- IRS forms
- Form 1127
Form 1127: Application for Extension of Time for Payment of Tax Due to Undue Hardship
Download Form 1127(link: https://fincent.com/blog/how-to-get-your-small-business-ready-for-tax-season text: Tax seasons) are a stressful time for many individuals and businesses alike. Meeting the deadline for filing your taxes is crucial, but what if circumstances prevent you from doing so? Fortunately, the IRS offers various options to help taxpayers navigate these situations.
One such option is Form 1127, also known as the "Application for Extension of Time for Payment of Tax Due to Undue Hardship," is a form provided by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that allows taxpayers to (link: https://fincent.com/blog/tax-filing-extention-deadlines-everything-you-should-know text: request an extension for paying their taxes). It is not an extension for filing tax returns; rather, it provides extra time to settle the tax liability owed.
In this blog, we will explore Form 1127 in detail, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding how it works and when it can be used.
Purpose of Form 1127
Form 1127 is a tax form used by individuals and businesses to request an extension of time to pay certain taxes owed to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). The purpose of Form 1127 is to provide taxpayers with an (link: https://fincent.com/blog/how-long-can-a-small-business-go-without-filing-taxes text: opportunity to delay the payment of taxes) if they are facing undue hardship or financial difficulties.
By filing Form 1127, taxpayers can request an extension of time to pay the taxes due without incurring penalties or interest charges. However, it's important to note that the form does not grant an extension for filing the tax return itself. Taxpayers must still file their tax returns by the original due date or request a separate extension using Form 4868 (for individuals) or Form 7004 (for businesses) if they need more time to complete their (link: https://fincent.com/blog/amend-a-tax-return-with-the-irs text: tax return).
Form 1127 is typically used in situations where taxpayers can demonstrate that paying the taxes on time would cause significant financial hardship or would be impractical due to circumstances beyond their control. The IRS reviews each request on a case-by-case basis and considers factors such as the taxpayer's financial situation, ability to pay, and the impact that immediate payment would have on their livelihood.
Benefits of Form 1127
The benefits of filing Form 1127 include:
Extended payment deadline: One of the primary benefits of Form 1127 is that it allows taxpayers to request an extension of time to pay their taxes. This extension can provide much-needed relief to individuals or businesses facing financial difficulties or unexpected circumstances that make it difficult to pay their (link: https://fincent.com/blog/what-is-income-tax-liability-and-how-do-you-calculate-it text: tax liability) by the original due date.
Penalty relief: By filing Form 1127, taxpayers may be able to avoid or reduce certain penalties associated with late payment of taxes. The IRS may waive or reduce the penalties for failure to pay taxes on time if the taxpayer can demonstrate reasonable cause or undue hardship.
**Additional time to gather funds: **If a taxpayer needs additional time to gather the necessary funds to pay their tax liability, filing Form 1127 can provide that extra time. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses facing temporary cash flow problems or individuals experiencing financial hardship.
Avoiding collection actions: By requesting an extension of time to pay through Form 1127, taxpayers may be able to avoid certain collection actions by the IRS. If the IRS grants the extension, they may hold off on initiating enforced collection methods, such as liens, levies, or wage garnishments, during the extended payment period.
Flexibility in payment arrangements: Form 1127 provides an opportunity for taxpayers to propose alternative payment arrangements to the IRS. Taxpayers can suggest installment plans or other payment options that suit their financial situation, making it easier to fulfill their tax obligations.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 1127?
To be eligible to file Form 1127, you must meet the following criteria:
Undue hardship: You must demonstrate that paying the tax liability by the due date would cause you or your business undue hardship. This means that you would experience significant financial difficulties or suffer an extreme financial loss if you were required to pay the tax on time.
Good faith effort: You must show that you have made a good faith effort to pay the tax liability. This includes exploring all reasonable options to obtain the funds necessary to pay the taxes, such as (link: https://fincent.com/glossary/liquidity text: liquidating assets), borrowing money, or negotiating payment arrangements.
Timely filing: You must submit Form 1127 before the tax liability is due. The due date for filing this form is typically the same as the due date for paying the tax, which is usually April 15 for individuals or the 15th day of the third month after the end of the tax year for businesses.
Keep in mind that specific requirements and eligibility criteria may vary, so it's recommended to consult the instructions provided by the IRS or seek professional advice.
How To Complete Form 1127: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to complete Form 1127:
Step 1: Obtain the form
Visit the IRS website and search for Form 1127. Download the form and the accompanying instructions. You can also request the form by calling the IRS at 1-800-829-3676.
Step 2: Provide your basic information
Enter your name, address, Social Security number (or employer identification number if applicable), and other relevant identification information in the designated fields at the top of the form.
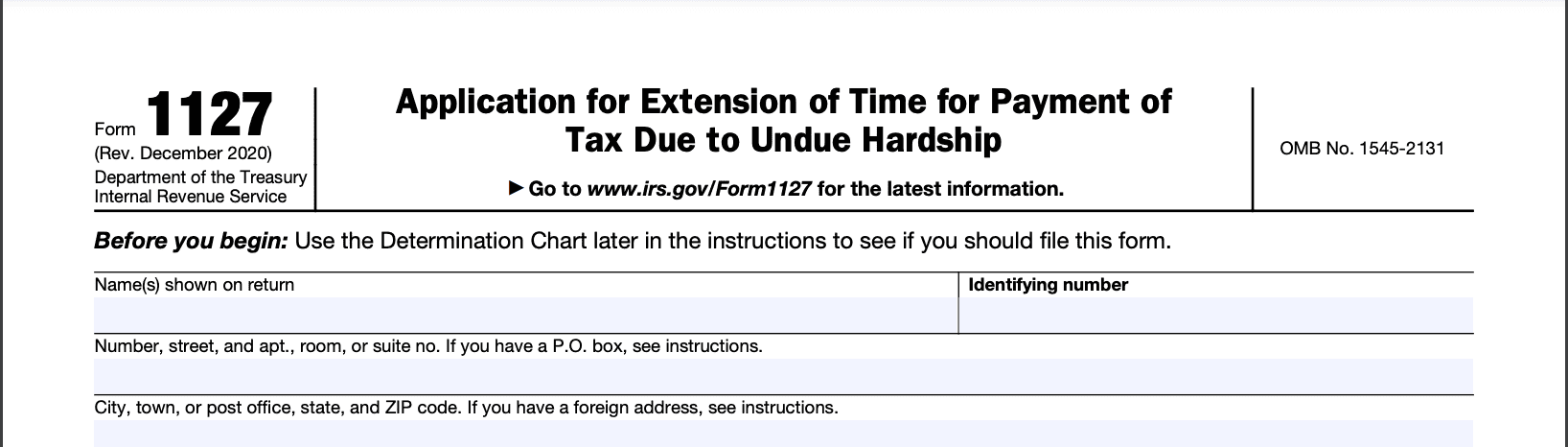
Step 3: Enter the type of tax and period covered
Specify the type of tax you're requesting an extension for (e.g., income tax, estate tax) and the tax period you are referring to (e.g., tax year, quarter).
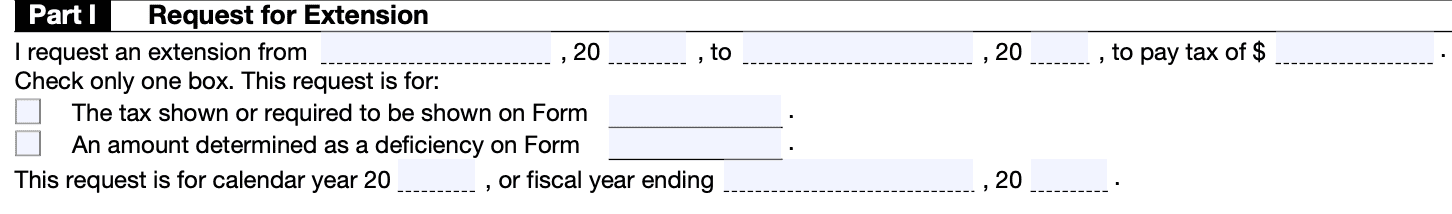
Step 4: Explain the reason for the request
Provide a detailed explanation of the reasons for your request for an extension of time to pay. This explanation should include any relevant facts and circumstances that justify the need for additional time.

Step 5: Calculate the estimated tax liability
Determine your estimated tax liability by completing the relevant sections of the form. This includes reporting your total tax liability, any payments made to date, and the balance due.
Step 6: Requested extension period
Indicate the requested extension period in terms of months or a specific date. Be realistic in your request, as the IRS will consider it based on the circumstances provided.
Step 7: Attach supporting documentation (if applicable)
If you have any supporting documentation that helps substantiate your request, such as (link: https://fincent.com/glossary/financial-statements text: financial statements), medical records, or other relevant documents, make copies and attach them to the form.

Step 8: Sign and date the form
 Review the completed form and ensure all the required fields are filled out accurately. Sign and date the form at the bottom.
Review the completed form and ensure all the required fields are filled out accurately. Sign and date the form at the bottom.
Step 9: Submit the form
Make a copy of the completed Form 1127 and all accompanying documents for your records. Mail the original form and attachments to the appropriate IRS address, as specified in the instructions. It is recommended to send it via certified mail or a reputable courier service to have proof of delivery.
Step 10: Follow up and payment arrangements
The IRS will review your request and may contact you for additional information if necessary. In the meantime, it's essential to continue making efforts to pay your tax liability as much as possible. If the extension is granted, the IRS will provide instructions on how to make payment arrangements for the deferred amount.
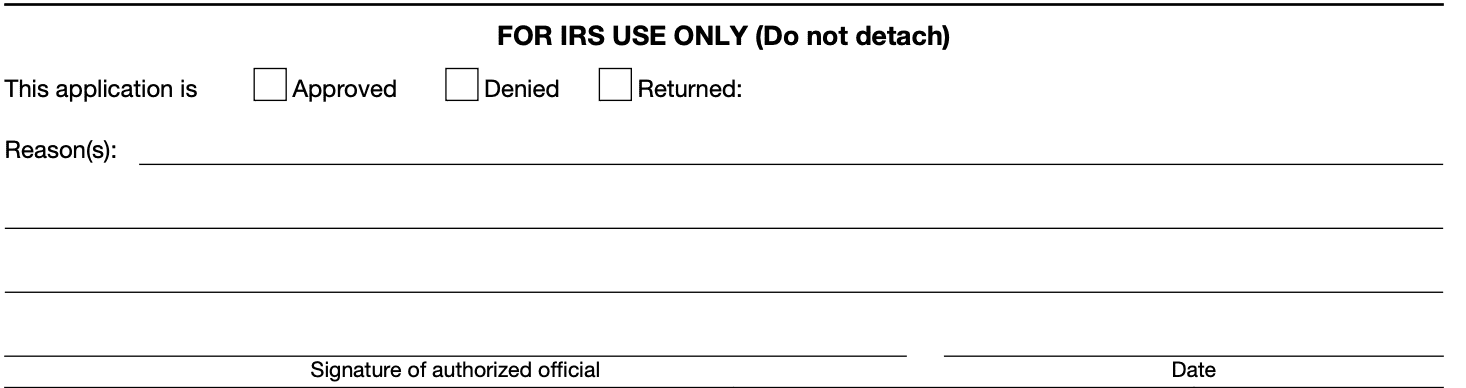
Remember, Form 1127 is a request for an extension of time to pay taxes, not an extension of time to file tax returns. If you also need an extension to file your return, you will need to submit the appropriate form for that purpose (e.g., Form 4868 for individual income tax returns).
Types, Schedules, and Deductions on Form 1127
Here are the main details regarding types, schedules, and deductions related to Form 1127:
Types
Form 1127 can be used for various types of federal taxes, including income tax, estate tax, gift tax, and certain excise taxes. It applies to both individual taxpayers and businesses.
Schedules
Form 1127 itself does not have any specific schedules. However, when submitting the form, you may need to provide supporting documentation to demonstrate the undue hardship you're facing. This documentation might include financial statements, bank statements, income and expense records, and any other relevant information that shows your inability to pay the tax liability.
Deductions
Form 1127 is not directly related to deductions. Instead, it focuses on requesting an extension of time for payment. Deductions are typically claimed on the appropriate tax return form, such as Form 1040 for individual income tax or Form 1120 for corporate income tax.
When filing your tax return, you can claim deductions that you qualify for based on the tax laws and regulations in effect for the tax year in question. Deductions reduce your taxable income, which can result in lower tax liability.
Filing Deadlines & Extensions on Form 1127
Here are some key timelines to understand about Form 1127:
Filing deadline for Form 1127: The form should generally be filed on or before the original due date of the tax return (typically April 15 for individuals). However, the IRS allows additional time to submit Form 1127 if the taxpayer demonstrates reasonable cause.
**Reasonable cause: **To qualify for an extension of time for payment under Form 1127, taxpayers must show that payment of the tax would result in undue hardship. This usually requires providing detailed financial information to support the claim.
Length of extension: If the IRS approves the request, the extension granted under Form 1127 can provide additional time, usually up to six months, for the taxpayer to pay the tax liability without incurring penalties.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 1127
When filing Form 1127, it's important to be aware of common mistakes that can be made. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
**Missing the deadline: **Ensure that you submit Form 1127 on or before the original due date of the tax payment. Failing to file on time may result in penalties and interest.
**Incomplete or inaccurate information: **Provide all the necessary information accurately on the form. Double-check your entries, such as your name, Social Security number, address, and the tax period for which the payment is due.
Insufficient explanation of undue hardship: When explaining your undue hardship circumstances, be clear and specific about why you are unable to make the tax payment on time. Provide supporting documentation if available, such as medical records, financial statements, or any other relevant evidence.
**Incorrect calculation of the amount owed: **Make sure you calculate the correct amount of tax due and clearly indicate it on the form. If you underestimate the amount or fail to include it, your request for an extension may be denied.
Filing the wrong form: Form 1127 is specifically for an extension of time for payment of tax due to undue hardship. If you are seeking an extension for filing your tax return, you need to file a different form, such as Form 4868 (for individual income tax returns) or Form 7004 (for business tax returns).
Ignoring correspondence from the IRS: If the IRS requests additional information or documentation to support your request for an extension, make sure to respond promptly. Ignoring their requests may lead to a denial of your application.
Not paying any tax at all: Even if you are facing an undue hardship, it's advisable to pay as much of the tax owed as you can with your application. This demonstrates your willingness to fulfill your tax obligations and can improve your chances of getting an extension.
How To File Form 1127: Offline/Online/E-filing
Form 1127 is used to request an extension of time for paying taxes & here is how you could file Form 1127:
Offline filing
To file Form 1127 offline, you would typically print the form, fill it out manually, and mail it to the appropriate address. Here's what you need to do:
a. Obtain the form: Visit the official website of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) at www.irs.gov and search for "Form 1127." Download and print the form along with its instructions.
b. Complete the form: Fill out the necessary information on Form 1127, including your personal details, tax liabilities, reasons for the extension, and the amount of time you are requesting.
c. Attach supporting documents: If required, attach any supporting documents that explain your circumstances and validate your need for an extension.
d. Mail the form: Once you have completed the form and attached the necessary documents, mail them to the appropriate IRS address provided in the instructions for Form 1127. It is advisable to send it via certified mail or a similar method to have proof of delivery.
Online/E-filing
As of September 2021, there is no specific online or electronic filing method available for Form 1127. It is primarily filed offline by printing and mailing the form to the IRS.
Conclusion
Form 1127 can provide a lifeline for taxpayers facing financial hardships that prevent them from meeting their tax payment obligations on time.
By understanding the purpose, eligibility criteria, and steps involved in completing this form, individuals and businesses can navigate tax season with greater confidence and ease.
Remember, if you find yourself in a situation where paying your taxes on time is unfeasible, consult with a tax professional or contact the IRS for guidance on how to proceed with Form 1127.


