- IRS forms
- Form 965-A
Form 965-A: Individual Report of Net 965 Tax Liability
Download Form 965-AAs a taxpayer, it is crucial to stay informed about the various tax forms and requirements to fulfill your obligations correctly. One such form is the Form 965-A, Individual Report of Net 965 Tax Liability, which relates to the tax reforms implemented under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017.
Form 965-A is an individual tax form used to report the net tax liability under Section 965 of the Internal Revenue Code (IRC). This section was introduced as part of the TCJA to address the deemed repatriation of deferred foreign income for certain specified foreign corporations. Essentially, it is a one-time tax imposed on accumulated earnings and profits held overseas by U.S. shareholders.
In this blog post, we will delve into the details of Form 965-A, its purpose, and who needs to file it.
Purpose of Form 965-A
Form 965-A is used for reporting the transition tax on accumulated foreign earnings of specified foreign corporations. This form is part of the U.S. tax law changes under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), specifically related to the repatriation of foreign earnings.
The transition tax, also known as the deemed repatriation tax, is a one-time tax imposed on the accumulated foreign earnings of certain foreign corporations that were previously untaxed by the United States. The TCJA introduced this provision to encourage the repatriation of offshore profits by U.S. shareholders.
Form 965-A is used by U.S. shareholders of specified foreign corporations to calculate and report the amount of the transition tax liability. It provides information regarding the accumulated post-1986 deferred foreign income of the foreign corporation and helps determine the applicable tax rate on that income.
By completing Form 965-A, U.S. shareholders determine their share of the deemed repatriation income and calculate the corresponding tax liability. The information reported on this form is used to report the transition tax on the shareholder's individual or corporate tax return, depending on their tax status.
It's important to note that Form 965-A is complex and requires detailed calculations, as it involves various elements such as previously taxed income, earnings and profits, and specified foreign corporations.
Benefits of Form 965-A
Here are some potential benefits associated with Form 965-A:
**Repatriation of deferred foreign earnings: **One of the key benefits of Form 965-A is that it allows individuals to report and repatriate previously untaxed foreign earnings held by specified foreign corporations. This provision provided an opportunity to bring back offshore profits to the United States at a lower tax rate.
Reduced tax liability: The transition tax provided a one-time tax on accumulated post-1986 foreign earnings, which were previously deferred from U.S. taxation. The tax rates applied under this provision were generally lower than the regular tax rates applicable to other income. By reporting the net 965 tax liability on Form 965-A, individuals could potentially benefit from reduced tax liability compared to regular income tax rates.
Installment payment option: The IRS allows taxpayers to pay the transition tax liability in installments over an eight-year period. This provided individuals with flexibility in managing their cash flow and mitigating the financial burden associated with the transition tax. Form 965-A facilitated the reporting and calculation of the installment payments.
Adjustment of earnings and profits: Form 965-A also allows for certain adjustments to the earnings and profits of specified foreign corporations. These adjustments can help individuals accurately calculate the transition tax liability and ensure compliance with the tax laws.
Compliance with tax obligations: By filing Form 965-A and reporting the net 965 tax liability, individuals can ensure compliance with their tax obligations. This form helps in fulfilling the reporting requirements related to the transition tax, which is crucial for avoiding potential penalties or legal consequences.
It's important to note that the benefits associated with Form 965-A are specific to the transition tax provisions introduced by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. The impact and benefits can vary based on individual circumstances.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 965-A?
The eligibility to file Form 965-A depends on the following criteria:
U.S. shareholders: Individuals who are considered U.S. shareholders of specified foreign corporations (SFCs) are eligible to file Form 965-A. A U.S. shareholder generally refers to a U.S. person or entity that owns shares in an SFC, either directly or indirectly.
**Transition tax inclusion: **If a U.S. shareholder has a transition tax inclusion, meaning they have untaxed foreign earnings of an SFC subject to the transition tax, they need to file Form 965-A to report and pay the tax liability.
**Ownership threshold: **U.S. shareholders who meet certain ownership thresholds in an SFC are subject to the transition tax. The ownership threshold differs based on whether the SFC is a controlled foreign corporation (CFC) or a specified foreign corporation (SFC) other than a CFC.
How To Complete Form 965-A: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Obtain the necessary forms and instructions
Download the most recent version of Form 965-A and its instructions from the IRS website (www.irs.gov) or request them by mail from the IRS.
Step 2: Gather the required information and documents
Collect all the necessary information related to the deemed repatriation of foreign income, including the relevant financial statements, earnings and profits calculations, and other supporting documents.
Step 3: Fill out the taxpayer information
Enter your name, social security number (SSN), and other identifying information at the top of Form 965-A.

Step 4: Complete Part I - Computation of the Net 965 Tax Liability
- Follow the instructions provided on Form 965-A to calculate the net tax liability resulting from the deemed repatriation.
- This involves various calculations and adjustments based on the specific circumstances of your foreign income and related tax obligations.
- Be sure to carefully review the instructions to ensure you are correctly applying the relevant provisions and calculations.
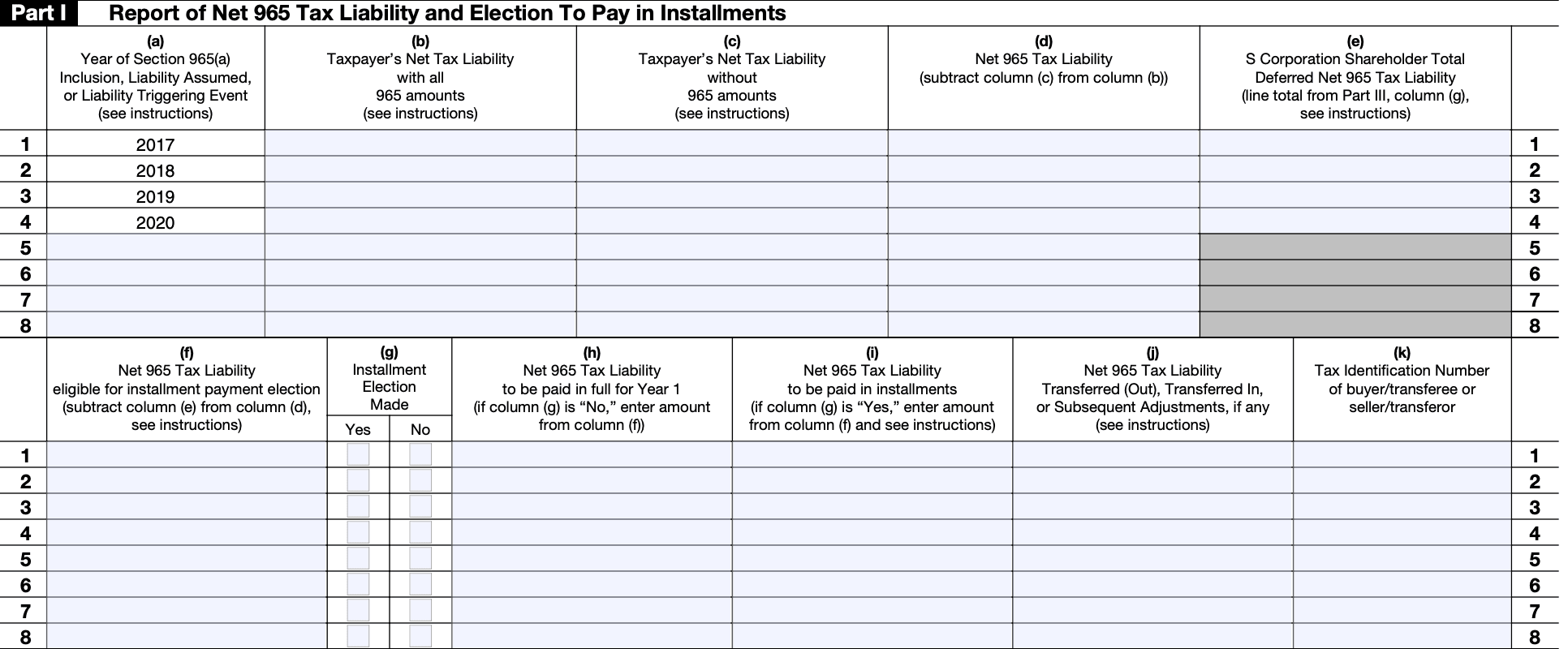
Step 5: Complete Part II - Foreign Income Subject to the Net 965 Tax Liability
- Provide the required details of the foreign income subject to the net 965 tax liability.
- This may include information such as the type of income, the amount of income, and any adjustments or deductions allowed under the tax law.
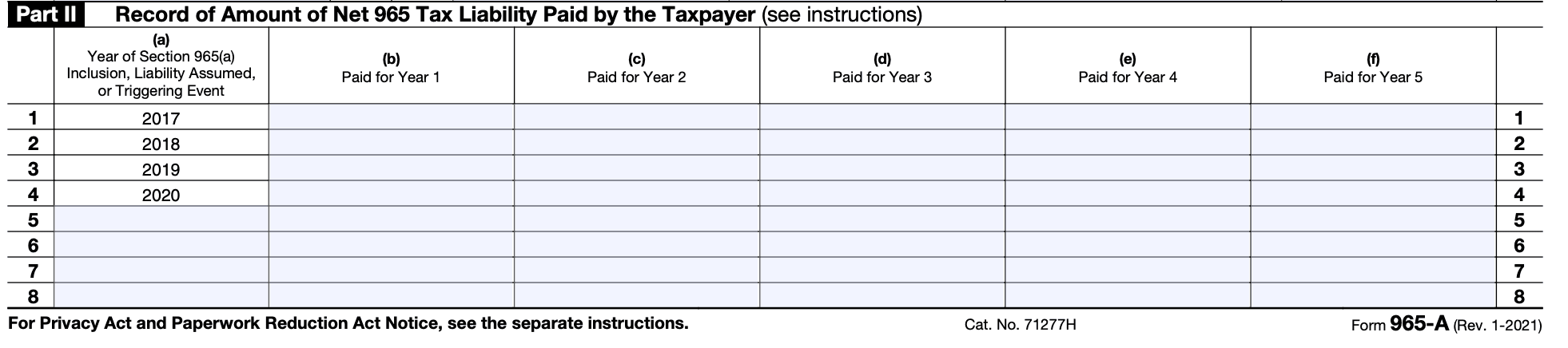
Step 6: Complete Part III - Net 965 Tax Liability
Report the net tax liability determined in Part I on Form 965-A, line 6.
Follow the instructions to make any required adjustments or computations to arrive at the final net 965 tax liability amount.
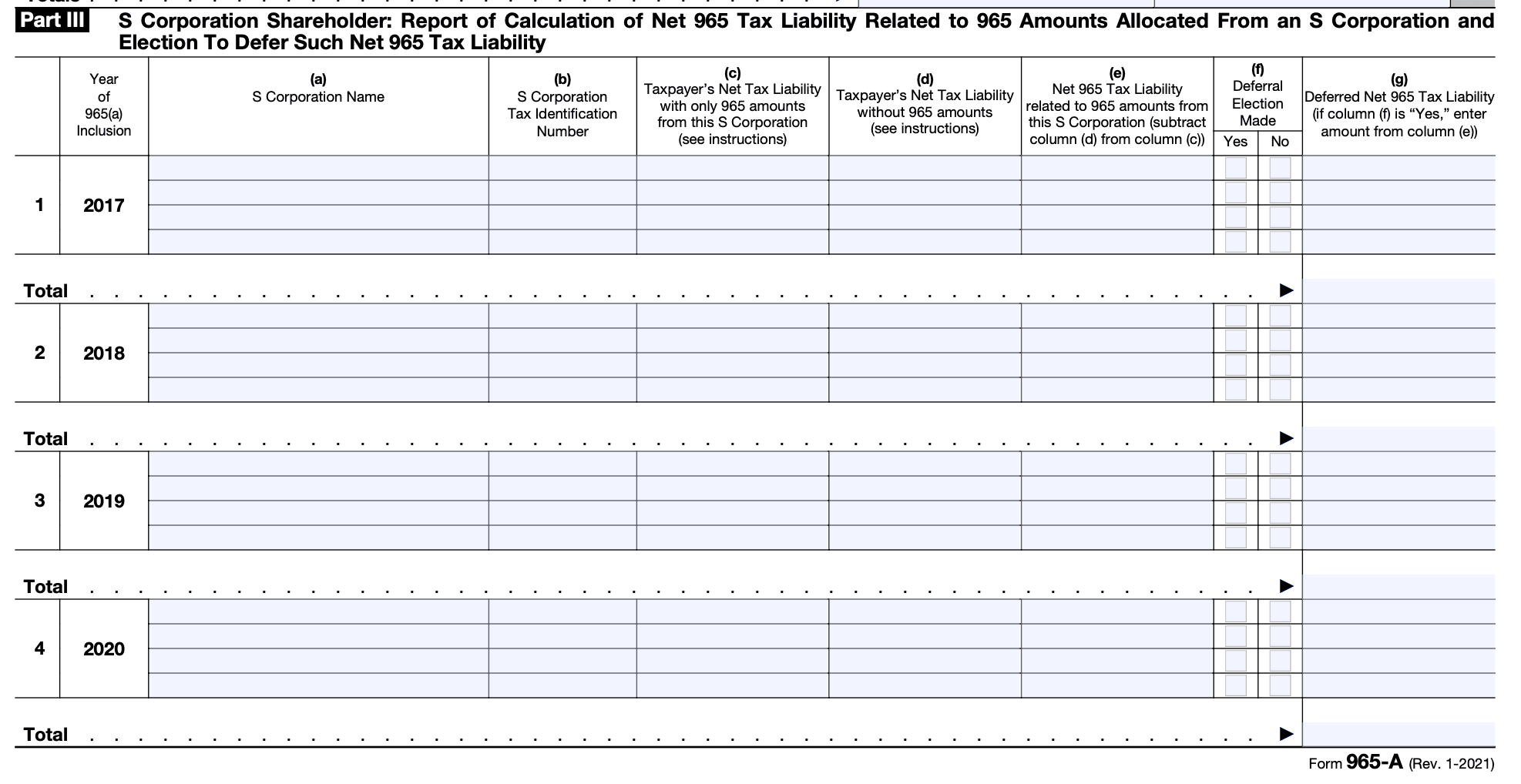
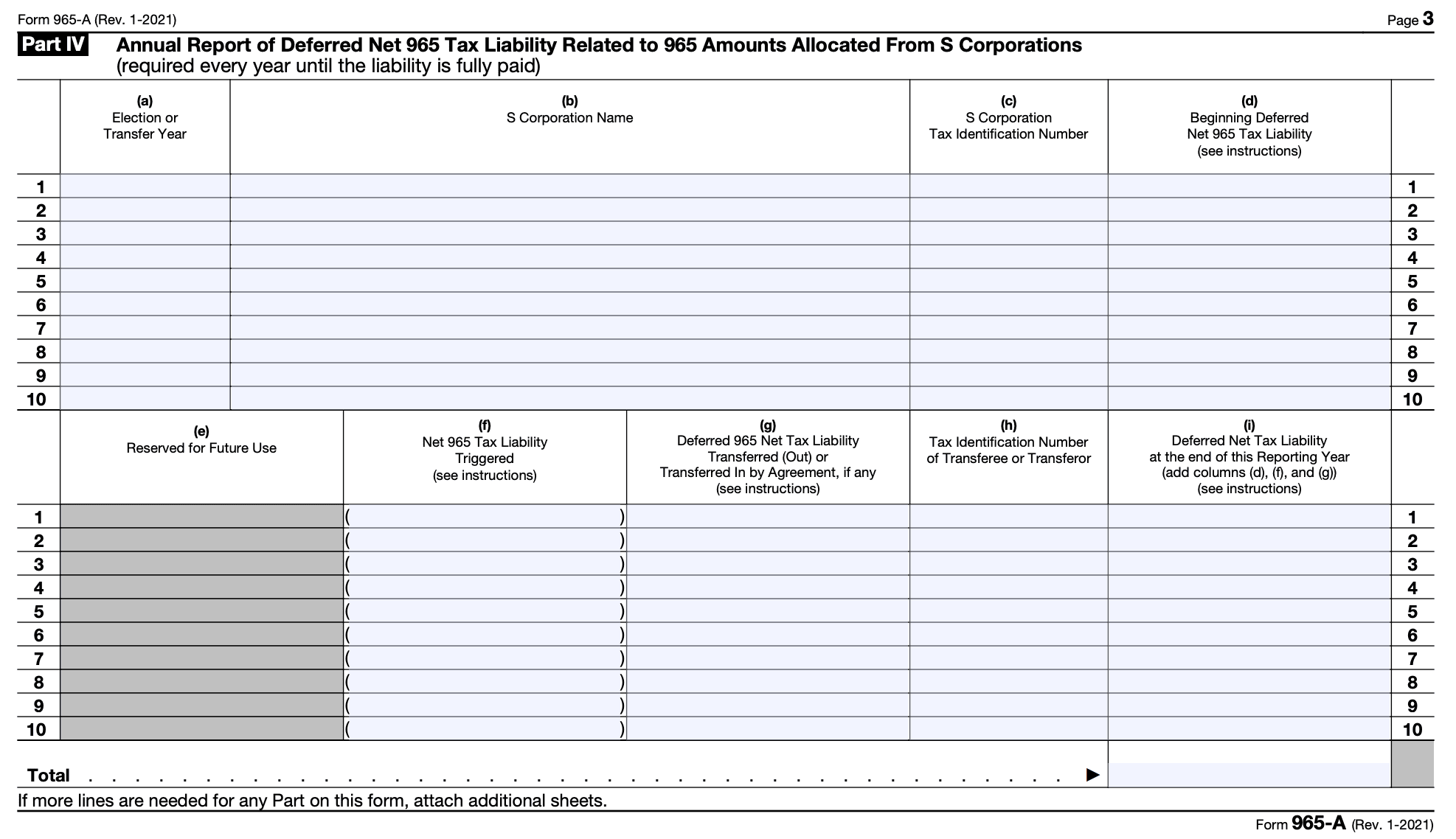
Step 7: Complete Part IV - Deferred Net 965 Tax Liability
Complete Annual Report of Deferred Net 965 Tax Liability Related to 965 Amounts Allocated From S Corporations
Step 8: Sign and date the form
Review the completed Form 965-A for accuracy and completeness.
Sign and date the form as required.
Step 9: Retain a copy for your records
Make a copy of the completed Form 965-A and all related supporting documents for your records.
It's important to keep copies of all tax-related documents in case of future inquiries or audits.
Step 10: File the form with the IRS
Mail the completed Form 965-A to the appropriate address provided in the instructions.
It's recommended to send the form using certified mail or a reputable delivery service to ensure proof of delivery.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 965-A
When filing Form 965-A, there are several special considerations to keep in mind:
-
Eligibility: Ensure that you meet the eligibility requirements for filing Form 965-A. Generally, this form is required for U.S. shareholders who own specified foreign corporations with accumulated post-1986 deferred foreign income.
-
Transitional tax calculation: The transition tax under section 965 involves calculating the "deemed repatriation" of accumulated foreign earnings. This requires determining the accumulated post-1986 deferred foreign income and applying the applicable tax rates. The calculations can be complex, so it's advisable to seek professional tax advice or use tax preparation software specialized in international tax.
-
Reporting foreign earnings: Form 965-A requires detailed reporting of the accumulated post-1986 deferred foreign income of specified foreign corporations. The form provides specific lines for reporting these amounts.
-
Payment of transition tax: If you have a transition tax liability, ensure that you pay it by the due date specified by the IRS. Failure to make the required payment may result in penalties and interest.
-
Completing related forms: Depending on your specific circumstances, you may need to complete other forms in addition to Form 965-A. For example, if you are a U.S. shareholder who owns at least 10% of a specified foreign corporation, you may also need to file Form 5471, Information Return of U.S. Persons With Respect to Certain Foreign Corporations.
-
Consult a tax professional: Given the complexities of the transition tax and international tax laws, it's highly recommended to consult with a qualified tax professional or international tax specialist to ensure compliance with all filing requirements and maximize any available deductions or credits.
Always refer to the most recent instructions provided by the IRS for Form 965-A to ensure accurate and up-to-date compliance with the reporting requirements.
Filing Deadlines & Extensions for Form 965-A
Typically, the filing deadline for Form 965-A coincides with the individual income tax return deadline, which is generally April 15 of each year. However, if April 15 falls on a weekend or a holiday, the deadline may be extended to the next business day.
If you need additional time to file Form 965-A, you can request an extension by filing Form 4868, "Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return." This extension typically grants you an additional six months to file your tax return, moving the deadline to October 15.
Please note that Form 4868 only extends the filing deadline, not the payment deadline. Any tax liability owed must still be paid by the original due date to avoid potential penalties and interest.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 965-A
Here are some common mistakes to avoid while filing Form 965-A:
**Failing to understand the instructions: **The instructions for Form 965-A provide crucial guidance on how to complete the form accurately. Make sure you thoroughly read and understand the instructions before filling out the form.
Incorrect calculations: The transition tax calculation involves complex calculations based on specific tax rates and the taxpayer's accumulated foreign earnings. Ensure that you accurately calculate the transition tax liability and any related adjustments or deductions.
Incorrect or missing taxpayer identification numbers (TINs): Enter the correct taxpayer identification numbers for the relevant entities or individuals. Missing or incorrect TINs can lead to processing delays or penalties.
**Inadequate documentation: **Maintain detailed records and supporting documentation for all amounts reported on Form 965-A. This includes documentation related to the calculation of the transition tax, the determination of accumulated foreign earnings, and any other relevant financial information.
Failing to report all required information: Be thorough and provide all necessary information required by Form 965-A. This includes details about the foreign corporations subject to the transition tax, such as their names, EINs (Employer Identification Numbers), and accumulated foreign earnings.
**Late or incomplete filing: **Ensure that you meet the filing deadline for Form 965-A. Late filing can result in penalties and interest. Additionally, make sure you complete all sections of the form accurately and provide all required schedules and attachments.
Not seeking professional guidance if needed: Filing Form 965-A can be complex, especially for individuals or entities with extensive foreign operations. If you're unsure about any aspect of the form or the transition tax rules, consider seeking assistance from a tax professional or accountant to ensure compliance and accuracy.
Remember, it's crucial to review your completed Form 965-A carefully for any errors or omissions before submission.
Conclusion
Form 965-A plays a crucial role in determining the net tax liability of U.S. shareholders with an ownership interest in specified foreign corporations. It is essential to understand the provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act and the requirements associated with Form 965-A to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with the IRS regulations.
As always, it is advisable to consult with a qualified tax professional or refer to the official IRS guidelines and instructions when preparing and filing Form 965-A. This will help ensure that you fulfill your tax obligations correctly and make informed decisions regarding your tax liabilities related to the deemed repatriation of foreign earnings.


