- IRS forms
- Schedule 3 (Form 1040)
Schedule 3 (Form 1040)
Download Schedule 3 (Form 1040)When it comes to filing your annual income tax return, understanding the various schedules and forms can be quite overwhelming. One such form is Schedule 3 (Form 1040), which focuses on Additional Credits and Payments. While the main Form 1040 covers the basic details of your income and deductions, Schedule 3 dives deeper into specific credits and payments that can help lower your tax liability or increase your refund.
Schedule 3 (Form 1040) is an additional form that you may need to complete and attach to your Form 1040, depending on your individual tax situation. It is used to report various tax credits and payments that can potentially reduce your overall tax liability or increase the amount of your tax refund.
In this blog post, we will explore the purpose and components of Schedule 3, shedding light on its significance in the tax filing process.
Purpose of Schedule 3 (Form 1040)
Schedule 3 is filed along with the main Form 1040, which is the standard individual income tax return form. It is used to report various types of income or adjustments, including:
Nonrefundable credits: Certain nonrefundable tax credits that you may be eligible for, such as the Foreign Tax Credit, Education Credits, Retirement Savings Contributions Credit, and Residential Energy Credits.
Other payments and refundable credits: This section is used to report certain refundable credits, such as the Premium Tax Credit, the Health Coverage Tax Credit, and the American Opportunity Credit.
Foreign tax credit: If you paid or accrued foreign taxes on income from a foreign country or U.S. possession, you may be able to claim a credit for those taxes to offset your U.S. tax liability. This section of Schedule 3 is used to calculate and report the foreign tax credit.
**Additional child tax credit: **If you qualify for the Child Tax Credit and the amount of the credit exceeds your tax liability, you may be eligible for the Additional Child Tax Credit. This section is used to determine the additional credit and report it.
Benefits of Schedule 3 (Form 1040)
Here are some potential benefits of Schedule 3 (Form 1040):
-
Additional income reporting: Schedule 3 allows you to report income that is not covered by other sections of Form 1040. For example, it includes lines for reporting income from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, and other sources that may not be covered elsewhere.
-
Deductions and adjustments: Schedule 3 also provides space for reporting certain adjustments to income. These adjustments can help reduce your overall taxable income, potentially lowering your tax liability. Examples of adjustments may include contributions to retirement accounts, student loan interest deductions, or self-employment tax deductions.
-
Foreign tax credit: If you have paid foreign taxes on income earned abroad, Schedule 3 provides a section to claim a foreign tax credit. This credit can help offset the taxes paid to a foreign country and avoid double taxation.
-
Other tax credits: Schedule 3 may include sections for claiming certain tax credits, such as the residential energy-efficient property credit or the general business credit. These credits can directly reduce your tax liability, potentially resulting in tax savings.
Who Is Eligible To File Schedule 3 (Form 1040)?
The following are some common situations that may make an individual eligible to file Schedule 3:
You received interest or dividend income: If you received interest income from a bank account, savings bond, or other investments, or if you received dividends from stocks or mutual funds, you would need to report these on Schedule 3.
You made certain adjustments to income: If you made adjustments to your income, such as deductible student loan interest, contributions to health savings accounts (HSA), or penalties on early withdrawal of savings, you would report these adjustments on Schedule 3.
**You had self-employment income: **If you had self-employment income from freelance work, independent contracting, or owning a small business, you may need to file Schedule C to report your business income. In this case, Schedule 3 would be used to calculate the self-employment tax and report it on your Form 1040.
You received unemployment compensation: If you received unemployment benefits, you would need to report them on Schedule 3.
How To Complete Schedule 3 (Form 1040): A Step-by-Step Guide
Schedule 3 is used to report certain types of income or adjustments to your income that cannot be entered directly on Form 1040. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to complete Schedule 3:
Step 1
Gather necessary information Collect all relevant documents and information, such as W-2s, 1099s, and other income statements. You'll need these to report your income accurately.
Step 2
Download Schedule 3 Obtain a copy of Schedule 3 from the IRS website (www.irs.gov) or any reliable tax preparation software. You can also consult a tax professional for assistance.
Step 3
Complete the identification section Enter your name and Social Security number at the top of Schedule 3. Make sure the information matches your Form 1040.
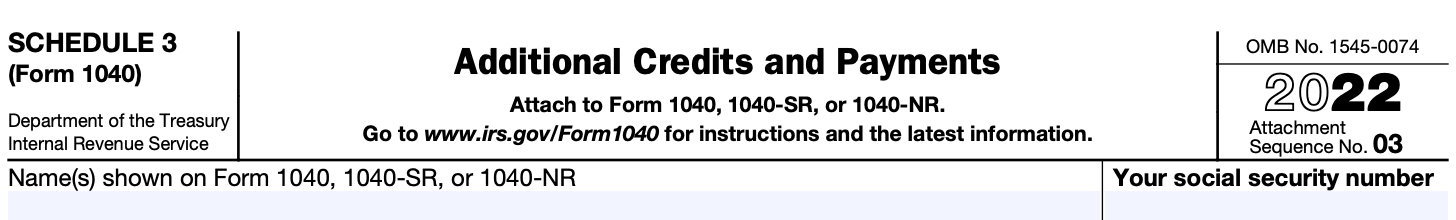
Step 4
Report additional income If you have income from sources other than your primary job, report it in the appropriate sections. Common examples include business income, rental income, and royalties. Follow the instructions on Schedule 3 to accurately report each type of income.
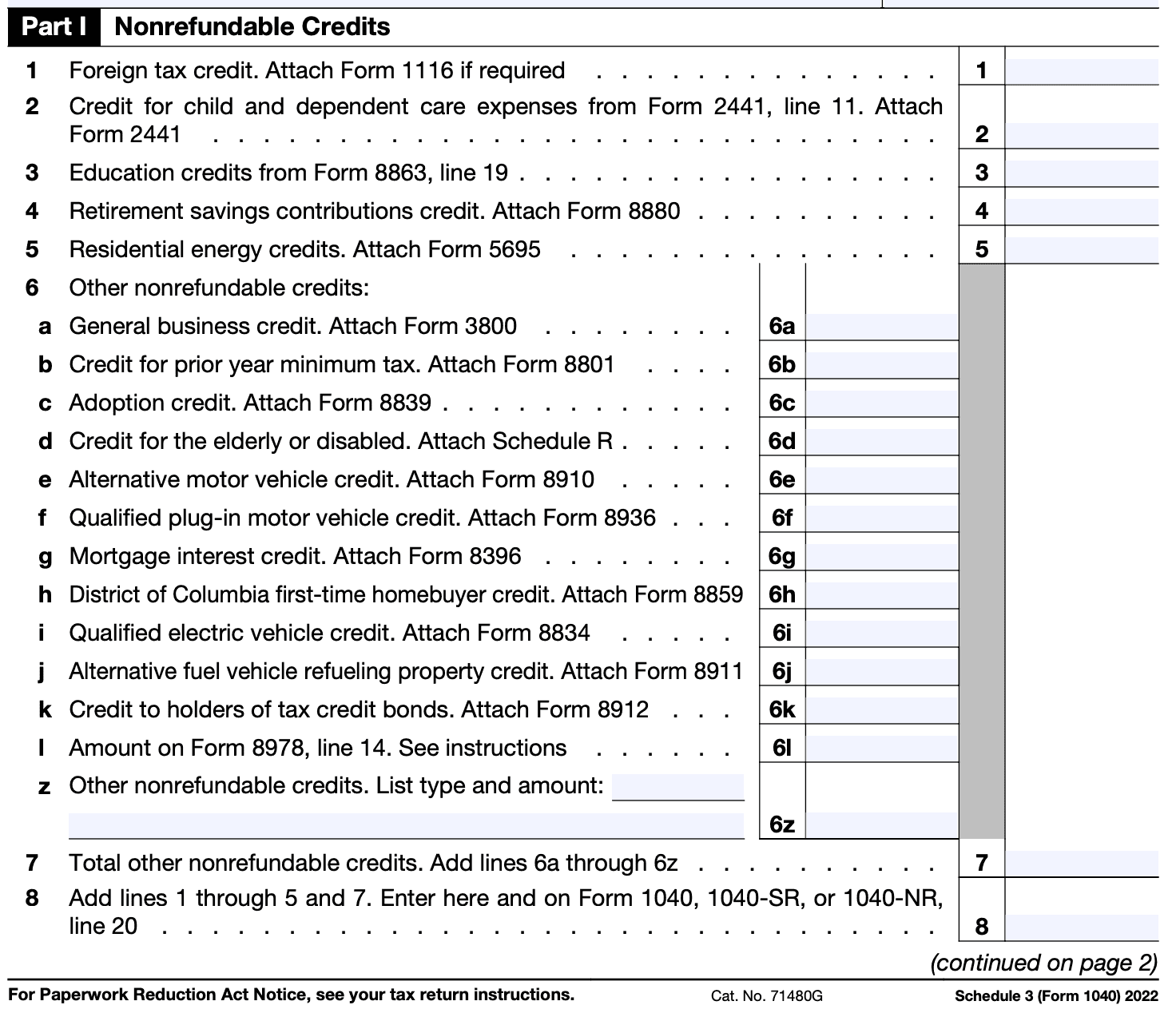
Step 5
Report adjustments to income Certain adjustments to your income can be claimed on Schedule 3. These adjustments can include deductible contributions to individual retirement accounts (IRAs), student loan interest deductions, and health savings account (HSA) contributions. Enter the appropriate amounts in the designated sections.
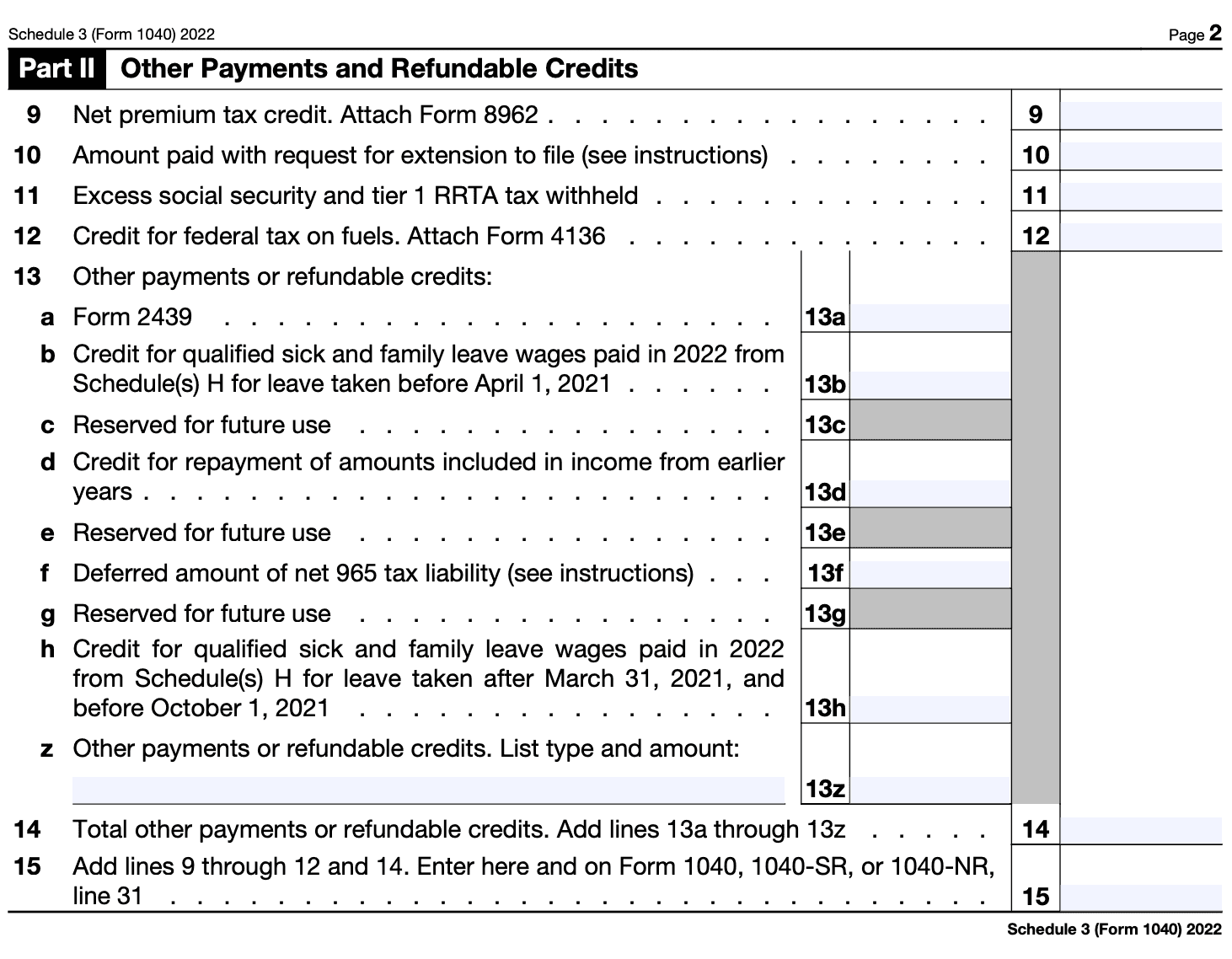
Step 6
Calculate the total Add up all the income and adjustments reported on Schedule 3 to calculate the total.
Step 7
Transfer total to Form 1040 Once you've completed Schedule 3, transfer the total to the appropriate line on Form 1040. The specific line number will depend on the version of the form you are using, so consult the instructions for Form 1040 to find the correct line.
Step 8
Review and double-check Carefully review all the information on Schedule 3 to ensure accuracy. Check for any errors or omissions, as mistakes can cause delays or potential issues with your tax return.
Step 9
Keep a copy for your records Make a copy of Schedule 3 and any supporting documents for your records. It's essential to maintain accurate records in case of future inquiries or audits.
Step 10
File your tax return Include Schedule 3 with your completed Form 1040 when filing your tax return. If you're filing electronically, follow the instructions provided by your chosen tax software. If you're filing a paper return, attach Schedule 3 to the front of your Form 1040.
Special Considerations When Filing Schedule 3 (Form 1040)
When filing Schedule 3 (Form 1040), there are several special considerations to keep in mind. Here are some key points to consider:
Eligibility: Ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria for the specific credits you plan to claim on Schedule 3. Each credit has its own set of requirements, which are outlined in the corresponding instructions and IRS publications.
Documentation: Maintain proper documentation to substantiate your eligibility for the credits claimed on Schedule 3. This may include forms, receipts, statements, or any other supporting documents required by the IRS. Retain these documents for at least three years in case of an audit.
Forms and instructions: Review the appropriate IRS forms and instructions related to the credits you plan to claim. The instructions provide specific guidance on completing Schedule 3, including where to report the credits and any additional information required.
Limits and phase-outs: Be aware of any limits or phase-outs associated with the credits you intend to claim. Some credits may have income limitations or gradually decrease as your income reaches certain thresholds. Review the instructions to determine if your circumstances affect the amount of credit you can claim.
Prior-year credits: If you are carrying forward any credits from a previous year, ensure you accurately calculate the carryover amount and properly report it on Schedule 3. Refer to the instructions for each credit to understand the carryforward rules.
**Tax software or professional assistance: **Consider using tax preparation software or seeking professional assistance when completing Schedule 3. These resources can help ensure accuracy and help you navigate any complex aspects of claiming credits.
How To File Schedule 3 (Form 1040): Offline/Online/E-filing
To file Schedule 3 (Form 1040), you have several options available to you, including filing offline by mail or filing online through electronic filing (e-filing) methods:
Offline filing (mail)
a. Obtain a physical copy of Form 1040 and Schedule 3: You can download and print these forms from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website at www.irs.gov or request them by mail by calling the IRS at 1-800-829-3676.
b. Fill out the forms: Complete your Form 1040, including the necessary information for Schedule 3.
c. Attach Schedule 3: Once you have filled out Schedule 3, attach it to your completed Form 1040.
d. Review and sign: Double-check all the information for accuracy, sign the forms, and provide any additional documentation required.
e. Mail the forms: Send your completed Form 1040 and Schedule 3 to the appropriate IRS address. The address to use depends on your location and whether you are including a payment. You can find the correct mailing address in the instructions provided with the forms.
Online filing
a. Use tax preparation software: Utilize tax preparation software approved by the IRS. These software options often provide step-by-step guidance and can help you complete your Form 1040 and Schedule 3 accurately.
b. Enter your information: Input all the required information into the software, including the details for Schedule 3.
c. Review and sign: Carefully review all the entered information, make any necessary corrections, and sign the forms electronically using the software.
d. Transmit the forms: Once you have completed the forms and reviewed them, follow the software's instructions to transmit your return electronically to the IRS.
E-filing
a. Use IRS Free File: If your income is below a certain threshold, you may be eligible to use the IRS Free File service, which provides free online tax preparation and filing options. Visit the IRS website to access the Free File options and select one that suits your needs.
b. Follow the instructions: Each Free File provider has its own set of instructions and interfaces, so follow the instructions provided by the chosen provider to fill out your Form 1040 and Schedule 3 accurately.
c. Review and sign: Carefully review all the entered information, make any necessary corrections, and sign the forms electronically as instructed by the provider.
d. Submit your return: Once you have completed the forms and reviewed them, submit your return electronically through the Free File provider's platform. They will then transmit your return to the IRS on your behalf.
Remember to keep copies of your filed tax documents and any supporting documentation for your records.
Common mistakes to avoid while filing Form Schedule 3 (Form 1040)
When filing Schedule 3 (Form 1040), it's important to be aware of common mistakes to avoid in order to ensure accurate and error-free tax filing. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
Incorrect or missing identification information: Ensure that you provide accurate personal information, such as your name, Social Security number (SSN), and other identification details. Double-check the information to avoid any errors or typos.
Failing to report all income: Schedule 3 is used to report certain types of income that are not listed on the main Form 1040. Make sure you include all relevant income sources, such as unemployment compensation, rental income, or gambling winnings, as required.
Errors in calculating deductions: Pay close attention when calculating deductions, such as student loan interest, self-employment tax, or educator expenses. Use the correct formulas, review the instructions, and double-check your calculations to avoid mistakes.
Not claiming eligible tax credits: Be aware of tax credits that you may qualify for, such as the Child Tax Credit, Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), or education-related credits. Review the eligibility criteria and ensure you claim all the credits you're entitled to.
**Neglecting to attach supporting documentation: **If you are claiming certain deductions or credits on Schedule 3, you may need to attach supporting documentation or forms. Failure to include the required documentation could lead to delays or potential audit issues.
Forgetting to sign and date: It's crucial to sign and date your tax return, including Schedule 3. Unsigned or undated returns may be considered invalid, leading to processing delays. Ensure that all required signatures are included.
Using outdated forms or instructions: Always use the most recent version of Schedule 3 and the corresponding instructions provided by the IRS. Using outdated forms or instructions could result in errors or incorrect reporting.
Incorrectly entering payment information: If you need to make a payment with your tax return, double-check that you've entered the payment information accurately. This includes providing the correct account numbers, payment amounts, and any necessary supporting documentation.
Failing to keep copies of your tax documents: It's essential to retain copies of all the filed forms, schedules, and supporting documents for your records. Keeping organized records will help you in case of future inquiries or audits.
**Not seeking professional assistance if needed: **If you're unsure about any aspect of filing Schedule 3 or your tax return in general, consider seeking help from a tax professional. They can provide guidance, answer questions, and help ensure accurate filing.
Taking the time to review your tax return, double-check all information, and avoid these common mistakes will help you file an accurate and error-free Schedule 3 (Form 1040).
Conclusion
Understanding Schedule 3 (Form 1040) is crucial for maximizing your tax benefits and ensuring accurate reporting of additional credits and payments. By carefully reviewing the instructions and guidelines associated with Schedule 3, you can identify the credits and payments that apply to your situation and reduce your tax liability or receive additional refunds.
Remember, tax laws and regulations are subject to change, so it's always advisable to consult with a qualified tax professional or refer to the latest IRS guidelines to ensure compliance and accuracy in your tax filings.
By leveraging Schedule 3 effectively, you can take advantage of the available tax benefits and potentially enhance your financial wellness.


