- IRS forms
- Form 1116
Form 1116: Foreign Tax Credit
Download Form 1116When it comes to international taxation, navigating the complexities of reporting and minimizing double taxation can be a challenging task for individuals and businesses. Fortunately, the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) offers a solution known as the Foreign Tax Credit (FTC). Form 1116 is the key tool used to claim this credit, allowing taxpayers to offset their U.S. tax liability by the foreign taxes they have paid on their foreign-sourced income.
The Foreign Tax Credit is a provision within the U.S. tax system that aims to prevent double taxation on income earned abroad. It enables taxpayers to claim a credit for income taxes paid to a foreign country or U.S. possession on their foreign-sourced income. The credit is available to both individuals and businesses, and it applies to various types of income, such as wages, interest, dividends, rental income, and business profits.
In this blog post, we will explore Form 1116 and shed light on how it helps taxpayers reduce their overall tax burden.
Purpose of Form 1116
Form 1116 is a tax form used by United States taxpayers who have foreign income and wish to claim a foreign tax credit. The purpose of Form 1116 is to calculate the amount of foreign taxes paid or accrued on foreign income and to determine the allowable foreign tax credit that can be claimed on the taxpayer's U.S. tax return.
The foreign tax credit is designed to prevent double taxation, where income is taxed both by the foreign country where it was earned and by the United States. By claiming the foreign tax credit, taxpayers can offset some or all of the U.S. tax liability on foreign income with the taxes paid to the foreign country.
To complete Form 1116, taxpayers need to provide information about their foreign income, the amount of foreign taxes paid or accrued, and calculate the allowable foreign tax credit. The form requires details such as the type of income, the country where it was earned, and the specific amount of foreign taxes paid or accrued.
It's important to note that Form 1116 is only applicable to individuals, estates, or trusts that are eligible to claim the foreign tax credit.
Benefits of Form 1116
Here are some benefits of filing Form 1116:
-
Avoidance of double taxation: The primary purpose of Form 1116 is to prevent double taxation on income earned in a foreign country. If you are a U.S. taxpayer who has already paid taxes on foreign income, you can use Form 1116 to claim a credit for those taxes paid, reducing your U.S. tax liability.
-
Reduction of overall tax burden: By claiming the foreign tax credit, you can reduce your overall tax burden. The credit is generally dollar-for-dollar, meaning that the amount of foreign taxes paid directly reduces your U.S. tax liability.
-
Flexibility in claiming the credit: Form 1116 allows you to choose between claiming a credit for foreign taxes paid or deducting those taxes as an itemized deduction. In many cases, claiming the credit results in greater tax savings.
-
Wide range of eligible taxes: The foreign tax credit can be claimed for various types of taxes paid to foreign countries, such as income taxes, withholding taxes, and certain value-added taxes (VAT). This allows you to benefit from the credit regardless of the specific tax structure in the foreign country.
-
Carryover and carryback provisions: If the foreign tax credit exceeds your U.S. tax liability in a given year, you can carry back the excess credit to the preceding tax year or carry it forward for future use. This provides flexibility in utilizing the credit effectively over multiple years.
-
Interaction with foreign tax treaties: The United States has tax treaties with many countries to prevent double taxation and provide additional benefits to taxpayers. Form 1116 takes into account the provisions of these tax treaties, allowing you to maximize the benefits available.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 1116?
The following individuals or entities may be eligible to file Form 1116:
**U.S. citizens: **U.S. citizens who have earned income from foreign sources and have paid foreign taxes on that income may be eligible to claim the foreign tax credit.
**U.S. resident aliens: **Resident aliens of the United States, who are considered tax residents for U.S. tax purposes, may be eligible to claim the foreign tax credit if they have paid foreign taxes on income earned from foreign sources.
U.S. corporations: Domestic corporations that have paid or accrued foreign taxes on income earned from foreign sources may be eligible to claim the foreign tax credit.
U.S. partnerships: Partnerships that have foreign tax expenses allocated to the partners may file Form 1116 to pass through the foreign tax credit to the partners.
**U.S. estates and trusts: **Estates and trusts that have paid or accrued foreign taxes on income earned from foreign sources may be eligible to claim the foreign tax credit.
How To Complete Form 1116: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here's a general outline of the process:
Step 1: Gather necessary information
Collect all the information and documents you'll need to complete Form 1116. This includes your foreign income tax returns, supporting statements, and any other relevant documentation that verifies the foreign taxes paid.
Step 2: Determine eligibility
Make sure you meet the eligibility criteria to claim the foreign tax credit. Generally, you must have paid or accrued foreign taxes on income, the income must be taxable in the United States, and you must have foreign source income.
Step 3: Complete general information
Provide your name, Social Security number or employer identification number (EIN), address, and other basic identification details as requested at the header.
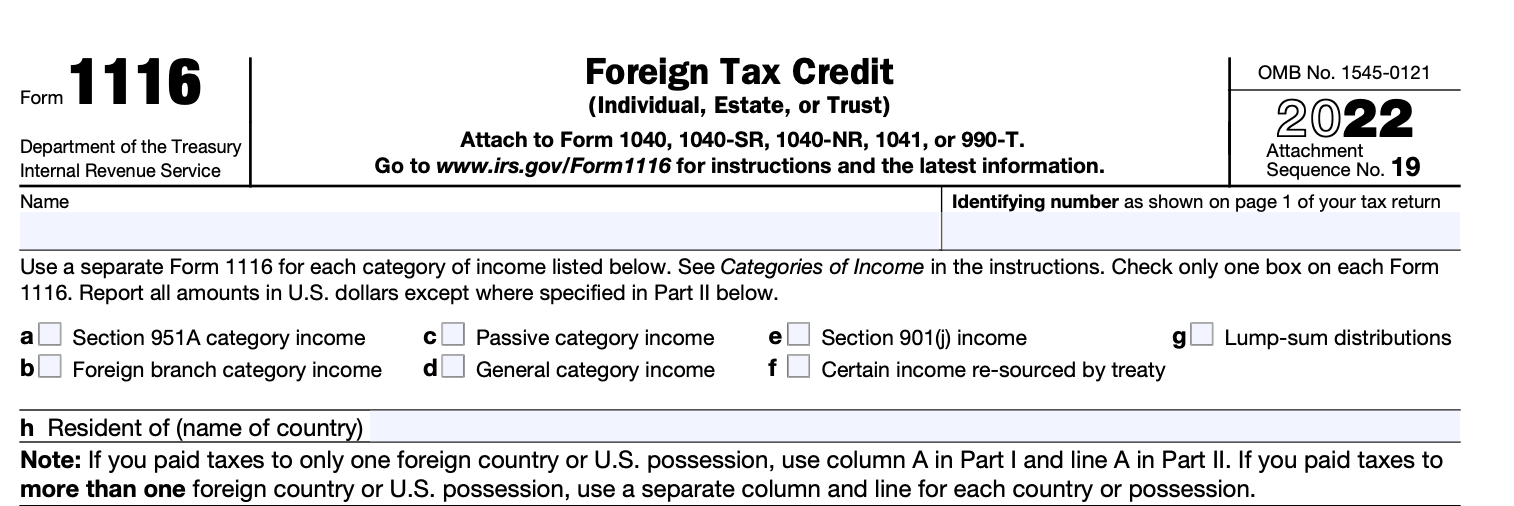
Step 4: Complete Part I - Income
In this section, you'll report your foreign income from various sources. This may include wages, dividends, interest, rental income, or other types of income. Follow the instructions provided on the form to report each income type separately.
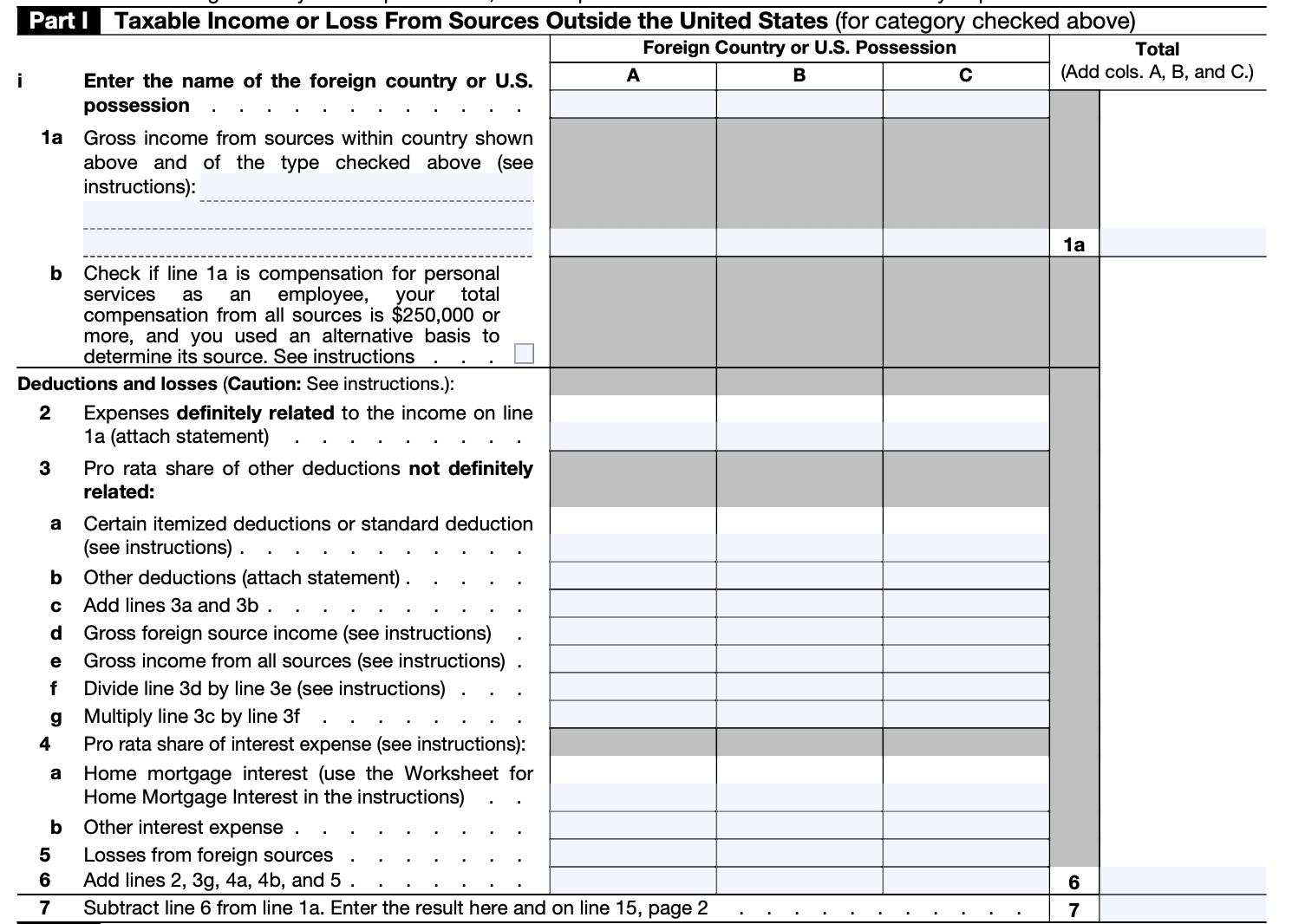
Step 5: Complete Part II - Income taxes paid or accrued
Here, you'll report the foreign taxes you paid or accrued during the tax year. Include the name of the foreign country or countries, the type of income the taxes were paid on, and the amount of foreign taxes paid. Use separate lines for each foreign country.
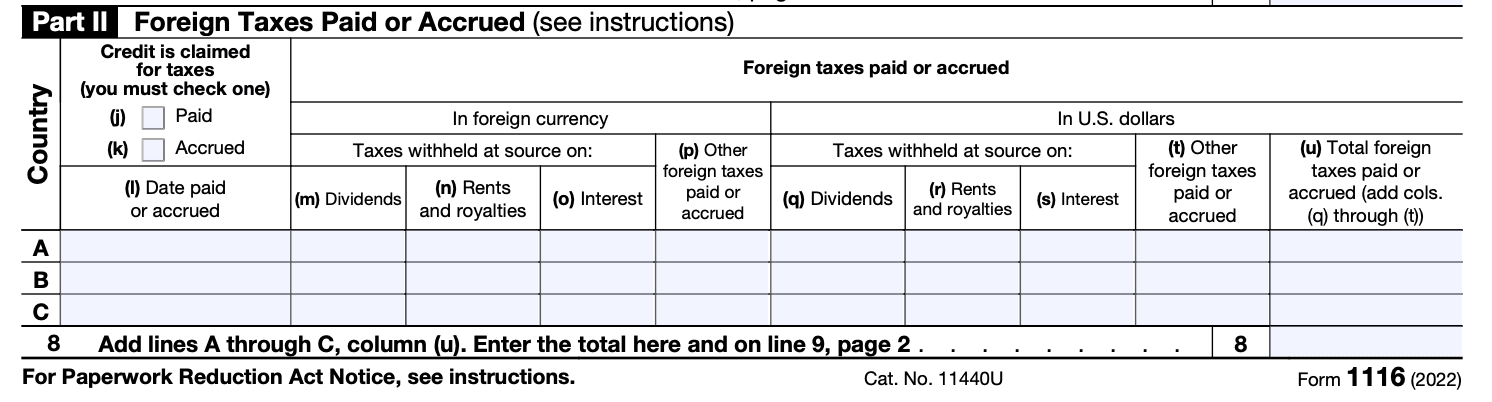
Step 6: Complete Part III - Foreign tax credit
This section calculates your foreign tax credit based on the information provided in Parts II and III. Follow the instructions carefully and use the appropriate worksheets, if required, to determine your allowable foreign tax credit.
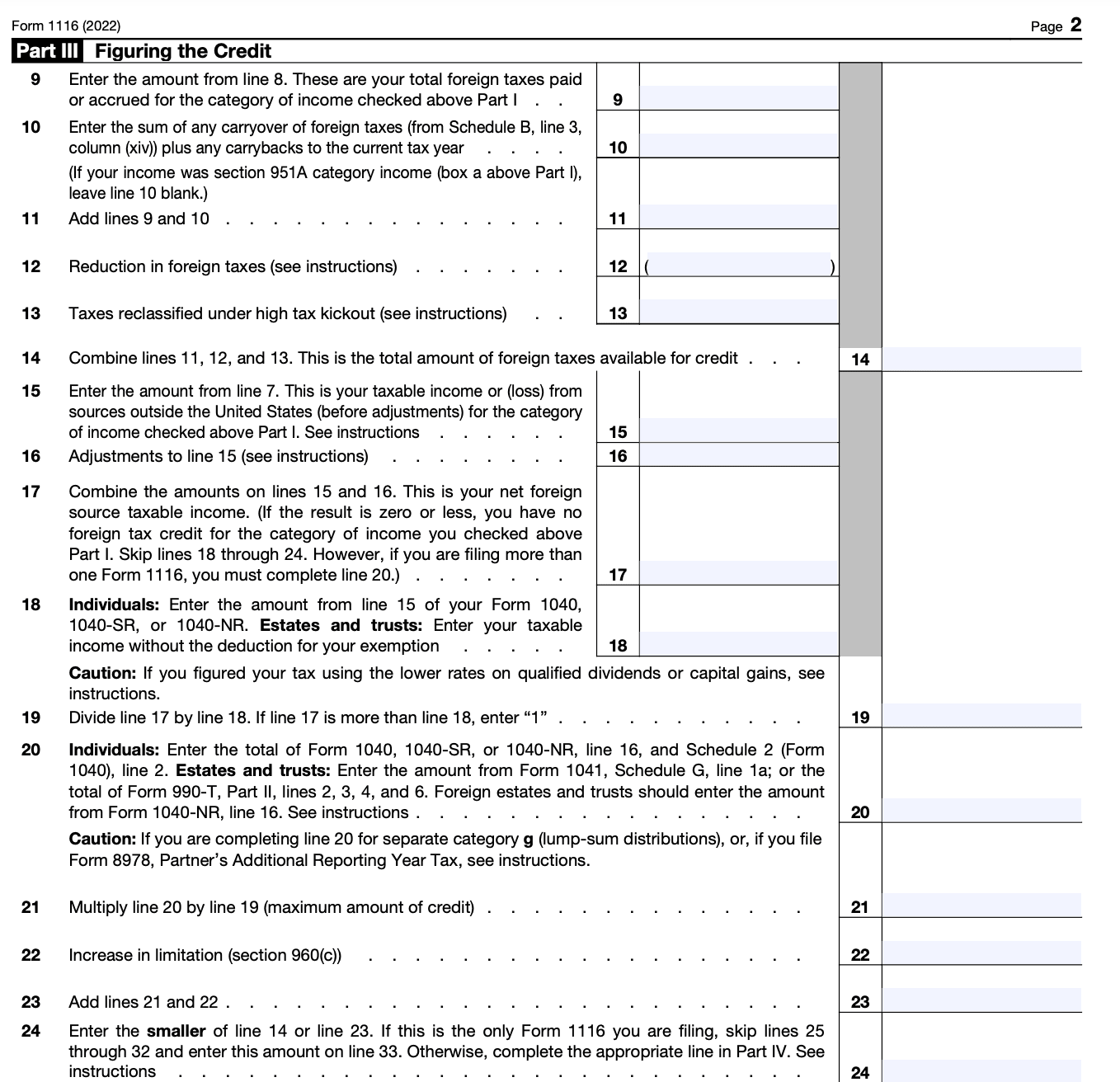
Step 8: Complete Part IV - Limitation on credit
If your foreign tax credit is limited in any way, such as the foreign source income being exempt from U.S. tax, you'll need to complete this section to calculate the limitation on your credit.
Step 9: Complete the remaining sections
Follow the instructions on the form to complete any remaining sections, including the signature area and any additional statements or disclosures that may be required.
Step 10: Review and file
Review your completed Form 1116 for accuracy and completeness. Attach any supporting documents as instructed. Make a copy for your records, and file the original form with your individual or corporate tax return.
Remember, this is just a general guide, and the specific requirements and calculations may vary depending on your individual circumstances.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 1116
When filing Form 1116, also known as the Foreign Tax Credit, there are several special considerations to keep in mind. Here are some important points to consider:
Qualifying income: Ensure that the foreign taxes you paid or accrued are eligible for the foreign tax credit. Generally, only income that is subject to both U.S. and foreign tax can be used to claim the credit.
Separate limitation income: If you have income from multiple countries, you may need to calculate the foreign tax credit separately for each country. This is known as Separate Limitation Income (SLI). The foreign taxes paid or accrued in each country are allocated to the corresponding SLI category.
Passive category income: Passive income, such as dividends, interest, royalties, and certain capital gains, falls under a separate category called Passive Category Income (PCI). There are specific rules and limitations for claiming the foreign tax credit on PCI.
Carryover and carryback: Unused foreign tax credits can generally be carried back one year or carried forward for up to ten years. If you have unused credits from a prior year or anticipate future foreign tax credits, you may need to consider the carryover and carryback provisions.
Tax treaty considerations: If there is a tax treaty between the United States and the foreign country, it may impact your eligibility for the foreign tax credit. Some tax treaties may modify the rules for calculating the credit or provide specific provisions for certain types of income.
Alternative minimum tax (AMT): The foreign tax credit may be limited if you are subject to the AMT. The rules for calculating the foreign tax credit under the AMT are different from the regular tax calculation.
Supporting documentation: It is crucial to maintain proper documentation to support your foreign tax credit claim. This includes records of foreign taxes paid or accrued, statements from foreign tax authorities, and any other relevant documentation.
Form 1116 instructions: Carefully review the instructions provided by the IRS for Form 1116. The instructions provide detailed guidance on completing the form correctly and addressing various scenarios.
How To File Form 1116: Offline/Online/E-filing
Here's a brief overview of how to file Form 1116 using different methods: offline, online, or e-filing.
Offline filing
a. Download the form: Visit the IRS website (www.irs.gov) and search for Form 1116. Download and print the form along with the instructions.
b. Fill out the form: Carefully fill out all the required information on the Form 1116 according to the instructions provided. Double-check your entries for accuracy.
c. Attach supporting documents: Gather the necessary supporting documents, such as foreign tax statements or proof of payment, and attach them to your completed Form 1116.
d. Mail the form: Once you have filled out the form and attached the required documents, mail it to the appropriate IRS address provided in the instructions for Form 1116. It is recommended to send it via certified mail or with a return receipt requested to have proof of mailing.
Online filing
a. Access tax preparation software: Use tax preparation software, such as TurboTax or H&R Block, to file your tax return online. Most software programs support the filing of Form 1116.
b. Enter the Information: Follow the instructions provided by the tax software to enter the relevant information from your foreign tax statements and income.
c. Complete Form 1116: The software will guide you through completing Form 1116 electronically. Provide the necessary details as prompted and ensure the accuracy of your entries.
d. Submit the return: Once you have completed all the required sections, review your return for accuracy and submit it electronically through the tax software. The software will provide instructions on how to file electronically.
E-filing
a. Use IRS Free File: If your income falls within certain thresholds, you may qualify for IRS Free File. Visit the IRS website (www.irs.gov) and look for the Free File option to see if you are eligible.
b. Choose an e-filing option: Select an IRS-approved e-filing service provider from the available options on the IRS website. These providers will guide you through the e-filing process, including Form 1116.
c. Enter the required information: Follow the instructions provided by the e-filing service to enter the necessary information from your foreign tax statements and income.
d. Submit the return: Review your return for accuracy, and once you're satisfied, submit it electronically using the e-filing service. The service will provide instructions on how to submit your return electronically.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 1116
When filing Form 1116, which is used to claim a foreign tax credit, it's important to be aware of certain common mistakes to avoid. Here are some mistakes you should watch out for:
Incorrect or incomplete information: Ensure that all the required fields on Form 1116 are completed accurately. Double-check your personal information, income figures, and tax calculations to avoid errors.
Using the wrong tax year: Make sure you are using the correct tax year for which you are claiming the foreign tax credit. The tax year on Form 1116 should match the tax year on your tax return.
**Failing to attach supporting documents: **Depending on the amount of foreign tax paid and other factors, you may need to attach certain supporting documents to your Form 1116. These may include statements from foreign tax authorities, receipts, or other documentation to substantiate your claim. Ensure that you have included all the necessary attachments.
Incorrect currency conversions: If you paid foreign taxes in a currency different from your country's currency, you'll need to convert the foreign tax amounts to your home currency for reporting on Form 1116. Use the appropriate exchange rates for the tax year in question and make sure your conversions are accurate.
Not reporting all eligible foreign taxes: Ensure that you include all eligible foreign taxes you paid or accrued during the tax year. This includes taxes withheld on foreign investment income, taxes paid to a foreign government, or taxes paid on foreign business activities.
Neglecting to account for limitations: Be aware of the limitations and restrictions that may apply when claiming the foreign tax credit. For example, there are limitations on the amount of foreign tax credit you can claim based on your foreign income and the foreign tax rate. Make sure you understand these limitations and calculate your credit accurately.
Ignoring carryovers: If you have excess foreign tax credits that cannot be used in the current tax year, be sure to properly track and carry them forward to future years. Failure to account for carryovers can result in lost tax benefits.
Not seeking professional advice when needed: The rules and regulations surrounding foreign tax credits can be complex, especially if you have multiple sources of foreign income or if you're subject to specific tax treaties. If you are unsure about any aspect of Form 1116, consider seeking advice from a tax professional or consulting the IRS instructions for the form.
Conclusion
Form 1116 provides taxpayers with a valuable opportunity to reduce their tax liability on foreign-sourced income. By carefully navigating the intricacies of the Foreign Tax Credit, individuals and businesses can avoid double taxation and mitigate the impact of foreign taxes on their U.S. tax obligations.
Understanding the requirements of Form 1116, maintaining accurate documentation, and considering the impact of tax treaties are crucial steps in successfully claiming the Foreign Tax Credit. Always consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance with IRS regulations and optimize the benefits of this credit.


