- IRS forms
- Form 7004
Form 7004: Your Guide to Business Tax Extension
Download Form 7004Introduction to Form 7004
Form 7004, officially known as the "Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns," is a form that businesses can use to request an automatic extension of time to file certain tax returns. Form 7004 applies to tax returns for partnerships, corporations, and S corporations.
Filing Form 7004 allows a business to extend the due date for its tax return, giving the business more time to prepare and file its tax return. However, it is important to note that filing Form 7004 only extends the deadline for filing the tax return, not the deadline for paying any taxes owed.
Who Needs to File Form 7004?
Businesses that need more time to file their tax returns should consider filing Form 7004. Specifically, Form 7004 is used to request an automatic extension of time to file tax returns for the following types of businesses:
- Partnerships ((link: https://fincent.com/blog/irs-form-1065-what-it-is-how-to-file-it text: Form 1065))
- Corporations ((link: https://fincent.com/blog/filing-form-1120-the-complete-guide-for-businesses-to-file-their-tax-returns text: Form 1120))
- S Corporations ((link: https://fincent.com/blog/filing-form-1120-s-heres-what-you-need-to-know text: Form 1120-S))
- Trust or Estate
Businesses that need more time to file their tax returns should file Form 7004 as soon as possible to ensure they receive the maximum amount of time to file their tax return. Note that other forms of business, such as sole proprietorships and limited liability companies (LLCs), do not need to file Form 7004 as they report business income on their individual tax returns (Form 1040).
Eligibility Criteria for Filing Form 7004
To be eligible to file Form 7004, a business must meet certain criteria. Specifically, the business must:
- Be filing a tax return for a partnership, corporation, S corporation or trust / estate that is filing Form 1041
- File Form 7004 before the original due date of the tax return
- Provide a reason for the extension request
- The IRS automatically grants an extension of time to file the tax return upon receipt of a timely filed Form 7004 that includes a valid reason for the extension request.
How to File Form 7004?
Filing Form 7004 is relatively straightforward. Businesses can file Form 7004 electronically or by mail. To file electronically, businesses can use the IRS e-file system or an authorized e-file provider. To file by mail, businesses must complete Form 7004 and mail it to the Form 7004 mailing addresses listed on IRS.
To file Form 7004 electronically, businesses will need the following information:
- Business name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN)
- Type of tax return being filed (partnership, corporation, or S corporation)
- Reason for the extension request
- Estimated tax liability for the tax return being extended
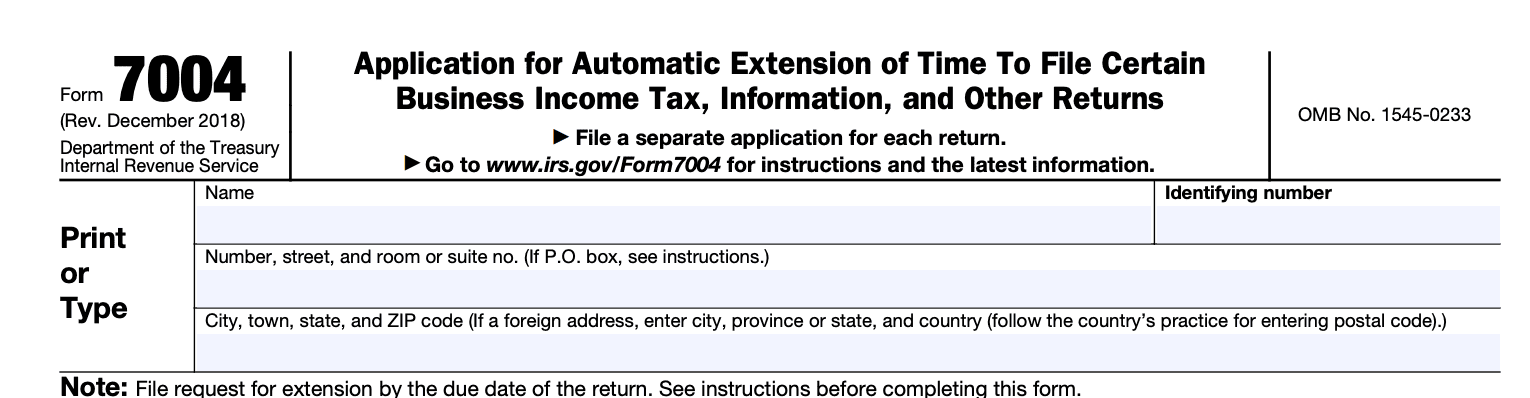
The IRS Form 7004 is used to request an extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns. Here are the key points to know:
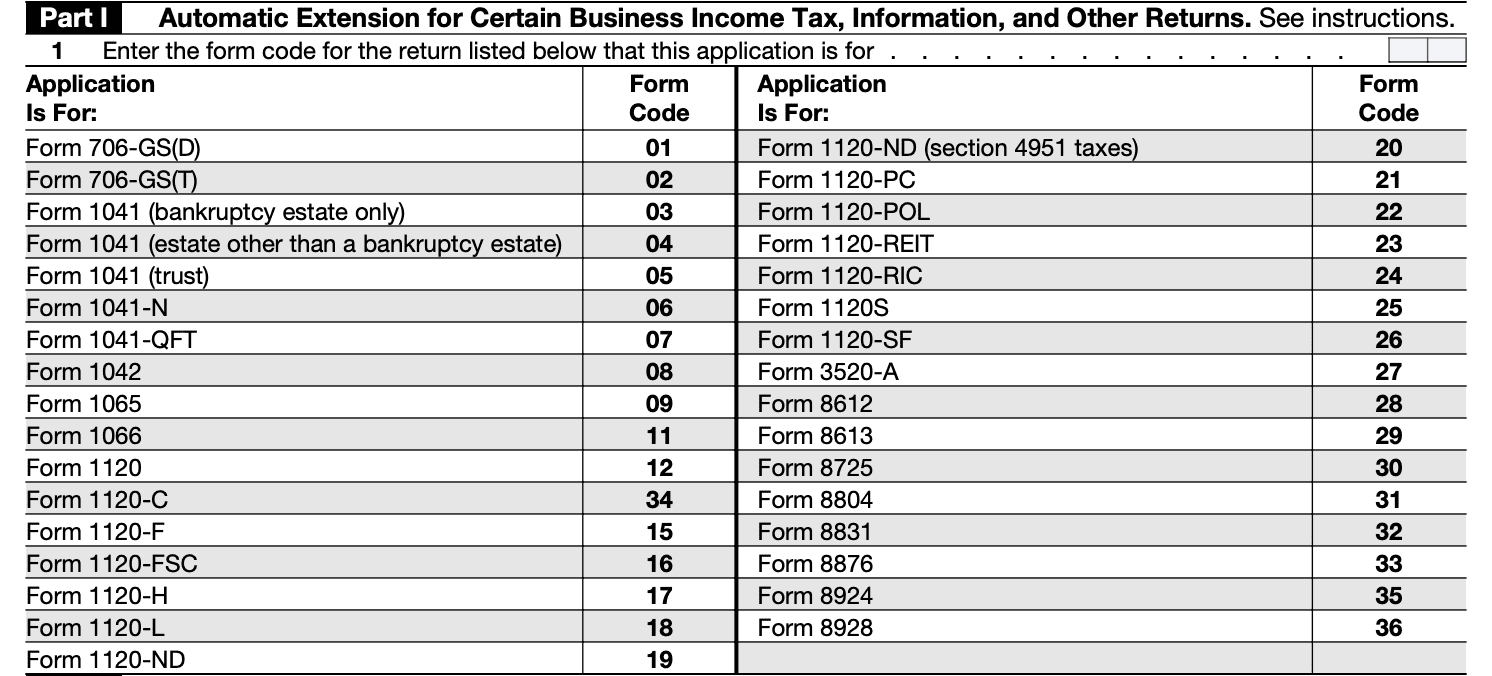
Part I — Automatic Extension for Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns
Line 1:
Enter the appropriate form code in the boxes on line 1 to indicate the type of return for which you are requesting an extension.
**Example: **If you are electing to file Form 1120-H, use the original form type assigned to the entity to file for an extension. Use Form 8868 instead of Form 7004 if you are the trustee of a trust required to file Form 1041-A.
Part II — All Filers Must Complete This Part
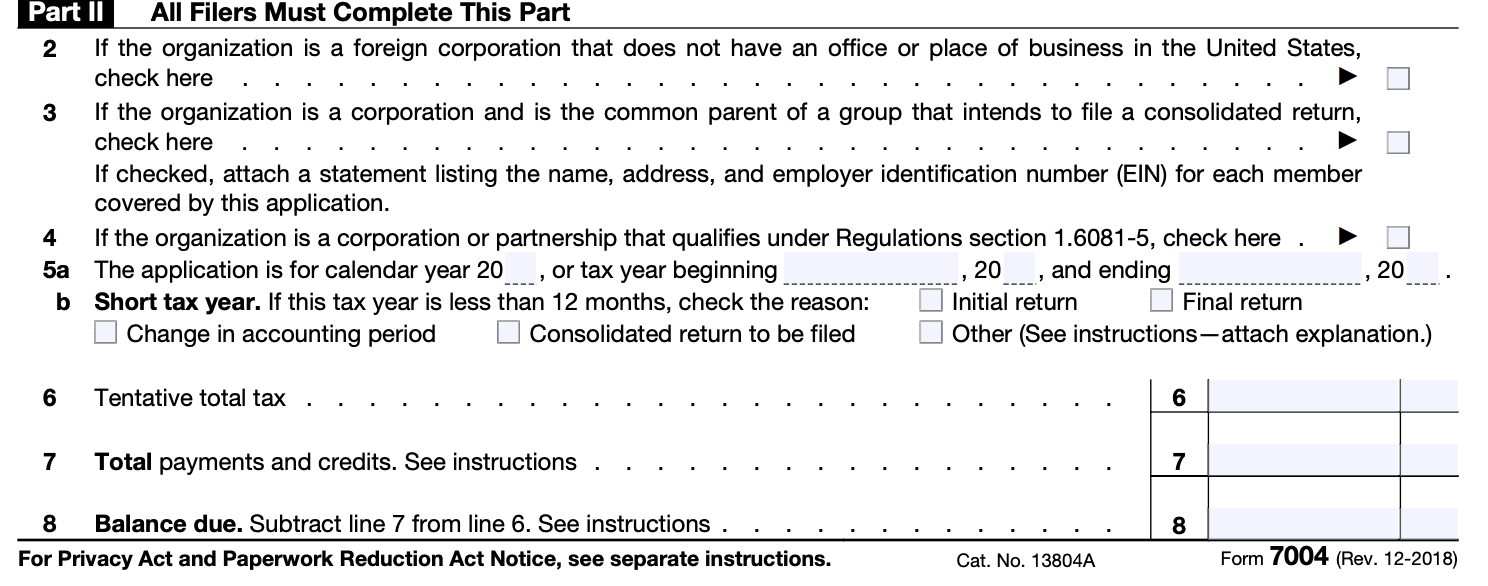
Line 2:
If you're a foreign corporation with no office in the US and want more time to file, check the box on line 2.
Line 3: Consolidated Group
Only the main company or representative of a group can request more time to file a consolidated return. Attach a list of all members of the group showing their name, address, and EIN. Follow the formatting instructions and leave two blank lines between listed members. If a member needs an extension for a short tax period, they need to file a separate Form 7004.
Line 4: Automatic Extension
- Certain foreign and domestic corporations and partnerships are entitled to an automatic extension of time to file and pay
- They do not need to file Form 7004 for this
- They must file their tax return and pay any balance by the 15th day of the 6th month after the end of the tax year
- They must also attach a statement to their tax return
- If they can't file on time, they can check the box on line 4 of Form 7004 to request an additional extension of time to file (not pay)
- The extension period is 3 months for partnerships and S corporations and 4 months for C corporations and Form 1120-POL filers.
Line 5a: Non-Calendar Year
If you do not use a calendar year, complete the lines showing the beginning and ending dates for the tax year.
Line 5b: Short Tax Year
- Check the box for the reason for the short tax year i.e., less than 12 months.
- If "Change in accounting period" is checked, approval must be obtained unless certain conditions apply. For more info, see Form 1128 and Pub. 538.
- If none of the listed reasons apply, check "Other" and attach a statement explaining the reason.
- Clearly explain the circumstances causing the short tax year.
- If filing for a return covering a short tax year ending in June, maximum extension.
Line 6:
To estimate the total tax amount, including any nonrefundable credits, that the entity is expected to owe for the tax year, refer to the specific instructions for the applicable return. If the entity expects to owe zero tax, enter "-0-".
Line 7:
The entity should enter the total payments and refundable credits. For more information on "write-in" payments and credits, refer to the instructions for the applicable return.
Line 8: Balance due
- Paying Tax Liabilities on Time
- Form 7004 does not extend the time to pay tax.
- Corporations or affiliated groups of corporations filing a consolidated return must pay the amount of unpaid tax liability shown on line 8 on or before the due date of the return.
- Electronic Funds Transfer for Tax Deposits
- Most entities must use electronic funds transfer for all federal tax deposits, including corporate income taxes.
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS) is generally used for electronic funds transfers. Visit EFTPS.gov or call 1-800-555-4477 for more information or to enroll in EFTPS.
- If the entity chooses not to use EFTPS, it may arrange for a third party to make deposits on its behalf.
- Payment can be made by Electronic Funds Withdrawal (EFW) if Form 7004 is filed electronically.
- Refer to the instructions for the entity's tax return for more information.
- Foreign corporations with an office or place of business in the US should pay their tax as described above. For foreign corporations without an office or place of business in the US, refer to the applicable tax return instructions.
- Extensions for Trusts and REMICs
- Trusts (Form 1041) or REMICs (Form 1066) are granted an extension even if they cannot pay the full amount shown on line 8.
- However, they should pay as much as possible to limit the amount of penalties and interest owed.
- Extension for Form 1042
- For an extension of time to file Form 1042, refer to the deposit rules in the Instructions for Form 1042 to determine how payment must be made.
Deadlines for Filing Form 7004
The deadline for filing Form 7004 varies depending on the type of tax return being extended. For most businesses, the deadline to file Form 7004 is the original due date of the tax return. However, for certain types of tax returns, the deadline to file Form 7004 may be different. The following table provides an overview of the deadlines for filing Form 7004:
| Type of Tax Return | Original Due Date | Deadline to File Form 7004 |
| Partnership | March 15 | September 15 |
| Corporation | April 15 | October 15 |
| S Corporation | March 15 | September 15 |
| Trust or Estate | April 15 | September 30 |
It is important to note that filing Form 7004 does not extend the deadline for paying any taxes owed. Businesses must still pay any taxes owed by the original due date of the tax return to avoid penalties and interest.
Understanding Extension Period, Termination, and Rounding Off for Form 7004
Maximum Extension Period
- The automatic extension period for filing a tax return is typically 6 months.
- Exceptions apply for certain filers of Form 1041 and C corporations with tax years ending June 30.
- Estate and trust filing Form 1041 can get an automatic 5½-month extension.
- C corporations with tax years ending **June 30 **can get an automatic 7-month extension (6-month extension if filing Form 1120-POL).
- Check the instructions for Part II, lines 2 and 4 for exceptions for foreign corporations, certain domestic corporations, and certain partnerships with books and records outside of the United States and Puerto Rico.
Note: If a corporation has a short tax year ending in June, it will be treated as though the short tax year ended on** June 30th.**
Termination of Extension Period
- The IRS can terminate the automatic extension at any time by mailing a notice of termination to the entity or person who requested the extension.
- The notice will be mailed at least 10 days before the termination date given in the notice.
Rounding Off to Whole Dollars
- The entity can round off cents to whole dollars on their return and schedules.
- If rounding off, all amounts must be rounded.
- To round, drop amounts under 50 cents and increase amounts from 50 to 99 cents to the nearest dollar (for example, $1.29 becomes $1, and $2.51 becomes $3).
- When adding two or more amounts to calculate the total, include cents and round off only the total amount.
Who should not file Form 7004?
While most tax forms can be e-filed, there are some forms that cannot be e-filed for various reasons.
Here are some returns for which Form 7004 cannot be e-filed:
- Forms 8612, 8613, and 8615: These are related to the taxation of a child's investment income.
- Forms 706-GS(D), 706-GS(T), and 706-GS(D-1): These forms are related to the generation-skipping transfer tax.
- Forms 1041-N, 1041-QFT, and 1041-T: These forms are related to trusts and estates.
- Forms 1120-C, 1120-FSC, and 1120-H: These forms are related to corporations, foreign sales corporations, and homeowners associations.
- Forms 8610 and 8611: These forms are related to low-income housing tax credit.
- Forms 8876 and 8924: These forms are related to excise taxes.
- Forms 2439 and 8805: These forms are related to the taxation of foreign investment in the U.S.
What to Do After Filing Form 7004?
After filing Form 7004, businesses should take the following steps:
- Keep a copy of the filed Form 7004 for their records.
- Pay any taxes owed by the original due date of the tax return.
- Complete and file the tax return by the extended due date.
Failure to file the tax return by the extended due date may result in penalties and interest.
Consequences of Not Filing Form 7004
If a business fails to file Form 7004 by the original due date of the tax return, it may face penalties and interest. The penalty for failing to file Form 7004 is 5% of the tax owed for each month (or part of a month) that the form is late, up to a maximum of 25% of the tax owed. Interest will also be charged on any unpaid taxes from the original due date of the tax return until the taxes are paid in full.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Form 7004
Q: Can a business file for an extension of time to pay taxes owed?
A: No. Filing Form 7004 only extends the due date for filing the tax return. Any taxes owed must be paid by the original due date of the tax return to avoid penalties and interest.
Q: How can a business check the status of its Form 7004?
A: Businesses can check the status of their Form 7004 by calling the IRS toll-free number at 1-800-829-1040.
Q: What happens if a business files Form 7004 but doesn't file its tax return by the extended due date?
A: If a business fails to file its tax return by the extended due date, it may face penalties and interest.
Q: Can a business file Form 7004 for multiple tax returns at once?
A: Yes. A business can file one Form 7004 to request an extension of time to file multiple tax returns. The form should indicate the type of tax return being extended and the tax year to which it applies.
Q: What happens if a business doesn't provide a reason for the extension request on Form 7004?
A: If a business doesn't provide a reason for the extension request, the IRS may reject the request for an extension of time to file the tax return. It is important to provide a valid reason for the extension request on Form 7004 to avoid rejection.
Q: Is a signature required when submitting Form 7004?
A: No, a signature is not required for Form 7004.


