- IRS forms
- Form 8038-T
Form 8038-T: Arbitrage Rebate, Yield Reduction and Penalty in Lieu of Arbitrage Rebate
Download Form 8038-TAs governments and (link: https://fincent.com/glossary/taxable-municipal-bonds text: municipalities issue bonds) to finance various projects, they often seek to maximize their investments by earning interest on the bond proceeds until the funds are spent. However, there are federal tax regulations in place to ensure that these earnings, known as arbitrage, are appropriately managed and not exploited for tax advantage.
One crucial aspect of this regulatory framework is the completion and submission of Form 8038-T. In this blog, we will dive into the key concepts surrounding Form 8038-T, namely Arbitrage Rebate, Yield Reduction, and Penalty in Lieu of Arbitrage Rebate
Understanding Form 8038-T
Arbitrage Rebate refers to the federal tax that may be imposed on the investment earnings derived from the difference between the interest rate received from the investment of bond proceeds and the higher interest rate the bonds were issued at. In simple terms, if the bonds are issued at a higher interest rate than what is earned from investing the bond proceeds, there is potential for arbitrage earnings.
To avoid excessive profiteering from arbitrage earnings, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) mandates that issuers of tax exempt bonds, such as state and local governments, set aside a portion of their earnings to pay the arbitrage rebate. The goal is to maintain fairness and prevent bond issuers from benefiting too much from the difference between bond issuance rates and investment rates.
Form 8038-T is the crucial document used to report and calculate the potential arbitrage rebate liability on tax exempt bonds. Issuers must file this form with the IRS to ensure compliance with tax regulations and to determine if any rebate payments are owed.
The form requires information such as bond issuance details, investment earnings, and bond expenditures. Accurate and timely submission of Form 8038-T is vital, as failure to file or errors in reporting could lead to penalties and further complications.
Benefits of Form 8038-T
Form 8038-T is a crucial form used in the context of tax exempt bonds to comply with various arbitrage-related requirements. Here are the benefits of Form 8038-T with regard to arbitrage rebate, yield reduction, and penalties in lieu of arbitrage rebate:
- ** Arbitrage rebate calculation**: Form 8038-T is primarily used to calculate the arbitrage rebate, which is a requirement under the tax law for issuers of tax exempt bonds. Arbitrage refers to the practice of earning a higher rate of return on the invested bond proceeds than the interest rate paid on the bonds. The IRS requires issuers to calculate and pay an arbitrage rebate to the federal government to prevent profiting from the tax exempt status of the bonds.
- Compliance with IRS regulations: By filing Form 8038-T, issuers can demonstrate compliance with IRS regulations regarding arbitrage rebate calculations. This helps ensure that issuers are adhering to the tax rules governing tax exempt bonds and (link: https://fincent.com/blog/how-to-avoid-tax-penalties-a-simple-guide text: avoiding any potential penalties) for non-compliance.
- Yield reduction payment calculation: If an issuer cannot meet the spending requirements outlined in the tax code for tax exempt bond proceeds, they may be required to make a yield reduction payment to the federal government. The purpose of this payment is to compensate for the lost tax revenue that would have been generated if the bond proceeds were spent as intended. Form 8038-T aids in calculating this yield reduction payment when applicable.
- Penalty in lieu of arbitrage rebate calculation: In some cases, an issuer may face difficulties in calculating the exact arbitrage rebate due to complexities in the bond issue. The IRS offers an option for issuers to pay a penalty in lieu of the arbitrage rebate calculation if certain conditions are met. Form 8038-T facilitates this process by providing the necessary information to assess the penalty amount, if applicable.
- Tax exempt status retention: By adhering to the rules and calculations outlined in Form 8038-T, issuers can maintain the tax exempt status of their bonds. This is crucial as it allows the interest earned by bondholders to remain tax-free, making the bonds more attractive to investors.
- Avoiding penalties and interest: Timely and accurate filing of Form 8038-T helps issuers avoid potential penalties and interest charges that might be imposed for non-compliance with arbitrage rebate and yield reduction requirements. Penalties for non-compliance can be substantial, making proper form filing essential.
It's essential for issuers of tax exempt bonds to understand and fulfill their obligations related to arbitrage rebate, yield reduction, and penalties in lieu of arbitrage rebate. Failure to do so can result in financial consequences and negative implications for the tax exempt status of the bonds.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 8038-T?
Eligibility to file Form 8038-T is typically limited to issuers of tax exempt bonds who have met the following conditions:
Issuance of tax exempt bonds: The issuer must have issued tax exempt bonds, which means the interest on these bonds is exempt from federal income tax.
**Bond proceeds investment: **The issuer invested the bond proceeds in higher-yielding investments (such as stocks, mutual funds, or other securities) during the temporary period before the bond's proceeds are used for their intended tax exempt purposes.
Exceptions: There are certain exceptions and thresholds for small issuers or for specific types of bond issues.
Compliance: The issuer needs to ensure compliance with arbitrage rules set forth by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to determine whether they owe any arbitrage rebate, yield reduction, or penalty in lieu of arbitrage rebate.
It's essential for issuers of tax exempt bonds to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor who is familiar with arbitrage rebate rules to determine if they are eligible to file Form 8038-T and to properly calculate any potential arbitrage rebate or penalties owed.
How To Complete Form 8038-T: A Step-by-Step Guide
Form 8038-T is used to calculate the rebate due to the federal government concerning arbitrage earnings on certain tax exempt bonds and to request relief from yield reduction requirements.
Step-by-step guide to completing Form 8038-T:
Step 1: Obtain the form
Visit the IRS website (www.irs.gov) and search for "Form 8038-T."
Download and print the most recent version of the form and its instructions.
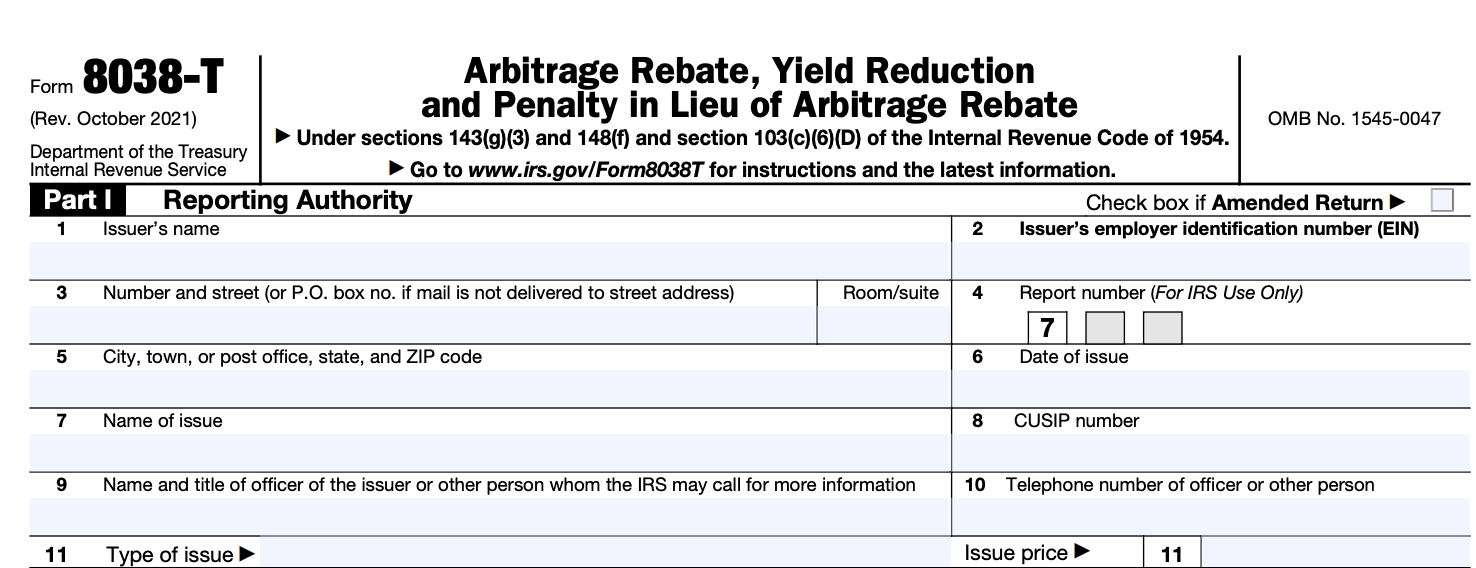
Step 2: Provide basic information
In Part I, fill in the basic details, such as the issuer's name, issuer's identifying number, and the issue price of the bonds.
Step 3: Calculate arbitrage rebate
In Part II, you'll calculate the rebate amount due to the federal government on arbitrage earnings. This involves determining the earnings and computing the rebate based on the applicable rates.

Step 4: Requesting relief from yield reduction
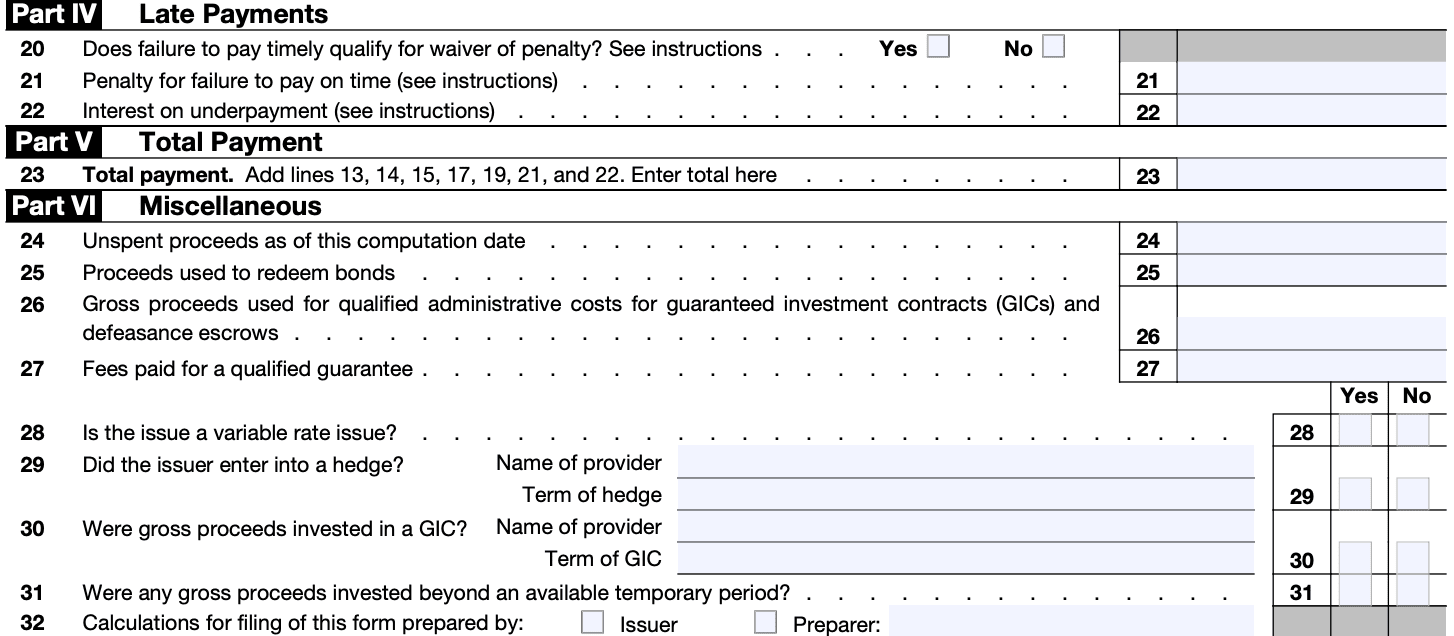
If the issuer wants to request relief from yield reduction requirements, complete Part III. The issuer needs to provide the required information and supporting documentation as specified in the instructions.
If the issuer wants to pay penalties in lieu of rebate, complete Part IV. The instructions will guide you through the process and calculation.

Step 5: Prepare supporting documents
Ensure that you have all the necessary documents ready to support the information provided on the form, such as bond documents, investment records, and calculations.
Step 6: Review and double-check
Review the completed form thoroughly to make sure all information is accurate and entered correctly.
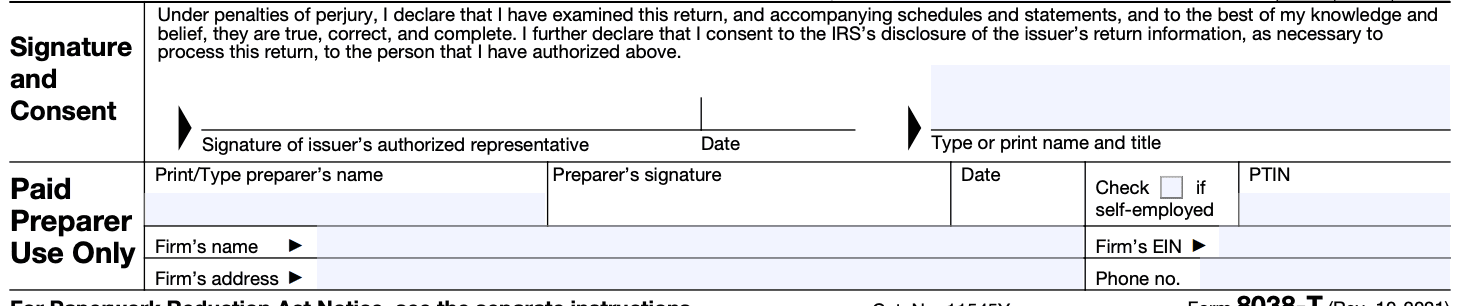
Step 7: Sign and submit the completed Form 8038-T
File the form with the appropriate IRS office by the due date specified in the instructions.
Step 8: Keep a copy
Make a copy of the completed and signed Form 8038-T and all supporting documents for your records.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 8038-T
Here are some special considerations when filing Form 8038-T for arbitrage rebate, yield reduction, and penalty in lieu of arbitrage rebate:
**Accurate calculation of rebate: **The primary purpose of this form is to report the calculation of arbitrage rebate due on tax exempt bonds. This calculation can be complex, involving various factors such as bond issuances, investment earnings, and allowable expenditures. Ensure that the rebate calculation is accurate and follows the IRS guidelines.
Comply with rebate requirements: Tax exempt bonds are subject to rebate requirements under the tax code, which limits the investment earnings that can be retained without triggering arbitrage rebate obligations. Make sure that the bond issuer complies with these requirements and remits any required rebate payments.
Consider yield reduction payments: In some cases, issuers may choose to make yield reduction payments to avoid the complexities of calculating and paying arbitrage rebates. Understand the requirements and implications of making yield reduction payments and report them accurately on Form 8038-T.
Penalty in lieu of arbitrage rebate: If a bond issuer fails to pay the required arbitrage rebate timely, they may be subject to penalties. Form 8038-T provides the means to report and pay these penalties.
Timely filing: File the form by the due date specified by the IRS. Missing the deadline may result in penalties or interest charges.
Attach required documentation: Depending on the specific transactions and calculations involved, you may need to attach additional documentation to support the information reported on Form 8038-T. Ensure that all required documentation is provided.
Seek professional advice: The rules and regulations related to arbitrage rebate and penalty in lieu of arbitrage rebate can be intricate and subject to change. Consider seeking advice from a qualified tax professional or legal advisor to ensure compliance and accuracy when preparing and filing Form 8038-T.
How To File Form 8038-T: Offline/Online/E-filing
Offline filing
In the past, you could obtain a physical copy of Form 8038-T from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or by downloading it from their website. Once you fill out the form manually, you would mail it to the IRS address designated for your specific region or state.
Online filing
The IRS might offer an online version of Form 8038-T on their official website. You would need to access their e-file platform, fill in the required information electronically, and submit the form online. If this option is available, the IRS would provide instructions on their website.
E-filing through approved software
Instead of using the IRS e-file platform, you might have the option to file Form 8038-T through approved tax preparation software. In this case, you would use the software's interface to enter the necessary details and submit the form electronically to the IRS.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 8038-T
Missing or late filing: Ensure that you file Form 8038-T by the required due date. Late or missing filings may result in penalties and interest charges.
Incomplete or inaccurate information: Double-check all the information provided on the form for accuracy. Incorrect details such as bond issuer information, bond description, and dates could lead to processing delays or incorrect reporting.
Incorrect tax exempt bond classification: Make sure you correctly classify the type of tax exempt bonds being issued. Different types of bonds may have specific reporting requirements, and misclassification could lead to compliance issues.
Failure to report material events: If there are any significant events related to the bonds, such as a change in use or private use limitations, it is crucial to report these events on Form 8038-T in a timely manner.
Incorrect calculations: Verify all financial information and calculations included in the form. Errors in calculating the issue price, yield, or arbitrage could lead to discrepancies in reporting.
Missing or incorrect attachments: Ensure you include all required attachments with the form. These may include copies of the official statement and any closing documents relevant to the bond issuance.
Failing to retain a copy: Always keep a copy of the filed Form 8038-T and all related documents for your records. This will help you in case of any inquiries or audits by the IRS.
Ignoring changes in regulations: Stay updated with any changes to tax laws and reporting requirements. Failure to adhere to updated regulations could lead to non-compliance issues.
**Not seeking professional advice: **If you are unsure about any aspect of filing Form 8038-T, consider seeking advice from a tax professional or legal expert with experience in tax exempt bond issuances.
Remember, Form 8038-T is a critical document for reporting tax exempt bond issuances, and mistakes can have serious consequences. Taking the time to review all details and seeking professional guidance when needed can help you avoid these common errors and ensure a smooth filing process.
Conclusion
Form 8038-T serves as a critical instrument in managing arbitrage earnings on tax exempt bonds. It helps ensure fairness in the tax system and prevents bond issuers from exploiting interest rate discrepancies for excessive profit.
By either paying the required arbitrage rebate, utilizing yield reduction, or opting for a penalty in lieu of arbitrage rebate, bond issuers can fulfill their obligations and comply with federal tax regulations.
As the regulatory landscape can be complex and subject to change, bond issuers should seek professional advice and stay updated on IRS guidelines to navigate Form 8038-T and related tax obligations successfully.
Being proactive and accurate in complying with these regulations will help foster a transparent and efficient bond market, benefiting both issuers and investors alike


