- IRS forms
- Form 8908
Form 8908: Energy Efficient Home Credit
Download Form 8908As our world becomes increasingly aware of the importance of sustainable living, individuals and businesses are actively seeking ways to reduce their carbon footprint and promote energy efficiency. The Energy Efficient Home Credit, also known as Form 8908, is a tax credit program offered by the U.S. government to incentivize the construction or renovation of energy-efficient homes.
Form 8908 is a tax form used to claim the Energy Efficient Home Credit, which was initially introduced as part of the Energy Policy Act of 2005 and subsequently extended by the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008. The credit aims to encourage the construction of energy-efficient homes by providing a financial incentive to builders and homeowners.
This article will delve into the details of Form 8908, explaining what it is, who is eligible, and how it can benefit taxpayers.
Purpose of Form 8908
Form 8908 is used for the purpose of claiming the energy efficient home credit. This credit is a tax incentive provided by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to encourage the construction of energy-efficient homes.
The energy efficient home credit was introduced as part of the Energy Policy Act of 2005 and has been extended and modified by subsequent legislation. It allows eligible contractors to claim a tax credit for the construction or manufacture of new energy-efficient homes or the production of qualified energy-efficient components used in the construction of such homes.
Form 8908 is used by eligible contractors to calculate and claim the energy efficient home credit. The form requires information about the energy-efficient features and specifications of the home or components, as well as details about the contractor and the project. It also includes calculations to determine the amount of the credit that can be claimed.
It's important to note that Form 8908 is subject to specific eligibility criteria, and the credit amount and rules can change over time as per updates in tax laws and regulations.
Benefits of Form 8908
Here are some of the benefits associated with Form 8908:
-
Tax credit: The primary benefit of Form 8908 is the ability to claim a tax credit for the expenses incurred when starting a new retirement plan. The credit is designed to offset some of the costs associated with setting up and administering a qualified retirement plan.
-
Cost offset: By claiming the credit, eligible employers can reduce their tax liability and offset the costs of establishing a retirement plan. This can be particularly advantageous for small businesses with limited financial resources, as it provides an incentive to offer retirement benefits to employees.
-
Encourages employee savings: Offering a retirement plan through the utilization of Form 8908 can help employers encourage employee savings. By providing a tax-advantaged retirement vehicle, employers can motivate their employees to contribute to their retirement savings, which can enhance employee satisfaction and overall financial well-being.
-
Competitive advantage: Offering a retirement plan can help small businesses attract and retain talented employees. By utilizing Form 8908 and providing retirement benefits, employers can differentiate themselves in the job market and create a competitive advantage in attracting qualified individuals to their workforce.
-
Long-term tax savings: Implementing a retirement plan through Form 8908 can provide long-term tax savings for both employers and employees. Contributions made to the plan are typically tax-deductible for the employer, while employees can benefit from tax-deferred growth on their retirement savings until withdrawal.
-
Retirement readiness: By establishing a retirement plan and utilizing Form 8908, employers can contribute to the overall retirement readiness of their employees. Helping employees save for the future can alleviate financial stress and promote a more secure retirement.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 8908?
The eligibility to file Form 8908 is limited to eligible contractors who meet certain criteria. Here are the general requirements:
**Eligible contractor: **The taxpayer filing Form 8908 must be an eligible contractor. An eligible contractor is defined as a person who constructed, manufactured, or produced a qualified energy-efficient home.
Qualified energy-efficient home: The home in question must be a qualified energy-efficient home. This means it must meet specific energy-saving standards and be certified as compliant by an authorized certifier.
Certification: The qualified energy-efficient home must be certified as compliant by an authorized certifier. The certification process ensures that the home meets the necessary energy-saving requirements.
How To Complete Form 8908: A Step-by-Step Guide
Form 8908, the Energy Efficient Home Credit, is used to claim a tax credit for qualified energy-efficient home improvements. Here's a step-by-step guide to completing Form 8908:
Step 1: Obtain the necessary documents
Before starting the form, gather all the relevant documentation related to your energy-efficient home improvements. This may include receipts, invoices, and certification statements from the manufacturer or contractor.
Step 2: Fill in your basic information
Enter your name, Social Security number, and other identifying information at the top of Form 8908. If you're filing jointly with your spouse, include their information as well.

Step 3: Determine the credit amount
Calculate the total amount of the energy-efficient home improvement credit you're eligible to claim. The credit is generally 30% of the cost of eligible improvements made to your main home, up to certain maximum limits.
Step 4: Fill in Part I - Qualified Energy-Efficient Home Improvement Credit
In Part I of Form 8908, provide information about the qualified energy-efficient home improvements you made. Include the type of improvement, the cost, and any other required details. You may need to attach additional sheets if you have multiple improvements.

Step 5: Fill in Part II - Residential Energy Efficient Property Credit from Form 5695
If you're also claiming the Residential Energy Efficient Property Credit, which is reported on Form 5695, complete Part II of Form 8908. Provide the credit amount you claimed on Form 5695, as well as any other requested information.
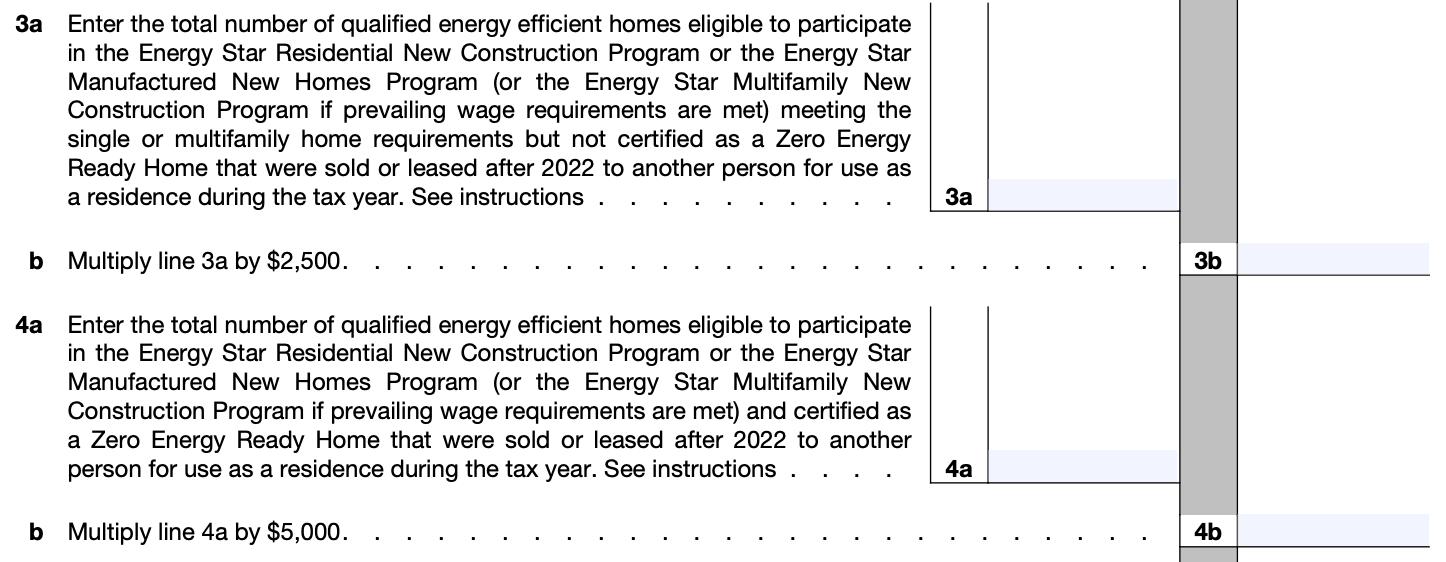
Step 6: Calculate the total credit amount
Add up the credit amounts from Part I and Part II to determine the total energy-efficient home credit you're claiming.
Step 7: Complete Part III - Credit from Other Sources
If you received any grants, subsidies, or other forms of assistance for the qualified improvements, report them in Part III. This may affect the amount of credit you can claim.
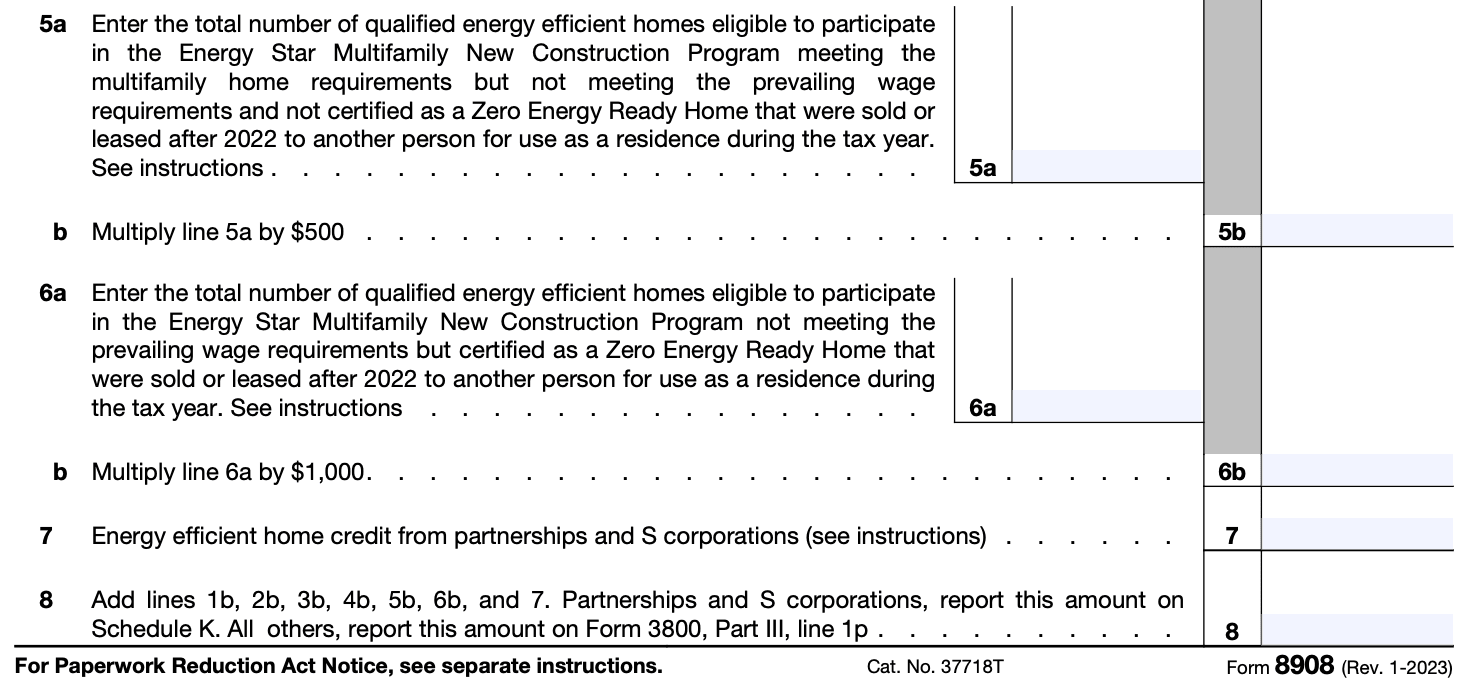
Step 8: Calculate the net credit
Subtract the credit amount reported in Part III from the total credit amount calculated in Step 6. This will give you the net credit you can claim.
Step 9: Complete Part IV - Credit to be used or carried forward
If you're not able to use the full credit amount in the current tax year, you can carry it forward to future years. Fill in Part IV to indicate whether you want to apply the credit against your tax liability for the current year or carry it forward.
Step 10: Sign and date the form
Review all the information on Form 8908 for accuracy. Once you're satisfied, sign and date the form to certify that the information provided is true and correct.
Step 11: Attach supporting documents
Make sure to attach any necessary supporting documents, such as receipts, invoices, and certification statements, to substantiate your claims.
Step 12: File the form
Submit the completed Form 8908, along with your other tax forms and attachments, to the appropriate tax authority. Check the filing instructions for your specific jurisdiction to determine the submission method (e.g., mail, e-file).
Special Considerations When Filing Form 8908
When filing Form 8908, there are several special considerations that you should keep in mind.
Here are some important points to consider:
Eligibility requirements: To claim the energy efficient home credit, you must be an eligible contractor who has constructed, reconstructed, or substantially renovated a qualified energy efficient home. Make sure you meet all the eligibility requirements outlined in the instructions for Form 8908.
**Documentation: **Maintain proper documentation to support your claim. This includes records of the homes you've constructed or renovated, certification statements from the homeowners, and any other relevant documentation required by the IRS. Be prepared to provide this documentation if requested.
Credit calculation: The energy efficient home credit is calculated based on the energy efficiency level of the qualified homes you've built or renovated. Make sure you accurately calculate the credit amount based on the specifications provided in the instructions for Form 8908.
Deadlines: File Form 8908 in a timely manner. Generally, it must be filed by the due date, including extensions, of the tax return for the year the qualified home was sold or leased. Failure to file on time may result in penalties and interest.
Coordination with homeowners: If you're claiming the energy efficient home credit, coordinate with the homeowners to ensure they are not claiming the credit on their tax return. Only one credit can be claimed for each qualified home, so it's important to communicate and avoid any duplicative claims.
Other requirements: Familiarize yourself with any other requirements and instructions provided by the IRS for Form 8908. These may include specific reporting obligations, record-keeping requirements, and additional documentation that needs to be submitted.
Professional assistance: Filing tax forms can be complex, and the energy efficient home credit is no exception. If you're unsure about any aspect of Form 8908 or need assistance, it's recommended to consult with a tax professional or accountant who can provide guidance based on your specific circumstances.
How To File Form 8908: Offline/Online/E-filing
The filing method for Form 8908 depends on the year of the form and the current IRS guidelines. Here are the general options for filing Form 8908:
Offline filing (paper filing)
a. Obtain a copy of Form 8908: You can download the form from the official IRS website (irs.gov) or request a printed copy by calling the IRS at their toll-free number (1-800-829-3676).
b. Fill out the form: Complete the required information on Form 8908, including the details of the energy-efficient homes you've constructed or manufactured.
c. Attach supporting documents: Gather and attach any necessary supporting documentation as outlined in the instructions for Form 8908.
d. Mail the form: Once you have completed the form and attached the required documents, mail it to the appropriate IRS address as specified in the form's instructions. Make sure to use certified mail or a reliable delivery method to ensure it reaches the IRS securely.
Online filing (IRS.gov)
The availability of online filing options may vary depending on the tax year and current IRS procedures. You should check the IRS website (irs.gov) for the most up-to-date information on whether online filing is available for Form 8908. If online filing is available, follow these steps:
a. Visit the IRS website: Go to the official IRS website and navigate to the section for filing tax forms online.
b. Select the appropriate tax year: Choose the correct tax year for Form 8908 filing.
c. Fill out the form: Enter the required information directly into the online form, following the instructions provided.
d. Submit the form: Once you have completed all the necessary fields, submit the form electronically through the IRS website.
E-filing through authorized software
If you use tax preparation software or work with a tax professional, they may have electronic filing options available for Form 8908. In this case, follow the instructions provided by the software or your tax professional to complete and submit the form electronically.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 8908
When filing Form 8908, there are several common mistakes that you should avoid to ensure accurate reporting and compliance.
Here are a few:
Incorrect or incomplete information: Make sure all the required fields on Form 8908 are accurately completed. Double-check your entries for accuracy and completeness before submitting the form.
Missing or incorrect taxpayer identification number (TIN): Ensure that the TIN provided on the form is correct and matches the information provided on other tax documents. This includes both the contractor's TIN and the homeowner's TIN.
Failure to attach required documentation: Form 8908 typically requires attachments such as the certification from the homeowner and a copy of the energy efficient home certification statement. Failing to attach these documents may lead to delays or rejection of the claim.
Claiming ineligible homes or improvements: The energy efficient home credit is only available for certain homes and specific energy-efficient improvements. Ensure that the homes or improvements you are claiming meet the eligibility criteria outlined in the instructions for Form 8908.
Inaccurate calculation of the credit: Take care when calculating the credit amount. Double-check your calculations to ensure they are accurate and properly supported by the documentation.
Late filing or missed deadlines: Be aware of the deadline for filing Form 8908. Failing to file the form on time may result in penalties or the loss of the credit. Stay updated with the current tax year's deadlines and make sure to submit the form before the due date.
Failure to keep copies for your records: It's essential to retain a copy of the completed Form 8908 and any supporting documentation for your records. This will help you in case of future inquiries or audits.
Conclusion
The Energy Efficient Home Credit, facilitated through Form 8908, provides a valuable incentive for builders and homeowners to invest in energy-efficient construction and renovation projects. By reducing energy consumption and promoting sustainable living, this tax credit program supports efforts to mitigate climate change while offering financial benefits to eligible taxpayers.
If you're considering building or renovating an energy-efficient home, be sure to consult with a tax professional or utilize tax software to understand the specific requirements, ensure compliance, and take advantage of the potential benefits offered by Form 8908. Together, we can embrace a greener future and make a positive impact on the environment and our financial well-being.


