- IRS forms
- Form 8962
Form 8962: Premium Tax Credit
Download Form 8962When it comes to managing your taxes, understanding the various forms and credits available can be a daunting task. One such form that often confuses taxpayers is Form 8962, Premium Tax Credit. The premium tax credit is a valuable financial resource that helps eligible individuals and families afford health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
In this blog, we will provide a comprehensive guide to Form 8962, covering what its purpose is, what the eligibility criteria are, how to fill it out accurately, and what to expect when claiming the premium tax credit.
What Is a Premium Tax Credit?
The premium tax credit (PTC) is a refundable tax credit intended to make health insurance more affordable for people and families with moderate incomes. It was established under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) to help make healthcare more accessible and affordable for those who purchase coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
To qualify for the PTC, individuals must meet specific criteria, including income limits and not being eligible for other qualifying coverage such as Medicaid or employer-sponsored insurance. The amount of the credit is based on a sliding scale, taking into account household income and the cost of health insurance premiums in the marketplace.
Who Is Eligible for Premium Tax Credit?
Here are the factors that come into play in determining eligibility for the premium tax credit:
**a. Income: **The PTC is available to individuals and families whose household income falls within certain limits. The income limits are calculated based on the federal poverty level (FPL) for the corresponding tax year.
b. Coverage through the marketplace: Eligible individuals must have obtained health insurance coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace, either during the open enrollment period or through a special enrollment period. Marketplace coverage includes plans purchased through Healthcare.gov or state-based exchanges.
**c. Not eligible for other coverage: **Individuals who are eligible for other types of coverage, such as medicaid, employer-sponsored insurance, or government-sponsored plans, are generally not eligible for the PTC.
d. Filing status: The premium tax credit is available to individuals and families who file their federal income tax return using one of the following statuses: single, married filing jointly, head of household, or qualifying widow(er) with a dependent child. Note that the PTC is not available to individuals who are claimed as a dependent on someone else's tax return, even if they meet the other eligibility criteria.
Change in Circumstances
By immediately informing the marketplace of any changes in circumstances, you will enable the marketplace to amend the data used to calculate your anticipated premium tax credit amount and modify the amount of your advance payment. The risk of a major discrepancy between your advance credit payments and your actual premium tax credit will be reduced as a result of this modification.
The following circumstantial changes may have an impact on the amount of your actual premium tax credit:
- Increase or decrease in your household income
- Social Security payouts in lump sums, including Social Security Disability Insurance
- Lump-sum taxable payouts from a retirement plan or individual retirement account
- Cancellation or forgiveness of debt, such as credit card debt
- Marriage
- Divorce
- Birth or adoption of a child
- Other changes to your household composition
- Gaining or losing eligibility for health insurance provided by the government or an employer
- Moving to another address
How Is Premium Tax Credit Computed?
The amount of premium tax credit is typically equal to the premium for the second-cheapest silver plan offered via the marketplace that covers the members in your coverage family, less a predetermined portion of your household income. However, the credit, referred to as your enrollment premiums, cannot exceed the premiums for the marketplace plan or plans in which you or your family register.
The members of your family who have signed up for coverage through the marketplace and are not qualified for non-marketplace coverage like Medicare, Medicaid, or reasonably priced employer-sponsored coverage make up your coverage family.
Filling out Form 8962: A Step-by-Step Guide
Form 8962 is used to calculate the amount of the premium tax credit and reconcile any advance payments of the credit received during the year.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to fill out Form 8962 accurately:
Step 1: Gather the necessary documents
Before you begin filling out Form 8962, gather all the relevant documents, including your Form 1095-A (Health Insurance Marketplace Statement) and your previous year's tax return.
Step 2: Complete Part I - Annual and Monthly Contribution Amount
In Part I of Form 8962, you will need to enter information from your Form 1095-A, such as the annual and monthly premium amounts, the second-lowest-cost silver plan, and the applicable percentages based on your income.
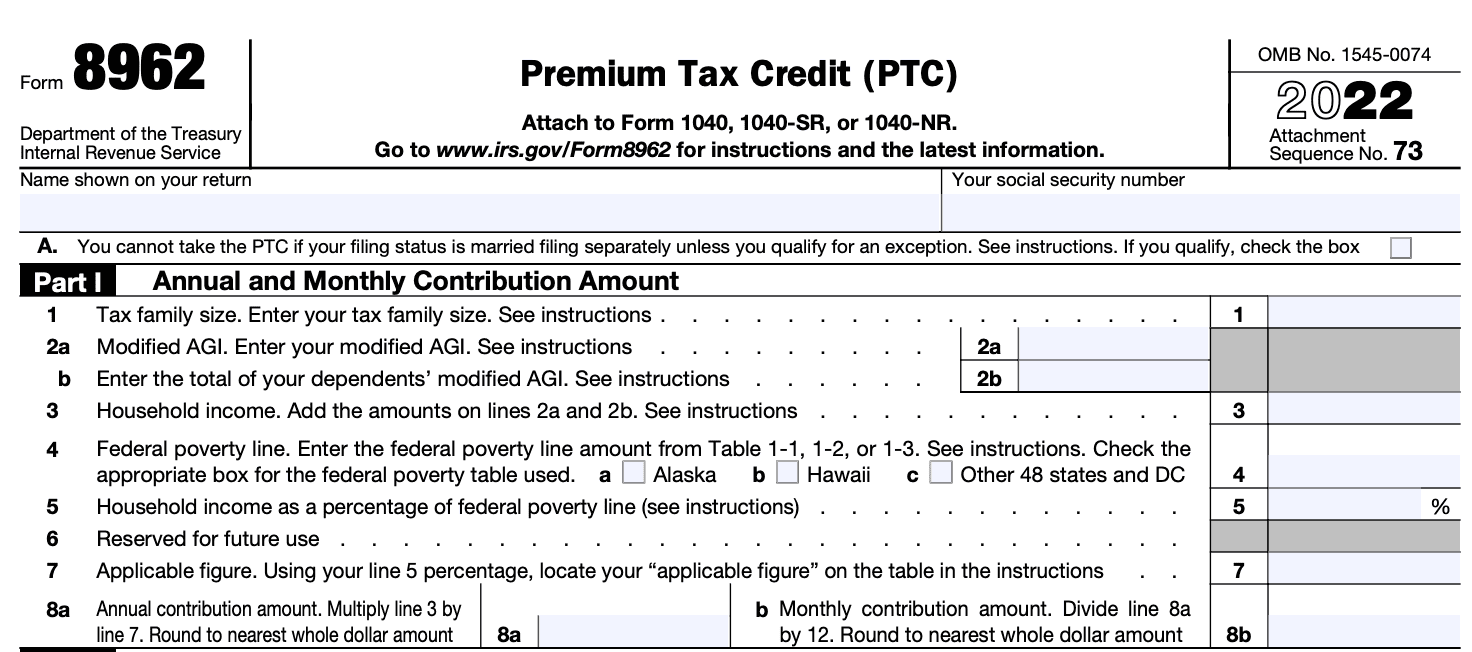
Step 3: Calculate the premium tax credit in Part II
In Part II of Form 8962, you will calculate your premium tax credit using the information from Part I. This section involves determining your household income, applying the applicable percentages, and finding the final premium tax credit amount.
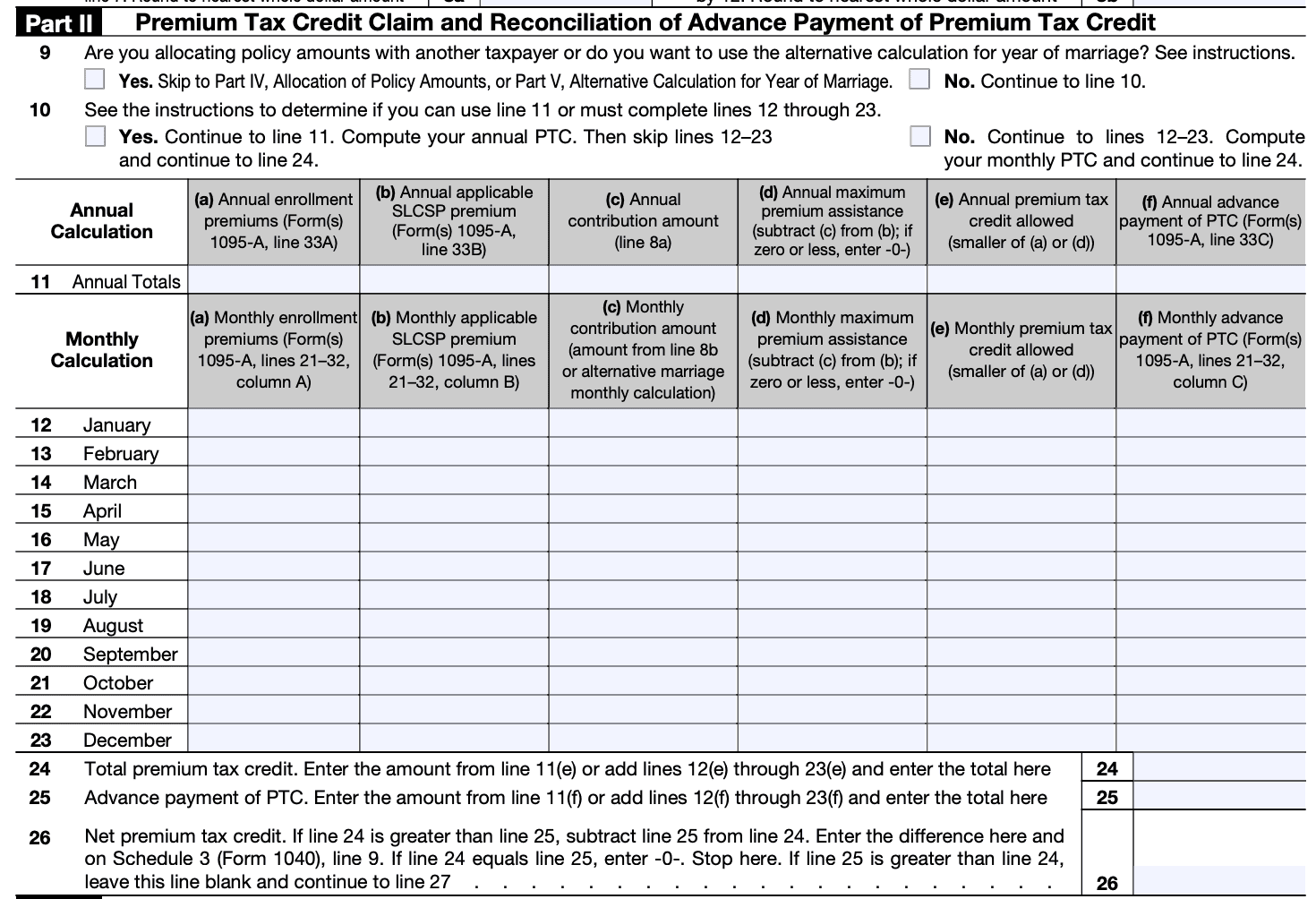
Step 4: Compare advance credit payments
If you have received advance payments of the premium tax credit throughout the year, you will need to complete Part III of Form 8962. This section allows you to reconcile the advance payments with the amount of credit calculated in Part II.
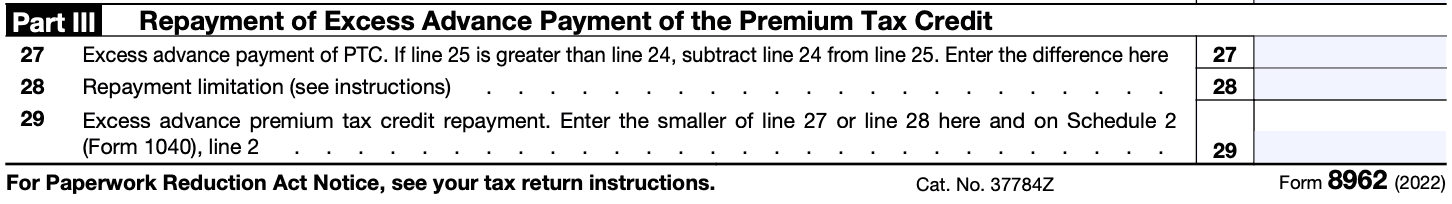
Step 5: Complete Parts IV and V
Part IV of Form 8962 is used to allocate the premium tax credit among household members if you're filing jointly, while Part V is for any additional information or explanations you need to provide.
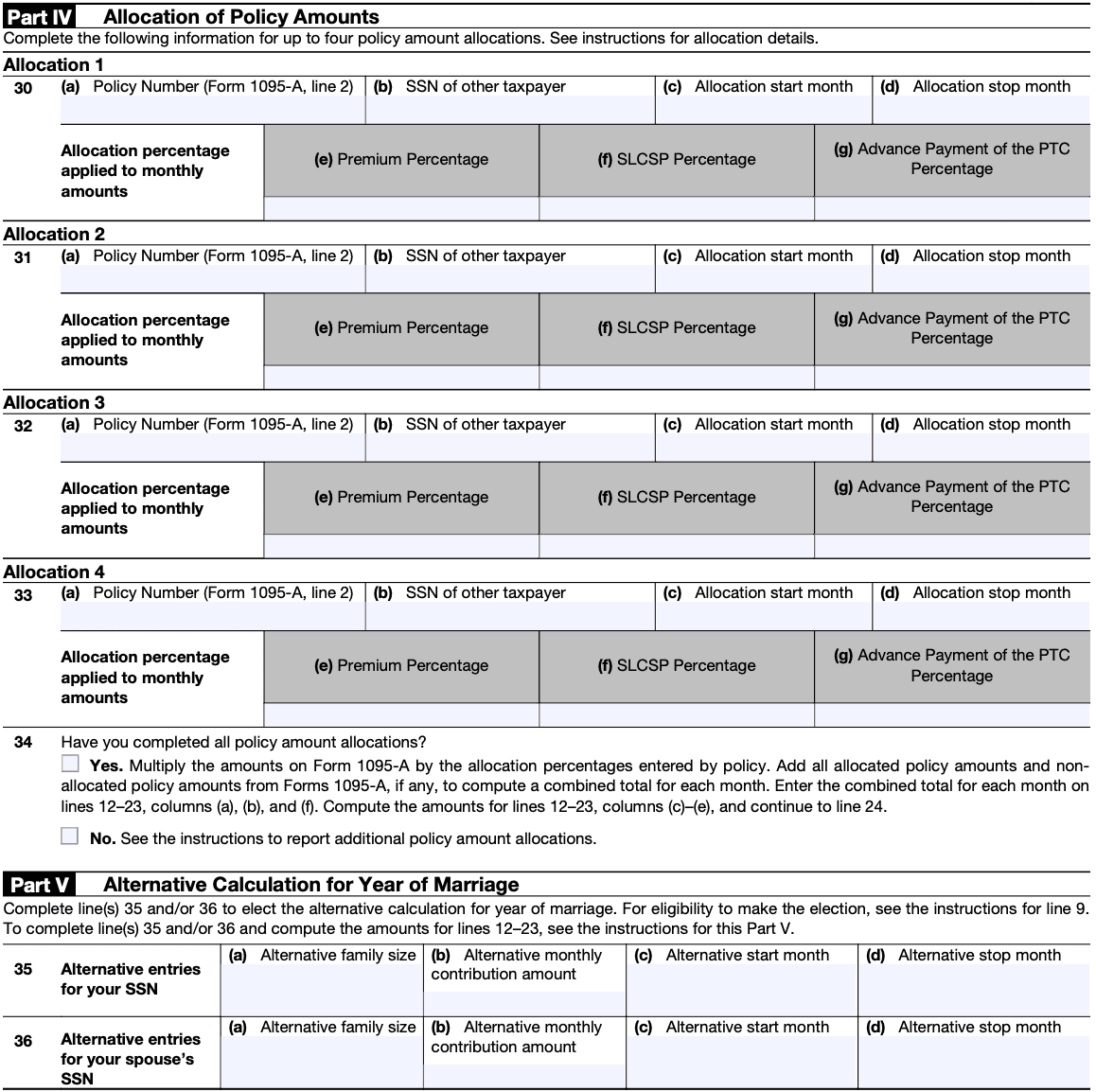
Step 6: Double-check and submit
Review your completed Form 8962 and ensure that all information is accurate and entered correctly. Attach the form to your federal income tax return, and submit it by the filing deadline.
Consequences of Errors in Form 8962
Form 8962 is used to reconcile the premium tax credit (PTC) received in advance with the actual credit amount a taxpayer is eligible for based on their income and family size.
Errors on Form 8962 can have several consequences, including the following:
Incorrect tax liability: Form 8962 affects the taxpayer's overall tax liability. If errors result in an underreporting of the premium tax credit, the taxpayer may owe additional taxes. Conversely, if errors result in an overreporting of the credit, the taxpayer may receive a larger refund or have a lower tax liability than they should.
Tax penalties and interest: If errors on Form 8962 lead to underpayment of taxes, the IRS may assess penalties and interest on the unpaid amount. Penalties can vary depending on the severity and intent of the error.
Delayed tax refunds: If the IRS identifies errors on Form 8962, it may delay the processing of the tax return and any associated refund until the issues are resolved. This can result in delays in receiving the refund, which can be frustrating for taxpayers who were relying on the funds.
**Increased scrutiny: **Form 8962 and the premium tax credit are subject to scrutiny by the IRS, particularly due to the potential for fraud or abuse. Errors on the form may trigger further examination by the IRS, leading to additional requests for documentation and potentially an audit of the taxpayer's return.
**Loss of future eligibility: **If errors on Form 8962 result in intentional misreporting or fraud, it can have serious consequences beyond the current tax year. The taxpayer may lose eligibility for the premium tax credit in future years and may face legal consequences.
It's important to carefully review and accurately complete Form 8962 to avoid these potential consequences. If you discover errors after filing, it's advisable to promptly file an amended tax return using Form 1040X to correct any mistakes and prevent further issues.
What To Expect When Claiming Premium Tax Credit
When you claim the premium tax credit on your tax return, it's essential to understand what to expect throughout the process. Here are a few key points to keep in mind:
a. Tax refund or reduced tax liability
If the premium tax credit exceeds your total tax liability, you may be eligible for a tax refund. The credit can reduce your tax liability, potentially resulting in a lower tax bill.
b. Reconciling advance credit payments
If you received advance payments of the premium tax credit, you must reconcile the amount you received with the credit calculated on Form 8962. This reconciliation determines whether you owe any excess advance credit payments or if you're entitled to additional credit.
c. Changes in circumstances
If you experienced changes in income, family size, or coverage during the year, you must report these changes to the Health Insurance Marketplace. Failing to do so could result in incorrect advance credit payments and complications when reconciling on Form 8962.
d. Potential tax implications
It's important to understand that changes in income or family size can affect your tax liability and eligibility for certain credits or deductions. Seeking professional tax advice can help you navigate any potential tax implications.
Deadlines & Due Dates
Form 8962 has specific deadlines and due dates that you need to be aware of. Here are some key points:
Annual filing requirement: Form 8962 is filed annually, usually along with your federal income tax return. The due date for filing your tax return, including Form 8962, is generally April 15 of the following year. However, if April 15 falls on a weekend or a holiday, the due date may be extended to the next business day.
Extension of time: If you need more time to file your tax return and Form 8962, you can request an extension by filing Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. This will give you an additional six months to file your tax return, moving the deadline to October 15. However, it's important to note that an extension to file does not grant you an extension to pay any taxes owed.
Amended returns: If you need to make changes or corrections to your Form 8962 after you have already filed your tax return, you will need to file an amended tax return using Form 1040X, Amended U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. The deadline for filing an amended return is generally within three years from the original due date of the return or within two years from the date you paid the tax, whichever is later.
It's important to consult the official IRS instructions and publications or seek advice from a tax professional to ensure you meet the specific deadlines and requirements for filing Form 8962, as they may be subject to change.
Conclusion
Form 8962 plays a critical role in determining eligibility for the premium tax credit and reconciling any advance credit payments received throughout the year. By understanding the purpose of the form, the eligibility criteria for the credit, and the step-by-step process for filling it out, taxpayers can navigate this tax provision with confidence.
When claiming the premium tax credit, it's crucial to keep accurate records, report any changes in circumstances, and seek professional tax advice if needed. The premium tax credit can make a significant difference in accessing affordable healthcare coverage, and by mastering Form 8962, individuals and families can maximize their tax benefits while staying compliant with tax regulations.
Remember, this blog is intended as a general guide and should not substitute personalized tax advice. If you have specific questions or need assistance, consult a tax professional or refer to IRS resources for more information on Form 8962 and the premium tax credit.


