- IRS forms
- Schedule E (Form 1040)
Schedule E (Form 1040): Supplemental Income and Loss
Download Schedule E (Form 1040)When it comes to filing taxes in the United States, it's important to understand the various forms and schedules that may be required. One such schedule is Schedule E (Form 1040), which is used to report supplemental income and loss.
Schedule E (Form 1040) is an Internal Revenue Service (IRS) form used to report supplemental income and loss from various sources, with the primary focus on rental real estate activities. This form is filed as an attachment to your individual income tax return (Form 1040) and provides a comprehensive overview of your rental income, expenses, and overall profitability.
In this blog post, we'll explore Schedule E in detail, helping you navigate through its sections and understand its significance.
Purpose of Schedule E (Form 1040)
The purpose of Schedule E is to provide a detailed breakdown of income and expenses related to rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and other sources of passive income.
Here are some common situations where Schedule E might be used:
Rental real estate: If you own rental properties, Schedule E is used to report rental income and deductible expenses such as mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, repairs, and depreciation.
Royalties: If you receive royalties from publishing a book, music, patents, or other intellectual property, Schedule E is used to report the royalty income and any associated expenses.
Partnerships and S corporations: If you are a partner in a partnership or a shareholder in an S corporation, Schedule E is used to report your share of the income, deductions, and credits from these entities.
Estates and trusts: If you are a beneficiary of an estate or trust and received income from it, Schedule E is used to report the income and related deductions.
The information provided on Schedule E is then transferred to Form 1040, the individual income tax return, where it is combined with other income and deductions to calculate the taxpayer's overall tax liability.
Benefits of Schedule E (Form 1040)
There are several benefits to using Schedule E:
- Rental income: Schedule E allows you to report rental income from real estate properties you own. This can include residential, commercial, or vacation rental properties. By reporting rental income on Schedule E, you can take advantage of various tax deductions and benefits related to rental properties.
- Expense deductions: Schedule E allows you to deduct various expenses associated with your rental properties, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, repairs and maintenance, utilities, property management fees, and depreciation. These deductions can help reduce your taxable rental income and potentially lower your overall tax liability.
- Passive activity losses: If you have rental properties or own interests in partnerships or S corporations, you may be able to use passive activity losses to offset your other income. Schedule E allows you to report these passive losses and potentially reduce your overall tax liability.
- Reporting royalties: If you receive royalty income from intellectual property, such as books, music, patents, or copyrights, you can report it on Schedule E. This form provides a specific section to report your royalty income and any associated expenses.
- Reporting partnerships and S corporations: If you are a partner in a partnership or own shares in an S corporation, Schedule E allows you to report your share of the income, losses, and deductions from these entities. It provides a comprehensive way to report your involvement in these types of businesses.
- Reporting estate and trust income: If you are the beneficiary of an estate or trust, Schedule E allows you to report the income you receive from these sources. It also allows you to report any expenses related to the estate or trust.
By utilizing Schedule E, you can take advantage of these specific tax benefits and deductions associated with rental properties, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and REMICs.
Who Is Eligible To File Schedule E (Form 1040)?
The following individuals or entities are eligible to file Schedule E:
- Individuals who receive rental income from real estate properties they own.
- Individuals who receive royalties from intellectual property, such as books, patents, or copyrights.
- Partnerships and limited liability companies (LLCs) that pass through income and losses to their partners or members.
- S corporations that pass through income and losses to their shareholders.
- Estates and trusts that generate income and distribute it to beneficiaries.
How To Complete Schedule E (Form 1040): A Step-by-Step Guide
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you complete Schedule E:
Step 1: Gather necessary information
Collect all the relevant documents, including rental property income and expenses, partnership or S corporation K-1 forms, royalty statements, and any other income or loss-related documents.
Step 2: Understand the sections
Schedule E is divided into three main sections: Part I - Income or Loss from Rental Real Estate and Royalties, Part II - Income or Loss from Partnerships and S Corporations, and Part III - Income or Loss from Estates and Trusts. Understand which sections apply to you based on your income sources.

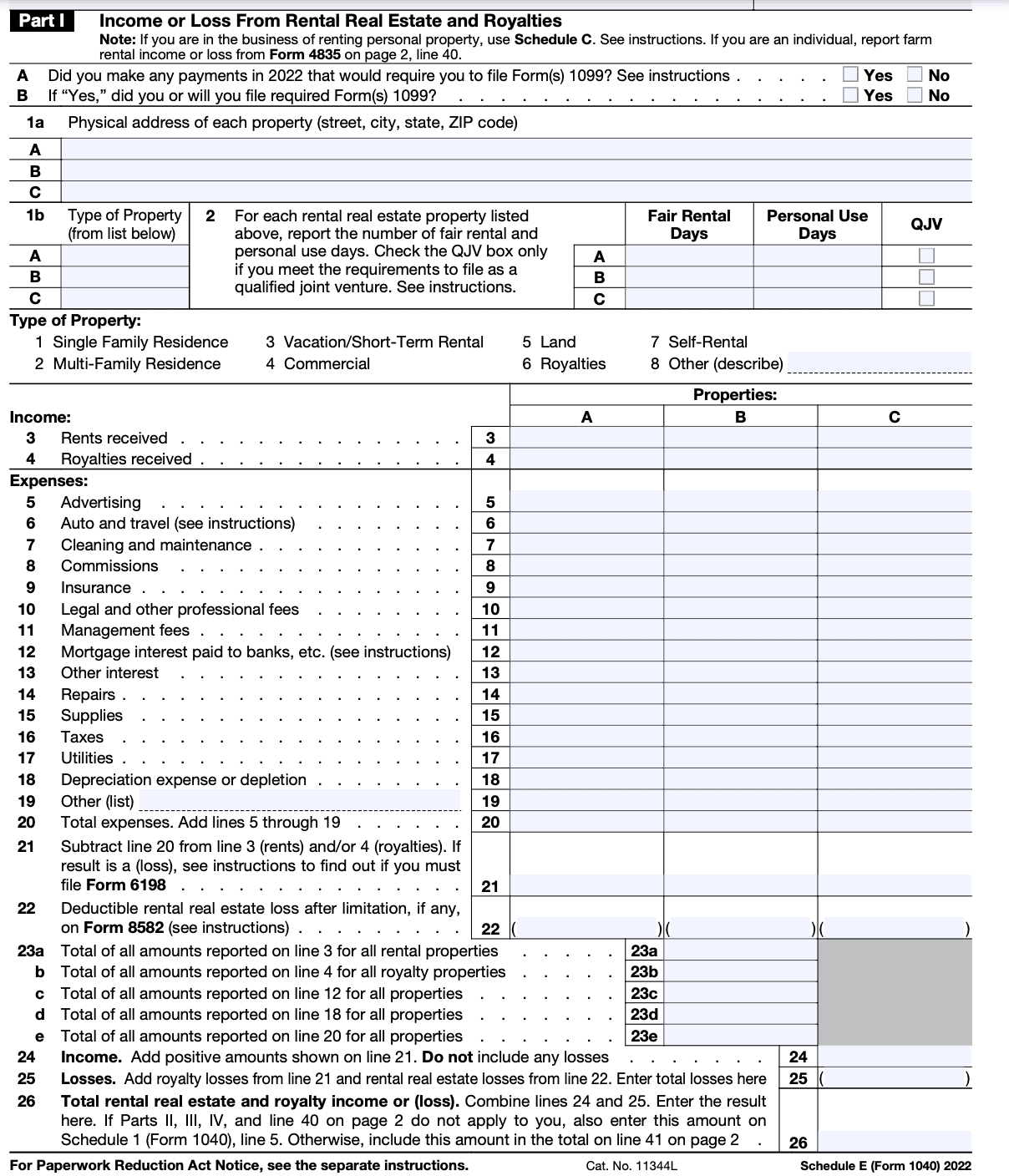
Step 3: Fill out Part I (Rental Real Estate and Royalties)
If you have income or loss from rental properties or royalties, fill out this section. Provide details of each property or royalty source, including addresses, type of property, and rental income. Deduct relevant expenses like mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, repairs, and management fees. Calculate the net income or loss for each property.
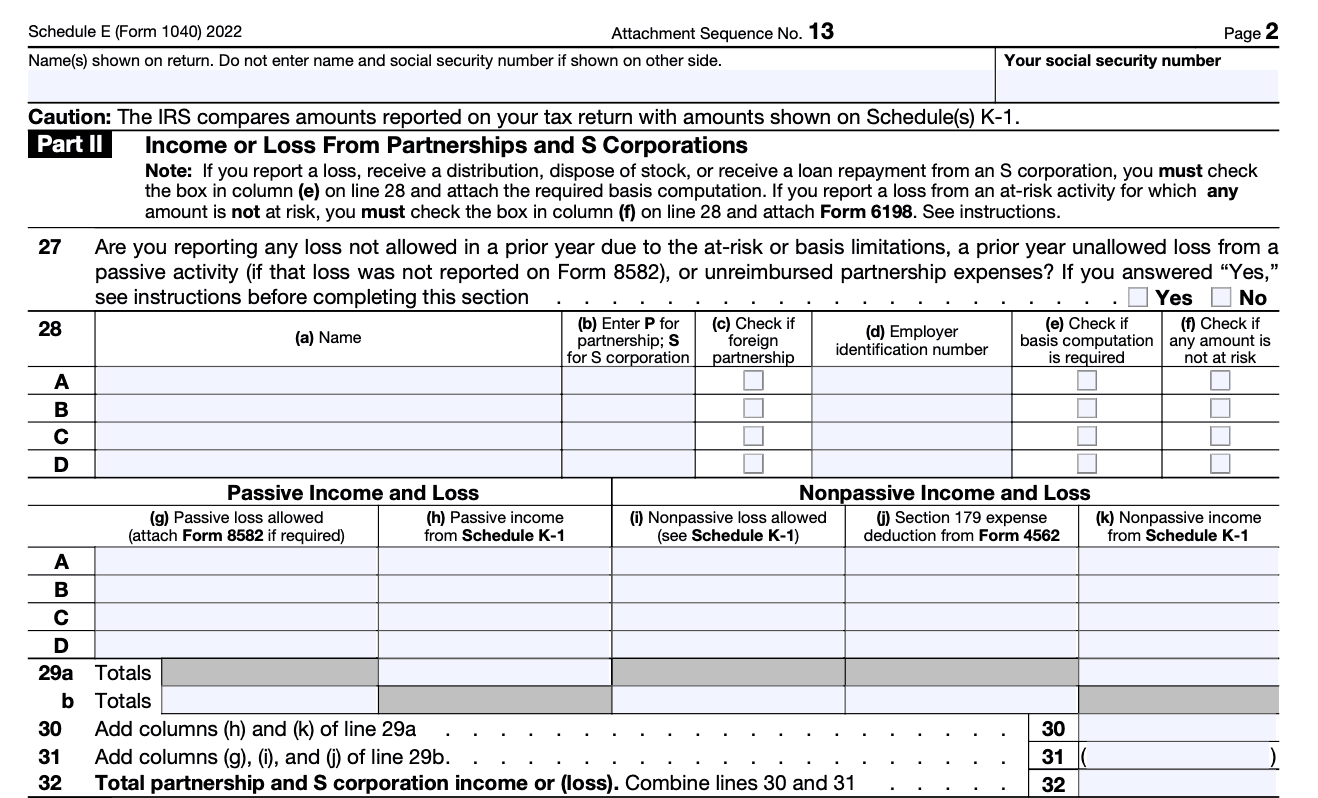
Step 4: Fill out Part II (Partnerships and S Corporations)
If you have income or loss from partnerships or S corporations, fill out this section. Use the K-1 forms you received from each partnership or S corporation to report the relevant income, deductions, and credits. Report each entity's name, employer identification number (EIN), and the income or loss details from the K-1 forms.
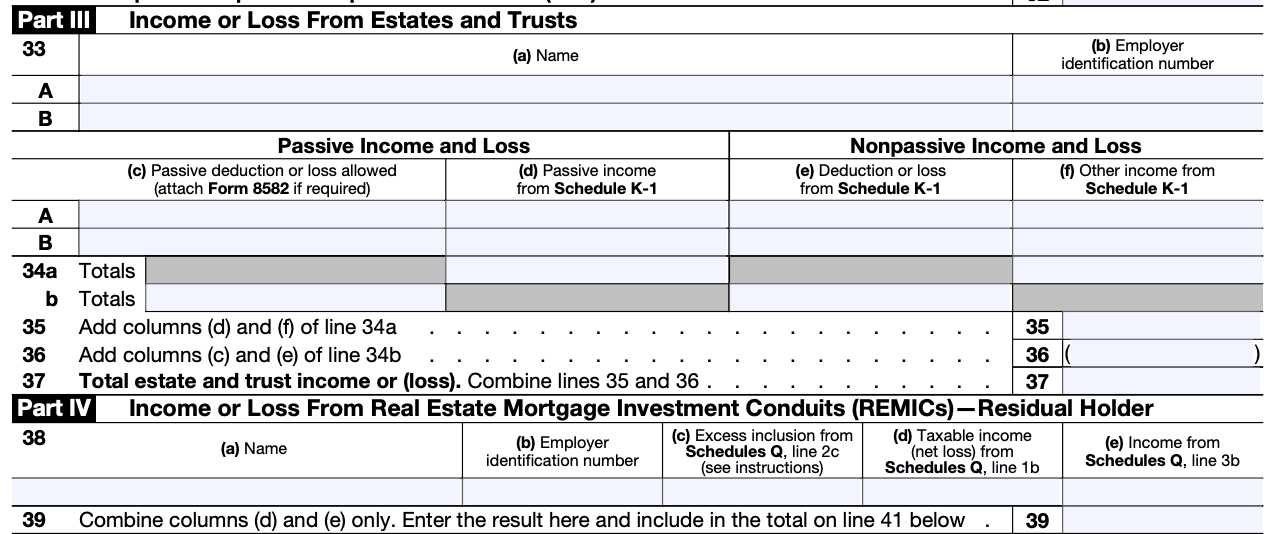
Step 5: Fill out Part III (Estates and Trusts)
If you have income or loss from estates or trusts, fill out this section. Use the information from the estate or trust's Schedule K-1 to report the income, deductions, and credits. Report the name, EIN, and income or loss details from the Schedule K-1.
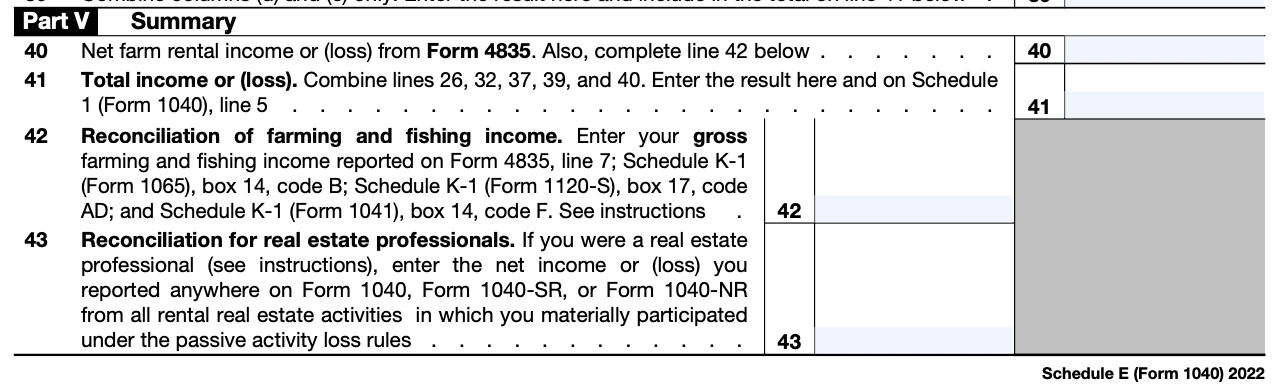
Step 6: Calculate totals
Calculate the totals of income, deductions, and net income or loss from all sources and enter them in the appropriate lines.
Step 7: Carryover amounts
If you have any carryover amounts from previous years, follow the instructions on the form to report them accurately.
Step 8: Transfer totals to Form 1040
Transfer the net income or loss amount from Schedule E to the appropriate line on Form 1040. Be sure to follow the instructions provided in the Form 1040 instructions.
Step 9: Retain records
Keep copies of all documents and supporting records used to complete Schedule E in case of any future audits or inquiries.
Step 10: Review and file
Review your completed Schedule E for accuracy and completeness. Once you are satisfied, attach it to your Form 1040 and file your tax return by the due date.
Special Considerations When Filing Schedule E (Form 1040)
When filing Schedule E (Form 1040), there are several special considerations to keep in mind. Here are some important points:
Classification of activity: Determine whether the activity falls under the passive activity rules or the non-passive activity rules. Passive activities typically include rental real estate and limited partnership interests, while non-passive activities can include self-rental activities and active participation in rental real estate.
Rental real estate: If you have rental properties, you need to report the income, expenses, and depreciation associated with each property. It's essential to maintain accurate records of rental income, expenses, and any improvements made to the property.
Depreciation: You may be eligible to claim depreciation on rental property, subject to certain rules. You'll need to determine the appropriate depreciation method (e.g., straight-line or accelerated) and the recovery period (e.g., 27.5 years for residential rental property). Keep track of the basis and any improvements to calculate accurate depreciation deductions.
Royalties: If you receive royalty income, report it on Schedule E. Provide detailed information about the nature of the royalties received and any expenses related to generating that income.
Partnerships and S corporations: If you are a partner in a partnership or a shareholder in an S corporation, you'll receive a Schedule K-1 from each entity. The information from these forms is used to report your share of income, deductions, and credits on Schedule E. Ensure that you accurately report the amounts from the Schedule K-1 forms.
Passive activity limitations: Passive losses generally cannot be used to offset non-passive income unless specific criteria are met. Review the passive activity loss rules to determine if you can deduct any losses or if they need to be carried forward to future years.
Material participation: If you actively participate in rental real estate activities, you may be able to offset rental losses against non-passive income. Familiarize yourself with the IRS rules for determining material participation and consult a tax professional if needed.
Multiple properties or activities: If you have multiple rental properties or engage in various activities reported on Schedule E, you'll need to provide separate details for each property or activity.
Documentation: Keep thorough records of income, expenses, and supporting documents for each property or activity reported on Schedule E. This documentation will help substantiate your tax return and provide evidence in case of an audit.
How To File Schedule E (Form 1040): Offline/Online/E-filing
To file Schedule E (Form 1040), you have multiple options: offline, online, or e-filing. Here's a brief overview of each method:
Offline filing
a. Obtain the necessary forms: You can download Schedule E and Form 1040 from the official Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website (irs.gov) or request paper copies by mail.
b. Fill out the forms: Complete Schedule E with accurate information about your rental income and expenses.
c. Attach supporting documents: Gather and attach any required documentation, such as rental agreements, receipts, and relevant financial records.
d. Mail the forms: Once you've completed the forms and attached the necessary documents, mail them to the appropriate IRS address based on your location. Be sure to check the IRS website for the correct mailing address.
Online filing
a. Use tax preparation software: Online tax preparation softwares can guide you through the process of filing Schedule E electronically. These software programs will prompt you to enter the necessary information, perform calculations, and generate the required forms.
b. Complete the forms: Follow the instructions provided by the software to enter your rental income and expenses into the Schedule E section.
c. Upload supporting documents: If required, the software will allow you to upload any supporting documents, such as receipts or rental agreements, in electronic format.
d. Submit the forms: Once you've completed all the necessary steps, review your return for accuracy, and submit it electronically through the software. The software will transmit your return to the IRS on your behalf.
E-filing
a. Use IRS-approved software or a tax professional: E-filing directly through the IRS requires the use of IRS-approved tax preparation software or a tax professional who can file electronically on your behalf.
b. Enter the information: Follow the software's instructions or provide the necessary details to your tax professional to complete the Schedule E section accurately.
c. Submit the forms: Once all the information is entered correctly, the software or tax professional will electronically submit your return to the IRS.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Schedule E (Form 1040)
When filing Schedule E (Form 1040), which is used to report rental income and expenses, there are several common mistakes that taxpayers should avoid. Here are some of them:
Reporting rental income incorrectly: Ensure that you accurately report all rental income received during the tax year. Include rental income from all sources, such as rental properties, vacation homes, or rental units within your primary residence.
Failing to report all expenses: Deductible expenses related to your rental activities should be reported on Schedule E. These may include mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, repairs, maintenance, utilities, property management fees, and advertising costs. Make sure to keep accurate records and include all eligible expenses.
Mixing personal and rental use: If you use your rental property for personal purposes, such as vacationing in a rental property you also rent out, you must prorate expenses based on the percentage of time the property was used for personal use. Avoid claiming personal expenses as rental deductions.
Forgetting depreciation: Depreciation is an important deduction for rental properties. Ensure that you calculate and include depreciation accurately. You may need to use Form 4562, Depreciation and Amortization, to report depreciation.
Misclassifying expenses: Be careful when categorizing your expenses. Some expenses, such as repairs, can be deducted fully in the year they occur, while others, like improvements, may need to be depreciated over time. Classify expenses correctly to maximize your deductions.
Neglecting to report rental losses: If your rental expenses exceed your rental income, resulting in a loss, you may still be able to deduct that loss against other income if you meet certain criteria. Report rental losses accurately and consult the IRS guidelines or a tax professional for specific rules.
Failing to report rental property changes: If you bought or sold a rental property during the tax year, or if there were any significant changes in your rental activities, ensure that you report them correctly on Schedule E. This includes changes in ownership, addresses, or any other relevant details.
Not keeping proper records: It is essential to maintain thorough and organized records for your rental activities. Keep track of income, expenses, and supporting documents, such as receipts, invoices, and contracts. Good record-keeping will help you avoid mistakes and provide evidence in case of an audit.
Conclusion
Schedule E (Form 1040) is an important component of your federal income tax return if you have supplemental income or loss from various sources. Whether you're a landlord, a partner in a business, a beneficiary of an estate or trust, or engaged in farming activities, understanding the reporting requirements of Schedule E is essential for accurate tax filing.
By carefully reviewing the instructions and seeking professional advice if needed, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations and make the most of the available deductions and credits related to your supplemental income and losses. Remember, accurate reporting leads to a smoother tax-filing process and helps you avoid unnecessary audits or penalties.
FAQs:
What if I have a loss from my rental property?
You can deduct rental losses up to $25,000 if your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is $100,000 or less. The deduction phases out between $100,000 and $150,000 MAGI.
What if I receive a Schedule K-1 after filing my tax return?
If you receive a Schedule K-1 after filing your tax return, you may need to file an amended return using Form 1040X to report the income or loss.
Is PA Schedule E the same as federal Schedule E?
No, while PA Schedule E serves a similar purpose, it is tailored to Pennsylvania state tax laws and requirements.


