- IRS forms
- Schedule 1 (Form 8849)
Schedule 1 (Form 8849): Non-Taxable Use of Fuels
Download Schedule 1 (Form 8849)Tax regulations can be complex, especially when it comes to fuel usage and taxation. For businesses that utilize certain fuels for non-taxable purposes, understanding the Schedule 1 (Form 8849) is crucial. This document allows eligible entities to claim refunds or credits for fuel taxes paid on specific types of fuel used for nontaxable purposes.
Schedule 1 (Form 8849) is a supplementary form used to claim refunds or credits for certain fuels used in non-taxable situations. It primarily addresses the nontaxable use of specific types of fuels, including gasoline, diesel fuel, kerosene, aviation gasoline, and aviation-grade kerosene.
In this blog post, we'll delve into the details of Schedule 1 (Form 8849) to provide a comprehensive understanding of how businesses can benefit from it.
Purpose of Schedule 1 (Form 8849)
The purpose of Schedule 1 is to provide a detailed breakdown of the various types of fuel-related tax credits or refunds that a taxpayer is claiming. It allows the taxpayer to specify the specific activities or uses for which they are eligible to claim these credits or refunds.
Some of the common tax credits and refunds claimed on Schedule 1 include:
Alternative fuel credit: This credit applies to the use of certain alternative fuels such as compressed natural gas (CNG), liquefied natural gas (LNG), liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and others.
Credit for fuel used on a farm: This credit is available for fuel used in farming operations, including gasoline, diesel, and certain other fuels.
**Biodiesel and renewable diesel fuels credit: **This credit applies to the use of biodiesel and renewable diesel fuels in qualified vehicles or equipment.
Credit for certain nontaxable uses of fuels: This credit is for fuels used in certain off-highway business activities, such as farming, aviation, and certain types of boats.
Who Is Eligible To File Schedule 1 (Form 8849)?
To be eligible for filing Schedule 1 (Form 8849), you must fall into one of the following categories:
**Registered ultimate vendors: **These are vendors who sell taxable fuel to consumers or users. They are entitled to claim credits or refunds for the nontaxable use of fuel sold.
State or local governments: Government entities at the state or local level that use fuel for their operations qualify for Schedule 1 (Form 8849).
Nonprofit educational organizations: Certain nonprofit educational organizations are eligible to claim credits or refunds for the nontaxable use of fuel.
**Exempt entities: **Entities that are exempt from federal excise tax on fuel, such as state and local governments, qualified blood collector organizations, and volunteer fire departments, can file Schedule 1 (Form 8849).
How To Complete Schedule 1 (Form 8849): A Step-by-Step Guide
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to complete Schedule 1 (Form 8849):
Step 1: Obtain Form 8849
(link: https://fincent.com/irs-tax-forms/form-8849 text: Download Form 8849) and Schedule 1 from the official website of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or obtain a printed copy from a local IRS office.
Step 2: Provide general information
At the top of Schedule 1, enter your name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN) or Social Security Number (SSN).
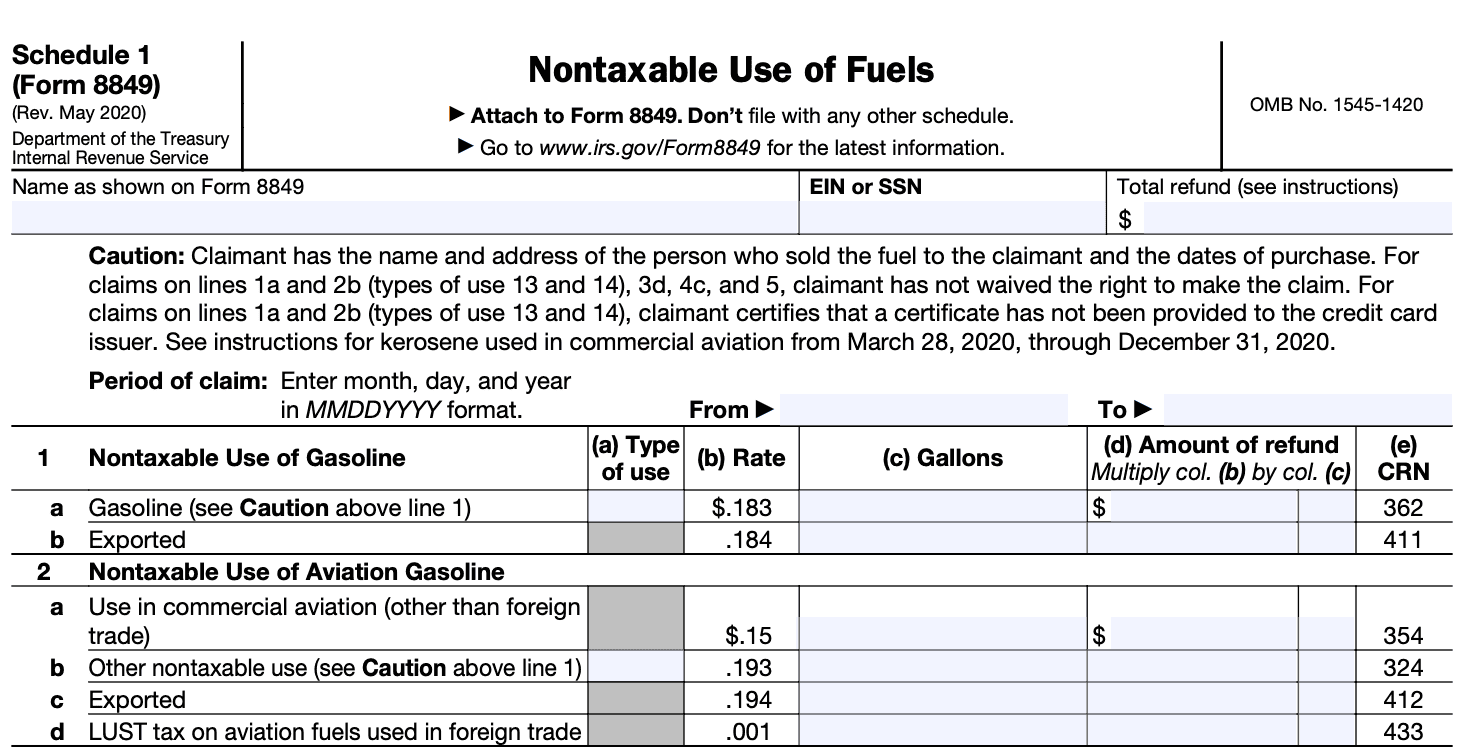
Step 3: Choose the appropriate tax category
Identify the category of tax for which you are seeking a refund or abatement. Schedule 1 provides various options such as:
Section 4081 - Certain Taxable Fuel Claims
Section 4041 - Tax on Aviation Gasoline
Section 4041 - Tax on Kerosene
Section 4041 - Tax on Diesel Fuel and Kerosene
Section 4041 - Tax on Gasoline
Section 4051 - Heavy Highway Vehicle Use Tax
Section 4071 - Tax on Tires and Tubes
Section 4080 - Gasoline and Aviation Gasoline Blendstocks
Select the appropriate tax category that corresponds to your claim or request.
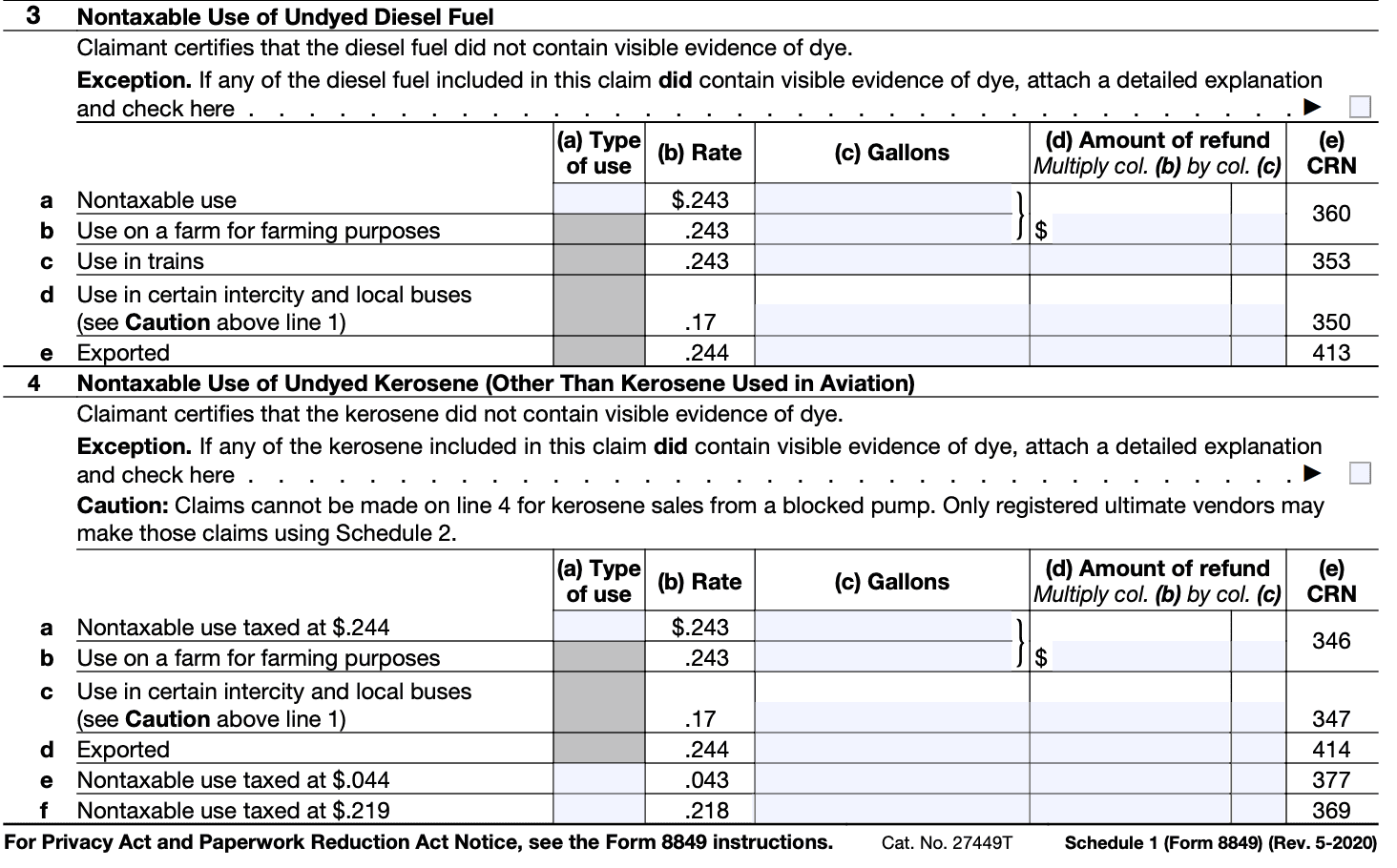
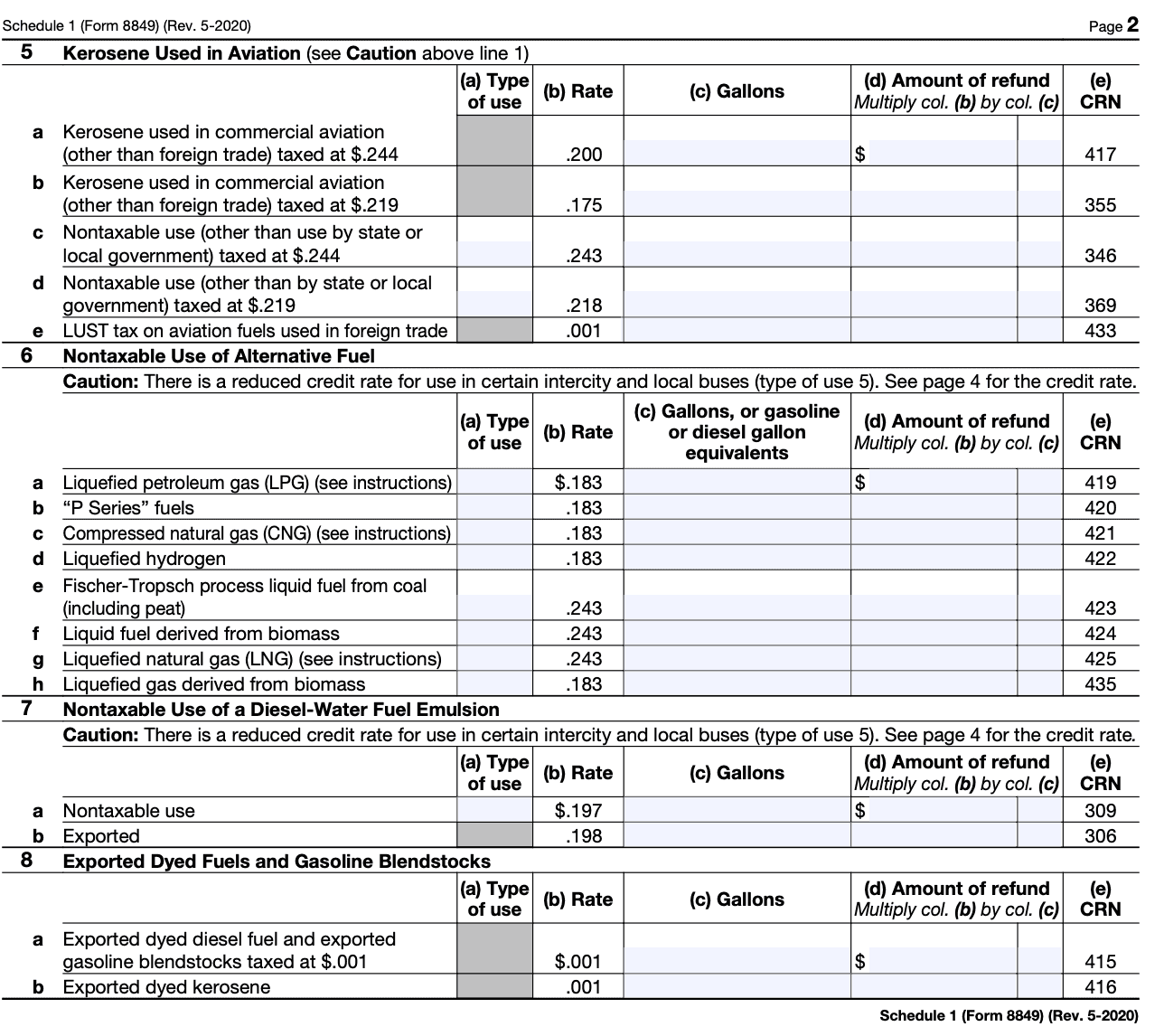
Step 4: Provide specific information
For the chosen tax category, complete the specific information required. This may include the amount of tax paid, the period to which the claim or request applies, and any additional details requested on the form.
Step 5: Calculate the claim amount
Depending on the tax category, you may need to perform calculations to determine the refund amount or abatement request. Follow the instructions provided on Schedule 1 to accurately calculate the claim amount.
Step 6: Attach supporting documents
Gather any necessary supporting documentation to substantiate your claim or request. This may include receipts, invoices, or other records that demonstrate your eligibility for the refund or abatement.
Step 7: Review and sign
Carefully review all the information you have entered on Schedule 1 to ensure accuracy and completeness. Sign and date the form at the bottom.
Step 8: Submit the form
Make a copy of the completed Schedule 1 and all supporting documents for your records. Then, mail the original form and attachments to the appropriate IRS address as specified in the form instructions. If you are unsure of the correct address, check the IRS website or contact the IRS for assistance.
Remember to keep a copy of the form and any supporting documents for your records.
Special Considerations When Filing Schedule 1 (Form 8849)
Here are some important points to consider:
Eligibility: Make sure you meet the eligibility requirements for the specific fuel tax credit or refund you are claiming. The instructions accompanying Form 8849 provide details on the eligibility criteria for each credit or refund.
Timely filing: Ensure that you (link: https://fincent.com/irs-tax-forms/form-8849#filing-deadlines-extensions-on-form-8849 text: file Form 8849) within the appropriate time frame. Generally, you must file the form by the last day of the quarter following the quarter in which the taxable use or sale of fuel occurred. Be aware of the deadlines to avoid any potential penalties or interest charges.
Proper documentation: Maintain accurate and complete records to support your claim. This includes invoices, receipts, and any other relevant documents that substantiate your fuel purchases, sales, or usage. The IRS may request these records to verify your claim, so it's important to have them readily available.
Multiple claims: If you have multiple claims for different types of fuel tax credits or refunds, make sure to complete separate Schedules 1 for each claim. Clearly indicate the type of claim being made and provide all necessary information for each specific credit or refund.
Correct calculations: Accurately calculate the amounts being claimed on Form 8849. Double-check your calculations to avoid errors or discrepancies that could delay the processing of your claim or lead to potential IRS inquiries.
Attachments: If required, attach any necessary supporting schedules or forms to Form 8849. For example, if you are claiming a biodiesel mixture credit, you must include Schedule C (Form 720) along with Form 8849.
Electronic filing: Consider electronic filing as it can expedite the processing of your claim. The IRS offers an online option called the Fuel Tax Credit Online Reporting System (FTCORS) for certain fuel tax credits. Check the IRS website for details and eligibility requirements.
Consult a tax professional: If you have complex tax situations or are unsure about any aspect of filing Schedule 1 (Form 8849), it's advisable to consult with a qualified tax professional. They can provide guidance based on your specific circumstances and help ensure accurate and timely filing.
Filing Deadlines & Extensions on Schedule 1 (Form 8849)
Typically, the filing deadlines for Form 8849 depend on the specific type of credit being claimed. Here are some general guidelines:
-
Alternative Fuel Credit (AFC): The filing deadline for claiming the AFC on Form 8849 is the last day of the calendar quarter following the quarter in which the fuel was used or sold. For example, if you used or sold alternative fuel in the first quarter (January to March), the deadline to file Form 8849 for claiming the AFC would be the last day of the second quarter (April to June).
-
Biodiesel Mixture Credit (BMC): The filing deadline for the BMC on Form 8849 is the last day of the calendar month following the calendar quarter in which the mixture was sold or used.
-
Alternative Fuel Mixture Credit (AFMC): The filing deadline for the AFMC on Form 8849 is also the last day of the calendar month following the calendar quarter in which the mixture was sold or used.
-
Second-Tier Biodiesel Mixture Credit: The filing deadline for this credit on Form 8849 is the last day of the calendar quarter following the quarter in which the mixture was sold or used.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Schedule 1 (Form 8849)
Here are some mistakes to avoid:
Incorrect or incomplete information: Make sure to provide accurate and complete information on your Schedule 1 form, including your name, address, tax identification number, and the tax period for which you are claiming the refund or credit. Any mistakes or missing information can lead to delays or rejection of your form.
Using outdated forms: Always use the most current version of Form 8849 and make sure you are using the correct form for the tax year you are filing. Using outdated forms can lead to errors and delays in processing.
Incorrectly calculating refund or credit amounts: Double-check all calculations to ensure you have correctly determined the refund or credit amounts you are claiming. Mistakes in calculations can result in either underpayment or overpayment, leading to potential issues with the IRS.
Filing the wrong form for the tax category: Schedule 1 (Form 8849) is used to claim refunds or credits for certain excise taxes, such as those related to fuel, environmental taxes, or communications taxes. Ensure that you are filing the correct form for the specific tax category you are seeking a refund or credit for.
Missing supporting documentation: Depending on the type of refund or credit you are claiming, you may need to include supporting documentation along with your Schedule 1 form. Failing to include the required documentation can result in delays or rejection of your claim. Check the instructions provided with the form to determine which documents are needed.
Filing late: Make sure to file your Schedule 1 form within the specified deadline. Late filings can result in penalties and interest charges. Check the IRS website or consult with a tax professional to determine the filing deadline for your specific situation.
Not reviewing the form before submission: Before submitting your Schedule 1 form, review it carefully to ensure all the information is accurate, all calculations are correct, and all necessary attachments are included. Taking the time to review your form can help prevent avoidable errors.
Conclusion
Schedule 1 (Form 8849) provides a valuable opportunity for eligible businesses, government entities, and nonprofit organizations to claim refunds or credits for certain fuels used for nontaxable purposes.
By understanding the components of the form, meeting the eligibility criteria, and following the filing procedures accurately, entities can optimize their fuel-related expenses and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
It is important to consult with a tax professional or refer to the official IRS guidelines to ensure accurate completion and submission of Schedule 1 (Form 8849). Taking advantage of this form can lead to substantial savings for eligible entities, promoting financial stability and growth.


