- IRS forms
- Schedule J (Form 1041)
Schedule J (Form 1041): Accumulation Distribution for Certain Complex Trusts
Download Schedule J (Form 1041)When it comes to tax forms and schedules, things can get complex, especially for trusts. One such schedule that often causes confusion is Schedule J (Form 1041). This schedule is specifically designed for certain complex trusts and is used to report the accumulation distribution.
Schedule J (Form 1041) is an attachment to Form 1041, U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts. It is used by certain complex trusts to report the accumulation distribution. An accumulation distribution refers to the taxable income that the trust retains instead of distributing it to the beneficiaries.
In this blog post, we will delve into the details of Schedule J (Form 1041), providing an overview of its purpose, who needs to file it, and how to complete it accurately. By understanding the requirements of this schedule, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations and avoid potential penalties.
Purpose of Form Schedule J (Form 1041)
Schedule J (Form 1041) plays a crucial role in reporting the accumulation distribution for certain complex trusts. It helps the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) determine the taxable income retained by the trust, ensuring appropriate taxation at the trust level.
If you are responsible for managing a complex trust, it is essential to understand the requirements of Schedule J and file it correctly. By doing so, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations, avoid potential penalties, and maintain the trust's integrity.
Remember, when dealing with complex tax matters, it is always best to consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate reporting and adherence to the latest IRS guidelines.
Benefits of Form Schedule J (Form 1041)
Schedule J (Form 1041) provides several benefits for estates and trusts, including:
-
Calculation of alternative minimum tax (AMT): Schedule J helps estates and trusts determine if they are subject to the alternative minimum tax. The AMT is a separate tax calculation that ensures certain taxpayers pay a minimum amount of tax, regardless of deductions and credits. Schedule J provides the necessary calculations to determine whether AMT is applicable.
-
Deductions and exemptions: Schedule J allows estates and trusts to claim deductions and exemptions that are specific to their tax situation. It helps determine the allowable deductions and exemptions, which can reduce the taxable income and, consequently, the tax liability.
-
Charitable deductions: Schedule J provides a section for estates and trusts to report charitable deductions. This allows the estate or trust to claim deductions for qualifying charitable contributions made during the tax year, reducing their taxable income and potentially lowering their tax liability.
-
Capital gains and losses: If an estate or trust has capital gains or losses, Schedule J helps calculate the net capital gain or loss. It provides a detailed breakdown of gains and losses from the sale of assets, which affects the overall tax liability.
-
Income tax calculation: Schedule J assists in calculating the income tax liability of the estate or trust. By aggregating various sources of income and applying the appropriate tax rates, the form determines the amount of tax owed for the tax year.
-
Refundable credits: In certain cases, estates and trusts may be eligible for refundable credits, such as the earned income credit or the child tax credit. Schedule J provides the necessary calculations to determine the eligibility and amount of these credits, potentially resulting in a refund.
-
AMT carryforwards: If an estate or trust incurs alternative minimum tax in one year but cannot fully utilize the credit, Schedule J helps track and carry forward the unused AMT credit to future tax years. This can reduce the tax liability in subsequent years.
Who Is Eligible To File Schedule J (Form 1041)?
Eligibility to file Schedule J (Form 1041) depends on the type of trust:
Simple trust
A simple trust is eligible to file Schedule J if it meets the following criteria:
- It distributes all its income to the beneficiaries currently.
- It distributes only income and no principal.
- It does not make charitable contributions.
- It does not have any income that is required to be distributed in future years.
Complex trust
A complex trust is eligible to file Schedule J if it meets any of the following criteria:
- It makes charitable contributions.
- It retains some or all of its income and does not distribute it currently.
- It has income that is required to be distributed in future years.
It's important to note that Schedule J is specific to Form 1041, which is the U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts. The eligibility for filing Schedule J applies to trusts subject to U.S. tax laws.
How To Complete Schedule J (Form 1041): A Step-by-Step Guide
Filling out Schedule J (Form 1041) requires specific information about the estate or trust's accumulated earnings and distributions. Here's a step-by-step guide to completing Schedule J:
Step 1: Obtain the necessary forms
Ensure you have the most recent version of Schedule J (Form 1041), which can be found on the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website or obtained from a tax professional.
Step 2: Gather relevant information
Before you begin filling out Schedule J, gather all the necessary information, including:
a) Trust or Estate's Employer Identification Number (EIN)
b) Accumulated earnings and profits (AEP) balance at the beginning of the tax year
c) Distributions made during the tax year
d) Taxable income of the trust or estate for the current tax year
Step 3: Complete Part I: Accumulated Earnings
In Part I, you'll calculate the trust or estate's accumulated earnings. Follow these steps:
a) Enter the beginning balance of accumulated earnings and profits on line 1.
b) Determine the taxable income of the trust or estate for the current tax year and enter it on line 2.
c) Subtract line 2 from line 1 to calculate the adjusted beginning balance of accumulated earnings on line 3.
d) If the trust or estate had any distributions during the tax year, enter the total amount on line 4.
e) Subtract line 4 from line 3 to calculate the adjusted accumulated earnings on line 5.
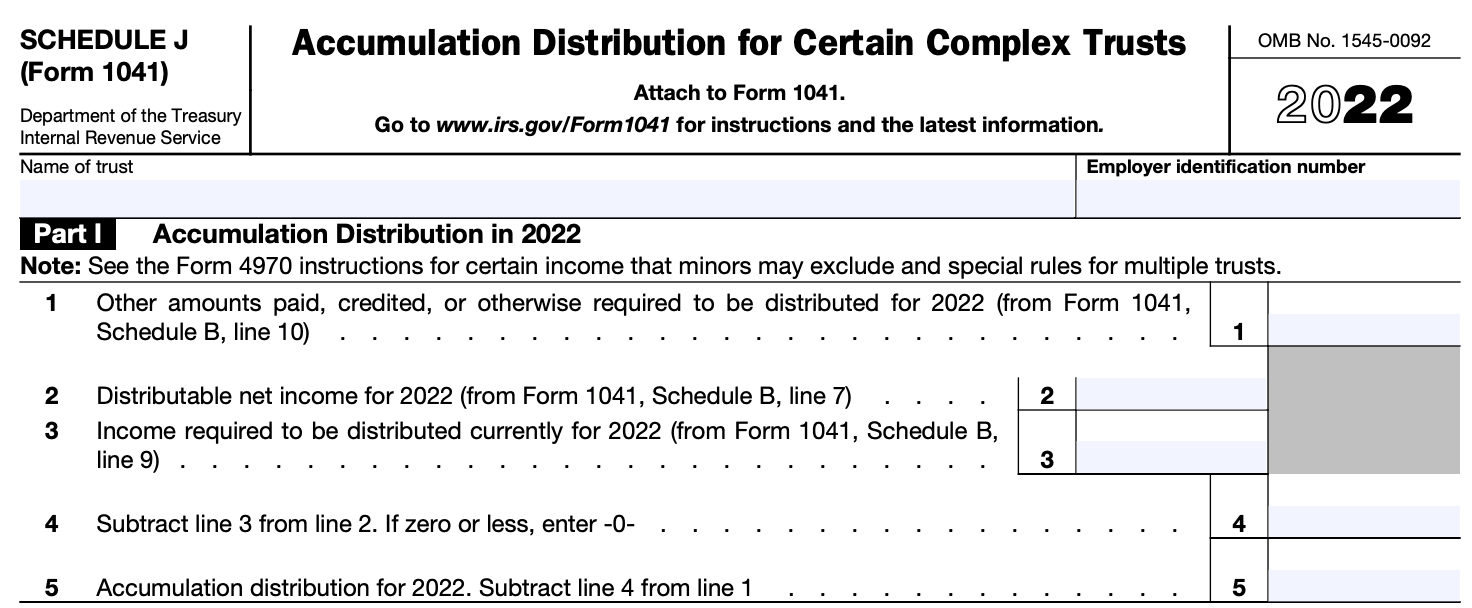
Step 4: Complete Part II: Distributions
In Part II, you'll report the distributions made by the trust or estate. Follow these steps:
a) If the trust or estate had distributions that resulted in a deficit in accumulated earnings and profits, enter the deficit amount on line 6.
b) If the trust or estate had distributions during the tax year, report them on lines 7 through 10 based on the type of recipient (beneficiary, charity, or other).
c) Calculate the total distributions by adding up the amounts from lines 7 through 10 and enter the total on line 11.
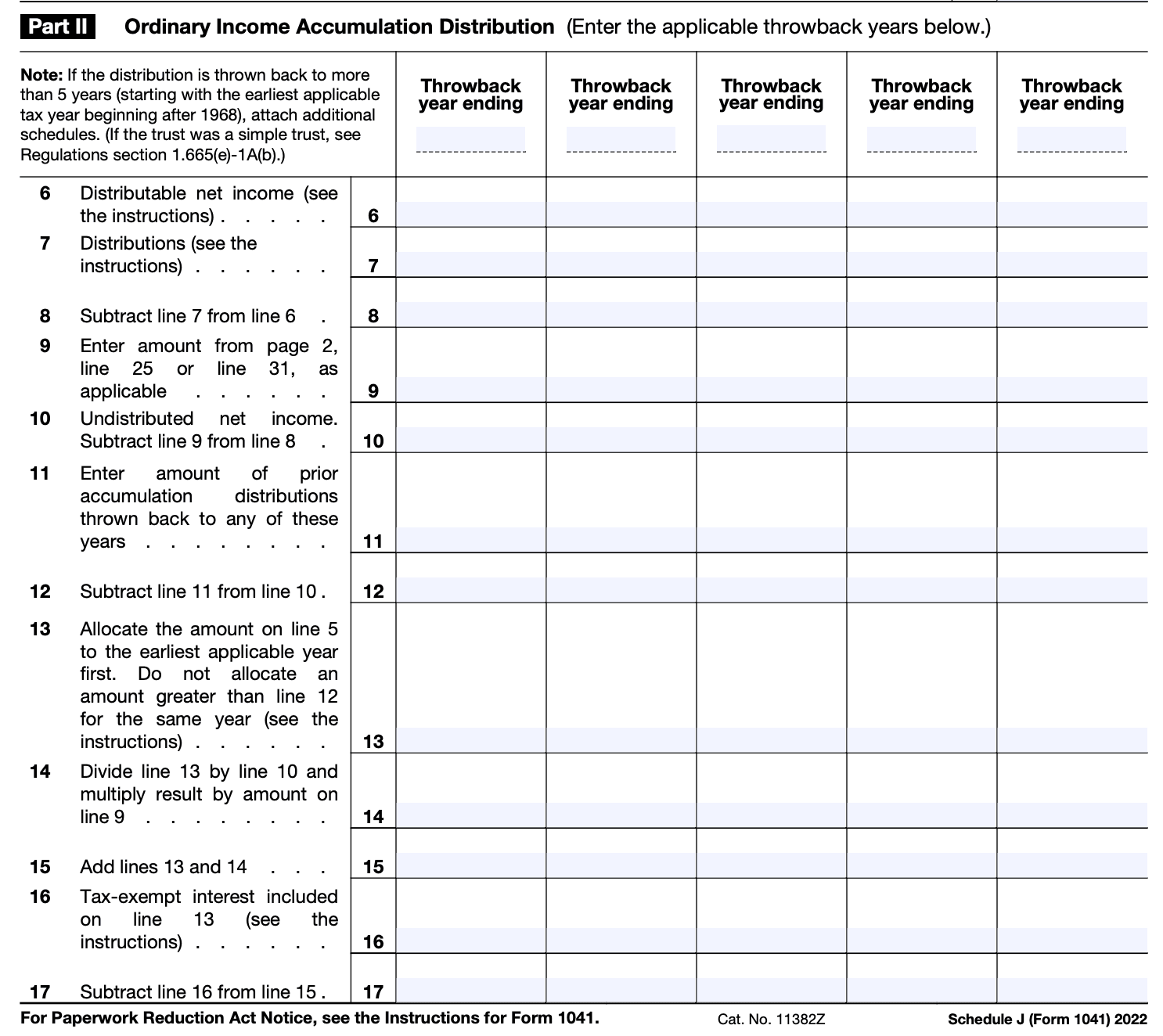
Step 5: Complete Part III: Accumulated Earnings (Distributions Not Deducible)
In Part III, you'll report the amount of accumulated earnings that are not deductible due to distributions. Follow these steps:
a) Enter the amount from line 5, which represents the adjusted accumulated earnings from Part I.
b) Enter the total distributions from line 11.
c) Subtract line 11 from line 5 to calculate the amount of accumulated earnings not deductible on line 12.
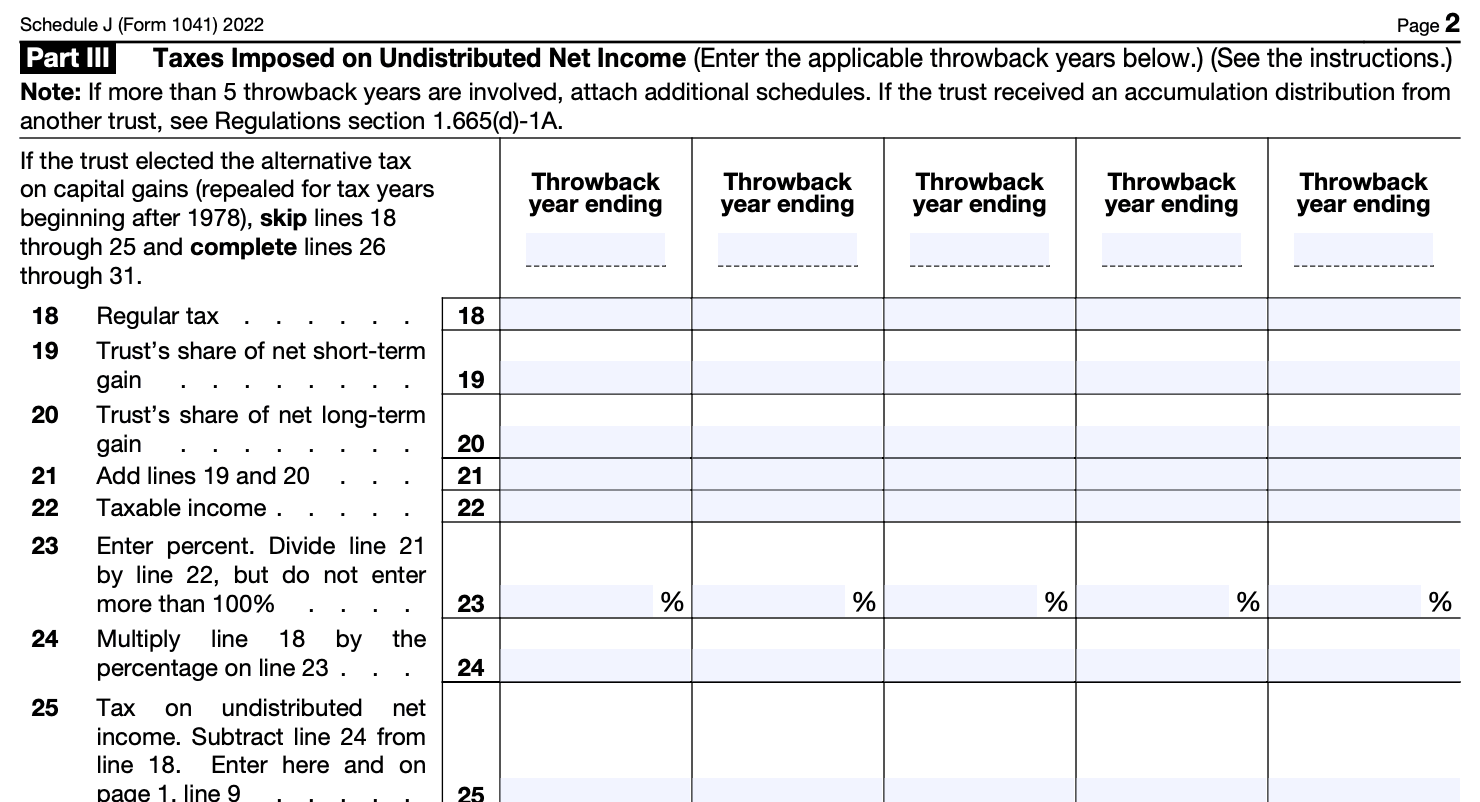
Step 6: Complete Part IV: Accumulated Earnings Subject to Tax
In Part IV, you'll determine the accumulated earnings subject to tax. Follow these steps:
a) Enter the amount from line 5, which represents the adjusted accumulated earnings from Part I.
b) Subtract the amount of accumulated earnings not deductible from line 12.
c) Enter the result on line 13.
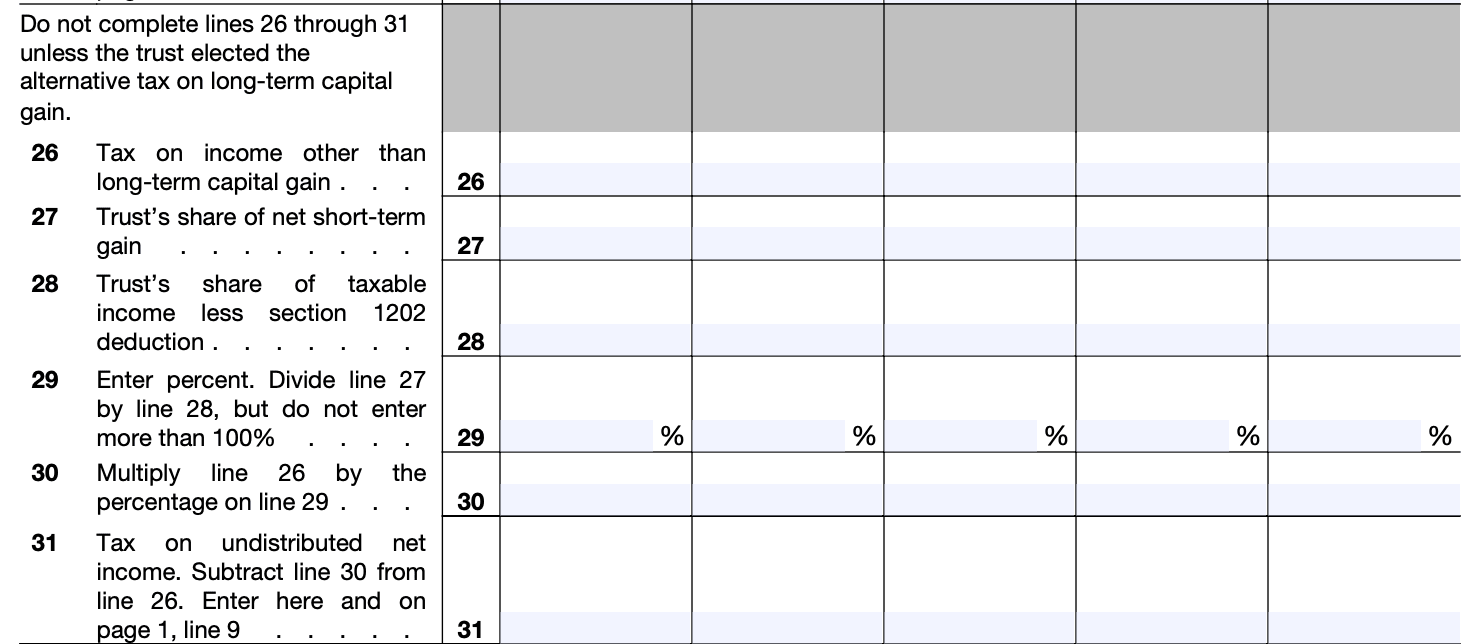
Step 7: Complete Part V: Tax on Accumulated Earnings
In Part V, you'll calculate the tax on the accumulated earnings subject to tax. Follow these steps:
a) Determine the appropriate tax rate based on the trust or estate's taxable income and refer to the tax rate table provided in the instructions.
b) Multiply the accumulated earnings subject to tax from line 13 by the tax rate.
c) Enter the tax amount on line 14.
Step 8: Complete Part VI: Credit for Tax Paid on Accumulated Earnings
In Part VI, you'll report any credits for tax paid on accumulated earnings from a prior year. Follow these steps:
a) Enter the credit amount on line 15.
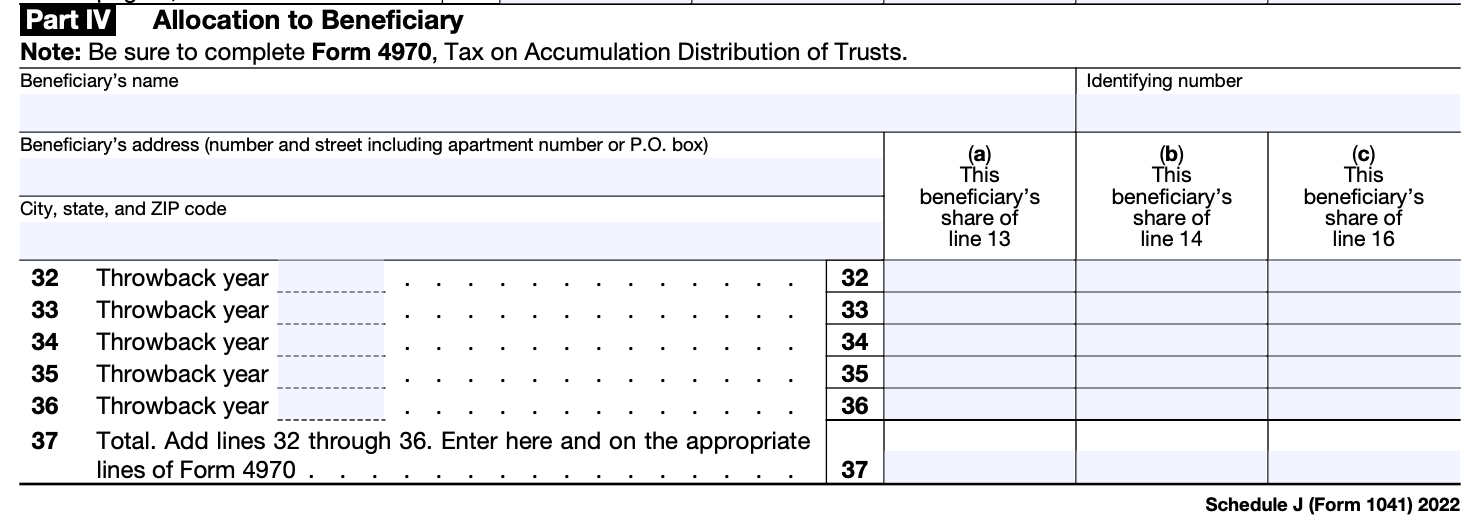
Step 9: Complete Part VII: Tax Due or Overpayment
In Part VII, you'll calculate the tax due or overpayment for the trust or estate. Follow these steps:
a) If the tax on accumulated earnings from line 14 is greater than the credit for tax paid on line 15, enter the tax due on line 16.
b) If the credit for tax paid on line 15 is greater than the tax on accumulated earnings from line 14, enter the overpayment on line 17.
Step 10: Sign and File
Sign and date Schedule J and attach it to Form 1041 when filing your tax return. Retain a copy for your records.
Special Considerations When Filing Schedule J (Form 1041)
When filing Schedule J (Form 1041), which is used to calculate the accumulation distribution for complex trusts and estates, there are a few special considerations to keep in mind. Here are some key points to consider:
Determine if Schedule J is required: Schedule J is only necessary if the trust or estate has undistributed net income and the fiduciary wants to accumulate or pay tax on the income at the trust or estate level. If there is no undistributed net income or if the fiduciary wants to pass the income to the beneficiaries, Schedule J may not be needed.
Understand the purpose of Schedule J: Schedule J is used to calculate the accumulation distribution and tax due on the accumulated income of the trust or estate. It helps determine the tax liability at the entity level rather than passing the income and tax liability to the beneficiaries.
Gather relevant information: To complete Schedule J, you will need the trust or estate's income statement, including all relevant income, deductions, and credits. Additionally, you'll need to know the distribution deductions, the distribution deduction carryover, and the undistributed net income from prior years.
Follow the instructions carefully: The instructions for Schedule J provide detailed guidance on how to calculate the accumulation distribution and complete the form correctly. Make sure to read and follow the instructions to ensure accurate reporting.
Understand tax rates and thresholds: The tax rates for accumulation distributions vary depending on the amount of undistributed net income and the type of trust or estate. Be familiar with the applicable tax rates and thresholds to accurately calculate the tax liability.
Consider state tax implications: While Schedule J is used for federal tax purposes, state tax laws may have different rules and requirements for accumulation distributions. Be sure to consult the relevant state tax guidelines or seek professional advice to address any state tax considerations.
Seek professional assistance if needed: Filing Schedule J can be complex, especially for intricate trusts and estates. If you're unsure about any aspect of completing the form or have complex circumstances, it's advisable to consult a tax professional or fiduciary accountant who specializes in trust and estate taxation.
How To File Schedule J (Form 1041): Offline/Online/E-filing
To file Schedule J (Form 1041), you have several options: offline filing, online filing, and e-filing. Here's a breakdown of each method:
Offline filing
a. Obtain the necessary forms: You can download the Schedule J (Form 1041) and other related forms from the official IRS website (irs.gov) or request them by mail.
b. Fill out the form: Complete Schedule J following the instructions provided. Make sure to accurately report the required information.
c. Attach the form: Once completed, attach Schedule J to your Form 1041.
d. Mail your return: Mail your completed Form 1041 with Schedule J to the appropriate IRS address based on your location. The address can be found in the Form 1041 instructions.
Online filing
a. Use tax preparation software: Utilize tax preparation software approved by the IRS to complete your Form 1041 and Schedule J electronically.
b. Enter the information: Follow the software's instructions to enter the necessary details for Schedule J accurately.
c. Submit your return: After completing the forms, you can submit your return electronically through the tax preparation software. The software will guide you through the process.
E-filing
a. Use an authorized e-file provider: If you're using a tax professional or an authorized e-file provider, they will assist you in preparing and filing your Form 1041 with Schedule J electronically.
b. Provide the required information: Furnish all the necessary information to your tax professional or e-file provider, including the details needed for Schedule J.
c. Review and submit: Review the completed forms for accuracy, and once you're satisfied, authorize your tax professional or e-file provider to electronically file your return on your behalf.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Filing Schedule J (Form 1041)
When filing Schedule J (Form 1041), it's important to be aware of certain common mistakes to avoid. Here are some of the key errors to watch out for:
Incorrectly calculating the accumulated income distribution deduction: The calculation for the accumulated income distribution deduction can be complex. Ensure that you accurately follow the instructions provided by the IRS and use the correct formula to calculate the deduction.
Failing to report all income and deductions: It's crucial to report all relevant income and deductions on Schedule J. Make sure you include all taxable income generated by the trust or estate, such as interest, dividends, and rental income. Additionally, ensure that you accurately report deductions such as expenses, taxes, and charitable contributions.
**Not properly documenting income and deductions: **Supporting documentation is essential for all income and deductions claimed on Schedule J. Keep detailed records of income received and expenses incurred, including receipts, statements, and other relevant documents. These records will be crucial in case of an audit or further inquiry from the IRS.
Neglecting to include all beneficiaries: If the trust or estate has multiple beneficiaries, each beneficiary's share of the accumulated income distribution deduction should be accurately calculated and reported on Schedule J. Ensure that you account for all beneficiaries entitled to the deduction.
Failing to file the form on time: Make sure to file Schedule J along with Form 1041 within the specified deadlines. Late filing may result in penalties and interest charges.
Not reviewing the form for accuracy: Before submitting your tax return, review Schedule J thoroughly to ensure accuracy. Check for any mathematical errors, transposed numbers, or missing information that could trigger discrepancies or issues with your return.
Conclusion
Schedule J (Form 1041) plays a crucial role in reporting the accumulation distribution for certain complex trusts. It helps the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) determine the taxable income retained by the trust, ensuring appropriate taxation at the trust level.
If you are responsible for managing a complex trust, it is essential to understand the requirements of Schedule J and file it correctly. By doing so, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations, avoid potential penalties, and maintain the trust's integrity.
Remember, when dealing with complex tax matters, it is always best to consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate reporting and adherence to the latest IRS guidelines.


