penalties on interest-bearing accounts, such as CDs, report that amount in Box 2.
Step 7: Specify federal income tax withheld
If you withheld any federal income tax from the interest income, report the amount in Box 4.
Step 8: Additional information
If there are any other relevant details or codes required for reporting purposes, you can enter them in the appropriate boxes or provide explanations in Box 6.
Step 9: Duplicate copies
Form 1099-INT is typically provided in triplicate, with one copy going to the recipient, one to the IRS, and one for your records. Make sure to complete all the necessary copies.
Step 10: File and distribute
Send Copy A of Form 1099-INT to the IRS, along with the transmittal form, which is usually Form 1096. Provide Copy B to the recipient by the deadline, which is usually January 31st following the tax year. Retain Copy C for your records.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 1099-INT
When filing Form 1099-INT, which is used to report interest income, there are several special considerations to keep in mind. Here are some important points:
Correctly identifying the recipient: Ensure that you have the correct recipient's information, including their name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN). The TIN can be their Social Security number (SSN) or employer identification number (EIN).
**Reporting threshold: **You are required to file Form 1099-INT if you paid at least $10 in interest to the recipient during the tax year. However, it's good practice to issue a Form 1099-INT for any amount of interest income paid, regardless of the threshold.
Multiple recipients: If you made interest payments to multiple recipients, you need to file a separate Form 1099-INT for each recipient. Ensure that you have accurate and separate information for each recipient.
Accurate interest reporting: Report the correct amount of interest income on Form 1099-INT. Ensure that you include all taxable interest paid to the recipient during the tax year, including both cash and non-cash payments.
Tax-exempt interest: If you paid tax-exempt interest, such as interest on municipal bonds, you still need to report it on Form 1099-INT. However, you should indicate the tax-exempt status of the interest on the form.
Deadline: The deadline for filing Form 1099-INT with the IRS is typically January 31st of the year following the tax year. However, if you're filing electronically, the deadline may be extended to March 31st. Ensure you comply with the applicable deadline to avoid penalties.
Furnishing copies to recipients: You are also required to provide a copy of Form 1099-INT to the recipient by January 31st of the year following the tax year. Furnish the form to the recipient to meet this requirement.
Penalties: Failure to file Form 1099-INT or furnishing incorrect information can result in penalties. The penalties vary depending on the delay period and the size of your business.
How To File Form 1099-INT: Offline/Online/E-filing
To file Form 1099-INT, you have the option to file it offline, online, or through e-filing. Here's a breakdown of each method:
Offline filing
a. Obtain the physical Form 1099-INT from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or an authorized distribution source.
b. Fill out the form with the necessary information, including your personal information, recipient's information, and interest income details.
c. Make copies of the form for your records.
d. Mail the completed Form 1099-INT to the appropriate IRS address, which can vary based on your location. Check the instructions provided with the form or the IRS website for the correct address.
Online filing
a. Access the IRS website (www.irs.gov) and search for the "Online Filing" section.
b. Follow the instructions to create an account or log in if you already have one.
c. Select the appropriate option for filing Form 1099-INT online.
d. Fill out the required information in the online form, following the prompts provided.
e. Review the form for accuracy and completeness.
f. Submit the form electronically through the online platform.
E-filing
a. Use a tax software or accounting software that supports e-filing of Form 1099-INT.
b. Enter the required information into the software, including your personal information, recipient's information, and interest income details.
c. Review the form for accuracy and completeness.
d. When ready, select the option to e-file the Form 1099-INT.
e. Follow the prompts to transmit the form electronically to the IRS.
Regardless of the filing method you choose, it's essential to keep copies of the Form 1099-INT and any related documentation for your records.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Filing Form 1099-INT
When filing Form 1099-INT, which is used to report interest income, it's important to be accurate and avoid common mistakes. Here are some common errors to avoid:
Incorrect recipient information: Ensure that the recipient's name, address, and Social Security number or taxpayer identification number (TIN) are accurately entered on the form. Double-check the details to prevent any typographical errors.
Missing or incorrect TIN: It is crucial to obtain the correct TIN from the recipient. If the recipient fails to provide their TIN, you should make reasonable efforts to obtain it. Failure to include or report the TIN accurately may result in penalties.
Failure to report all interest income: Make sure you report all interest income earned during the tax year on Form 1099-INT. Include interest income from bank accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), savings accounts, loans, and any other applicable sources.
Omitting backup withholding: If backup withholding is required, ensure that you indicate it on the form. Backup withholding is when a payer withholds a portion of the payment to ensure the IRS receives the appropriate tax amount.
Incorrect amounts reported: Be diligent in reporting the correct amounts on Form 1099-INT. Double-check the calculations and ensure that you include interest earned, early withdrawal penalties, and any other relevant amounts.
Filing late or failing to file: Ensure that you meet the deadline for filing Form 1099-INT. The due date is typically January 31 of the following year, but it may vary based on certain circumstances. Failing to file or filing late can result in penalties.
Using the wrong form: Make sure you are using the correct version of Form 1099-INT for the tax year you are reporting. The form may undergo periodic updates, so always use the most recent version available from the IRS.
Neglecting to provide copies to recipients and the IRS: After completing Form 1099-INT, provide a copy to the recipient by January 31, and file the form with the IRS. Failing to provide copies to the recipient or the IRS can lead to penalties.
Not keeping proper records: Maintain accurate records of all Form 1099-INT filings, including copies of the forms, receipts, and other relevant documents. These records will be helpful in case of any discrepancies or audits.
Ignoring state filing requirements: In addition to the federal filing requirements, some states may have their own reporting requirements for interest income. Research and comply with the specific state regulations to ensure compliance.
Conclusion
Form 1099-INT is an important tax document that ensures accurate reporting of interest income earned throughout the year. By understanding the purpose and contents of Form 1099-INT, you can effectively include your interest income when filing your taxes.
Remember to review the form carefully, report the income accurately, and seek professional advice if you have any doubts or questions. Being knowledgeable about tax forms like Form 1099-INT empowers you to fulfill your tax obligations with confidence.


