- IRS forms
- Schedule 2 (Form 1040)
Schedule 2 (Form 1040): Additional Taxes
Download Schedule 2 (Form 1040)Tax season can often feel overwhelming, with its complex forms and various schedules. One such schedule that may appear on your Form 1040 is Schedule 2, which deals with additional taxes. While it may sound intimidating, understanding Schedule 2 is crucial for accurately reporting your tax liabilities and avoiding any surprises.
Schedule 2 is an attachment to your Form 1040, which is used to report additional taxes that go beyond the standard income tax. It is essential to complete Schedule 2 if you owe any of the following types of taxes: self-employment tax, unreported social security and Medicare tax on tip income, repayment of the premium tax credit, excess advance premium tax credit, and the net premium tax credit for individuals who received advance payments.
In this blog post, we will demystify Schedule 2 and shed light on the various additional taxes it encompasses.
Purpose of Schedule 2 (Form 1040)
Schedule 2 is typically used to report certain types of taxes, such as the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT), excess advance premium tax credits, or the repayment of the Premium Tax Credit. It is also used to report any additional taxes, such as the self-employment tax if you have self-employment income.
The purpose of Schedule 2 is to provide a detailed breakdown of the additional taxes owed, allowing taxpayers to calculate their total tax liability accurately. It helps ensure that taxpayers properly report and pay the various types of taxes required by the IRS.
However, it's important to note that tax laws and forms can change over time. The IRS may introduce new schedules or modify existing ones. Therefore, for the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding Schedule 2 or any other tax-related questions, it is always advisable to consult the official IRS website (www.irs.gov) or seek guidance from a qualified tax professional.
Benefits of Schedule 2 (Form 1040)
Form Schedule 2 (Form 1040) is a supplementary form used for reporting additional taxes owed or credits claimed by taxpayers. Here are some benefits of using Schedule 2:
**Enhanced tax reporting: **Schedule 2 provides a clear and organized way to report additional taxes and credits that may not be accounted for on the main Form 1040. By using this form, taxpayers can ensure that all relevant information is accurately reported to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Additional tax payments: If you owe additional taxes beyond what is already reported on your main Form 1040, Schedule 2 allows you to provide detailed information about the type and amount of tax owed. This helps ensure that your tax liability is accurately calculated.
Tax credits: Schedule 2 also allows taxpayers to claim certain tax credits that are not directly reported on the main Form 1040. By providing the necessary information and calculations, you can take advantage of credits that may reduce your overall tax liability or even result in a refund.
Deductions and adjustments: Schedule 2 includes certain deductions and adjustments to income that are not accounted for on the main Form 1040. These deductions and adjustments can help reduce your taxable income and potentially lower your tax liability.
Comprehensive tax filing: By using Schedule 2, you can have a more comprehensive tax filing that captures all the relevant information required by the IRS. This can help minimize errors and potential issues with your tax return, ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Who Is Eligible To File Schedule 2 (Form 1040)?
These are the situations where individuals may need to file Schedule 2:
Additional taxes: You may need to file Schedule 2 if you owe any of the following taxes:
- Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
- Excess advance premium tax credit repayment
- Additional tax on IRAs, qualified retirement plans, or other tax-favored accounts
- Self-employment tax
- Additional tax on early distributions from IRAs or retirement plans
- Additional tax on qualified plans (including IRAs) and other tax-favored accounts
- Recapture taxes (such as recapturing the first-time homebuyer credit)
Other adjustments to income: If you have certain adjustments to income, they should be reported on Schedule 2. These adjustments may include:
- Deductible portion of self-employment tax
- Self-employed SEP, SIMPLE, and qualified plans
- Penalty on the early withdrawal of savings
- Alimony paid (for divorces or separations finalized before 2019)
- Student loan interest deduction
How To Complete Schedule 2 (Form 1040): A Step-by-Step Guide
Here's a general guide to completing Schedule 2:
Step 1: Gather necessary documents
Collect all relevant documents such as your W-2s, 1099s, receipts, and other financial records that will be used to report income or deductions.
Step 2: Fill out Form 1040
Before completing Schedule 2, you need to fill out Form 1040, the main tax return form. Enter your personal information, filing status, and any other required information. If you're using tax software or a tax preparer, this step may be automated.
Step 3: Determine if you need Schedule 2
Review the instructions for Form 1040 to determine if you need to complete Schedule 2. Schedule 2 is typically used for reporting additional taxes owed or claiming certain tax credits.
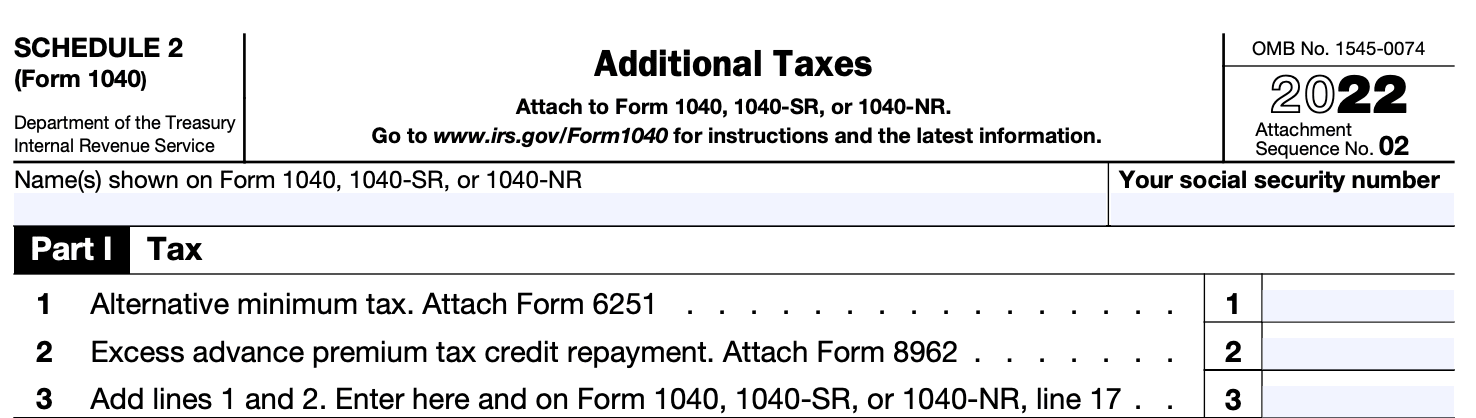
Step 4: Report additional taxes owed
If you have additional taxes owed that are not reported on other schedules or forms, you'll need to complete Part II of Schedule 2. This may include self-employment tax, household employment taxes, or other taxes not reported elsewhere.
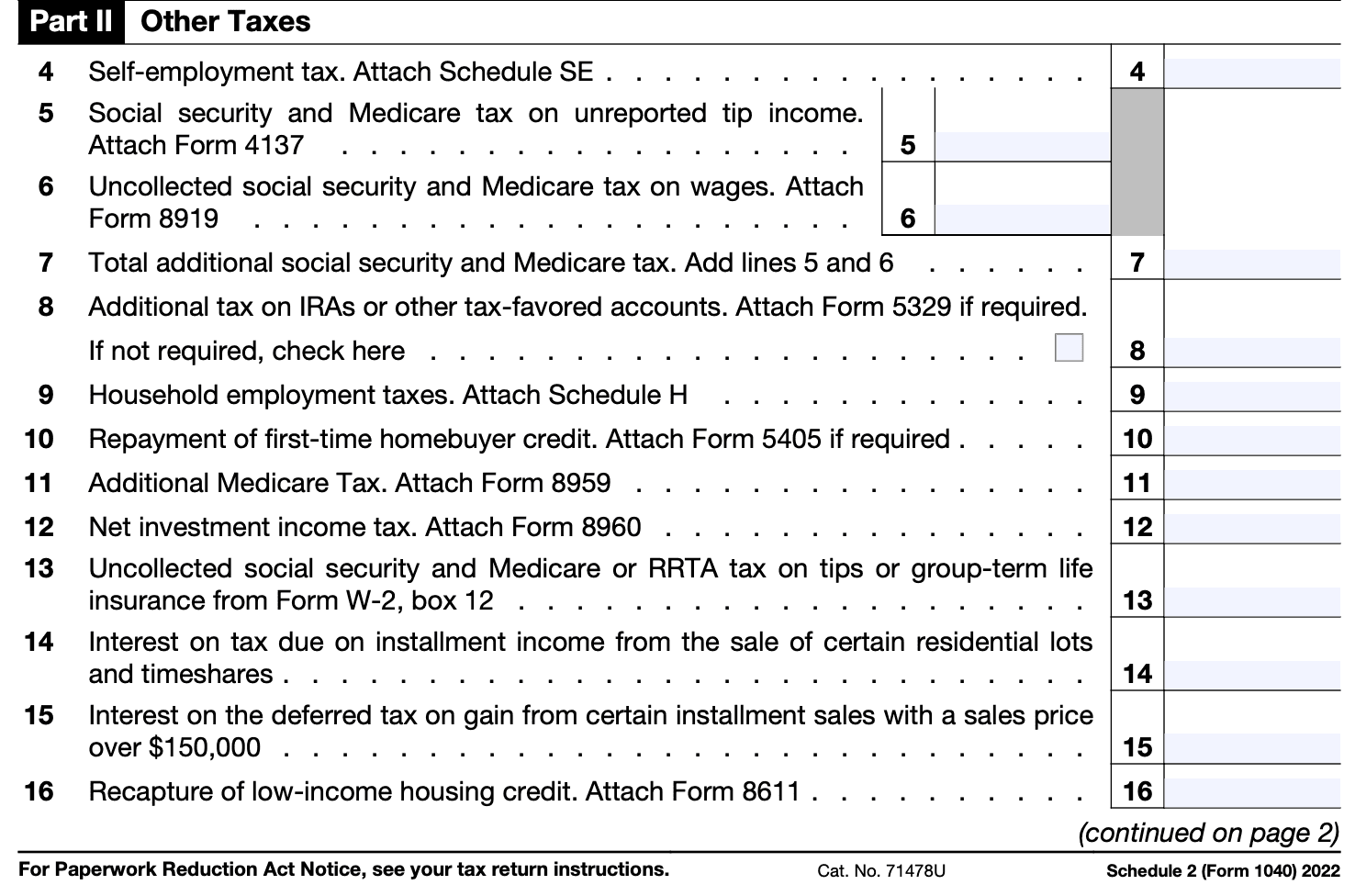
Step 5: Report the Health Care Individual Responsibility Payment
If applicable, you may need to report any shared responsibility payment related to the Affordable Care Act (ACA). This requirement was applicable for previous tax years, but it's important to check the current tax laws to see if this provision is still in effect.
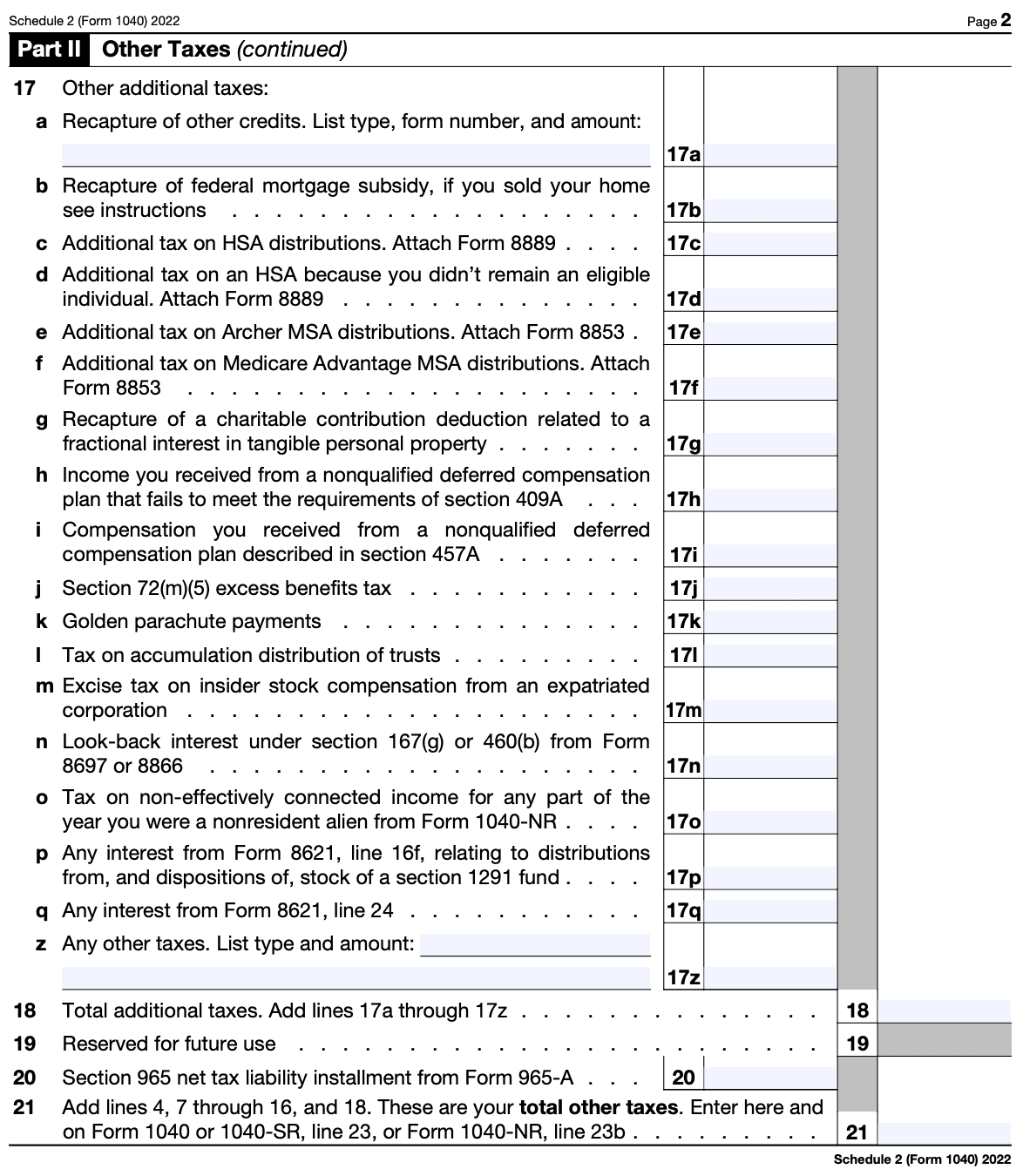
Step 6: Report other taxes and credits
Schedule 2 is also used to report certain tax credits, such as the foreign tax credit, residential energy credits, and certain other nonrefundable credits. If you qualify for any of these credits, follow the instructions provided to report them correctly.
Step 7: Attach Schedule 2 to Form 1040
Once you've completed Schedule 2, attach it to your Form 1040. Make sure to review your entire tax return for accuracy and completeness before proceeding.
Step 8: Complete other necessary schedules and forms
Depending on your tax situation, you may need to complete additional schedules or forms. Review the instructions for Form 1040 to identify any other schedules or forms you need to include.
Step 9: File your tax return
Once you have completed all the necessary forms, including Schedule 2, you are ready to file your tax return. You can e-file your return using IRS-approved software or mail a paper copy to the appropriate IRS address.
Special Considerations When Filing Schedule 2 (Form 1040)
When filing Schedule 2 (Form 1040), there are a few special considerations to keep in mind. These considerations may apply depending on your specific tax situation. Here are some key points to consider:
Determine if Schedule 2 is necessary: Review the instructions for Form 1040 to determine if you need to complete Schedule 2. Schedule 2 is typically used for reporting additional taxes owed or claiming certain tax credits. Make sure you meet the criteria that require the use of this schedule.
Review the latest instructions: The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) updates tax forms and instructions annually. It's crucial to refer to the most recent instructions available on the IRS website or consult a tax professional to ensure accurate completion of Schedule 2.
Understand the purpose of Schedule 2: Schedule 2 is primarily used to report additional taxes owed, such as self-employment tax, household employment taxes, or other taxes not reported elsewhere. It's also used to claim certain nonrefundable tax credits. Familiarize yourself with the specific sections and parts of Schedule 2 that are relevant to your tax situation.
Pay attention to deadlines: Make sure you are aware of the tax filing deadlines. The deadline for filing federal income tax returns is typically April 15th, but it can vary depending on weekends, holidays, and other factors. If you need more time to file, you can request an extension using Form 4868.
**Check for changes in tax laws: **Tax laws can change from year to year, and this can impact the requirements for completing Schedule 2. Stay updated with any changes in tax laws that may affect your filing obligations or eligibility for tax credits.
Seek professional advice if needed: If you have a complex tax situation, it's wise to consult a tax professional or certified public accountant (CPA). They can provide personalized guidance based on your circumstances, help you navigate Schedule 2, and ensure that you maximize your deductions and credits while staying compliant with tax laws.
How To File Schedule 2 (Form 1040): Offline/Online/E-filing
To file Schedule 2 (Form 1040) for your federal income taxes, you have several options: offline filing, online filing, or e-filing. Here's a brief overview of each method:
Offline filing
a. Obtain a physical copy of Form 1040, Schedule 2 from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website, local IRS office, or a tax preparation service.
b. Fill out the form manually using a pen or typewriter, following the instructions provided.
c. Attach Schedule 2 to your completed Form 1040 when mailing it to the appropriate IRS address. Make sure to include any other required forms or schedules.
Online filing
a. Use a tax preparation software or an online tax service that supports the filing of Schedule 2. These platforms will guide you through the process step-by-step.
b. Enter the required information and answer any relevant questions.
c. The software or service will automatically generate the necessary forms, including Schedule 2.
d. Review your completed tax return to ensure accuracy.
e. Follow the platform's instructions to electronically file your return.
E-filing
a. E-filing is the process of electronically submitting your tax return directly to the IRS using IRS-approved software or through a tax professional.
b. Start by using an IRS-approved e-filing software or service. This can be a tax preparation software or an online tax service.
c. Enter your tax information and complete the necessary sections, including Schedule 2.
d. The software or service will handle the transmission of your return to the IRS securely.
e. Review your tax return for accuracy before submitting it electronically.
It's worth noting that the availability and options for filing Schedule 2 may vary depending on the tax year and any updates to tax regulations or IRS procedures
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Schedule 2 (Form 1040)
When filing Schedule 2 (Form 1040), which is used to report additional taxes owed or additional credits, it's important to avoid certain common mistakes. Here are some mistakes to watch out for:
Failing to complete all the necessary information: Make sure you fill out all the required fields on Schedule 2 accurately. This includes providing your name, Social Security number, and other personal details.
Not attaching Schedule 2 to your Form 1040: If Schedule 2 is required based on your tax situation, ensure that you attach it to your Form 1040 when filing your taxes. Forgetting to include it can lead to processing delays or potential penalties.
**Incorrectly calculating additional taxes owed: **When using Schedule 2 to report additional taxes, such as the Additional Medicare Tax or the Net Investment Income Tax, double-check your calculations. Errors in calculations can result in underpayment or overpayment of taxes.
Neglecting to report eligible tax credits: Schedule 2 is also used to claim certain tax credits, such as the Credit for Excess Social Security or Tier 1 RRTA Tax Withheld. Ensure that you report all eligible credits accurately, as this can affect your tax liability.
Failing to include supporting documentation: Depending on the credits or taxes you're reporting on Schedule 2, you may need to include supporting documentation or additional forms. Be sure to review the instructions for Schedule 2 and gather any required documents to avoid potential issues or audits.
**Missing the filing deadline: **Make sure you file your taxes and any required schedules by the appropriate deadline. Failing to file on time can result in penalties and interest charges.
Not reviewing for errors: Before submitting your tax return, take the time to review all the information you've entered on Schedule 2 and other forms. Look for any typos, omissions, or inconsistencies that could lead to errors.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of the tax code can be a daunting task, but understanding Schedule 2 is crucial for accurately reporting additional taxes on your Form 1040. Whether you are self-employed, have unreported tip income, received advance payments of the Premium Tax Credit, or are required to repay any excess credits, Schedule 2 provides a dedicated space to calculate and report these amounts.
By carefully completing this schedule, you can ensure compliance with the tax laws and avoid any penalties or surprises down the road.
While this blog post aims to provide an overview of Schedule 2, it is always advisable to consult with a tax professional or refer to the official IRS guidelines for specific situations or questions. With a clear understanding of Schedule 2 and its implications, you can confidently navigate the tax season and fulfill your tax obligations.


