- IRS forms
- Form 1098-T
Form 1098-T Guide: Claim Education Tax Credits
Download Form 1098-TIntroduction
As the tax season approaches, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the different forms that you may need to file. One such form that is commonly used in the education sector is the Form 1098-T. This form is used by colleges and universities to report the amount of tuition and related expenses paid by a student or on their behalf during the tax year. In this blog, we will delve deeper into what Form 1098-T is, who needs to file it, steps on how to file it, when to file it, common mistakes to avoid when filing, and what to do if you encounter an issue.
What is Form 1098-T?
Form 1098-T is also known as the Tuition Statement. It is a form that is used by colleges and universities to report the amount of qualified tuition and related expenses paid by a student or on their behalf during the tax year. The form also includes scholarships and grants received by the student during the tax year. The information reported on Form 1098-T is used by taxpayers to claim educational tax credits, such as the American Opportunity Tax Credit or the Lifetime Learning Credit, on their tax returns.
Who Needs to File Form 1098-T?
Colleges and universities are required to file Form 1098-T for each student who is enrolled and for whom a reportable transaction is made. A reportable transaction includes any payments received for qualified tuition and related expenses, as well as any scholarships or grants received by the student. If a student's tuition and related expenses are entirely paid by scholarships and grants, the institution is not required to file Form 1098-T.
Step by Step Guide: How to File Form 1098-T
To file Form 1098-T, colleges and universities must follow the steps outlined by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). The steps are as follows:
Obtain a TIN: The institution must obtain the taxpayer identification number (TIN) of the student to whom they are reporting.
Gather Required Information: The institution must gather the required information, including the amount of qualified tuition and related expenses paid by the student, scholarships and grants received by the student, and any adjustments made to prior-year tuition and related expenses.
Complete Form 1098-T: The institution must complete Form 1098-T and send a copy to the student by January 31st of the following year.
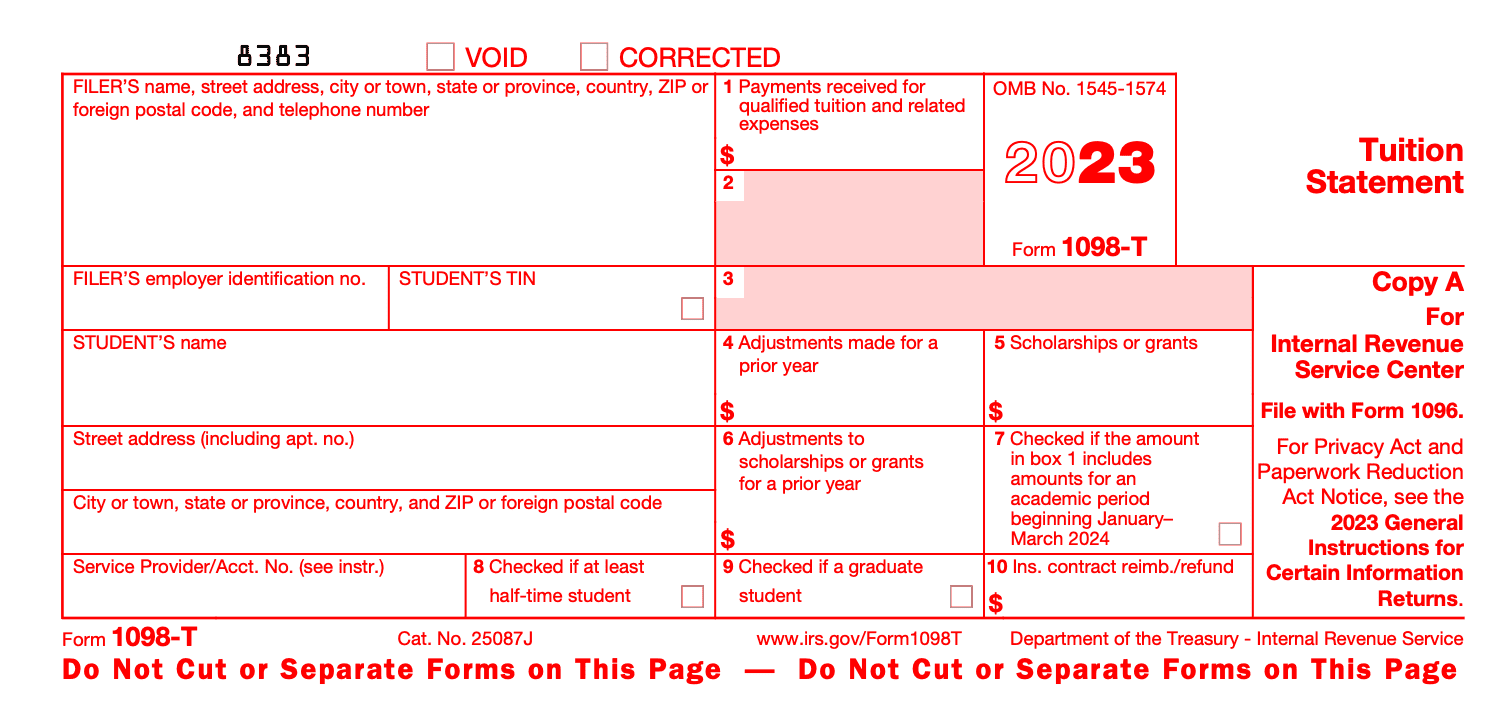
Contents of Form 1098-T: In Form 1098-T, there are three copies: Copy A, Copy B, and Copy C.
Copy A: This copy is intended for the IRS. The institution must file Copy A of Form 1098-T with the IRS by the end of February, using either paper or electronic filing.
Copy B: This copy is intended for the student. The institution must send Copy B of Form 1098-T to the student by January 31st of the following year.
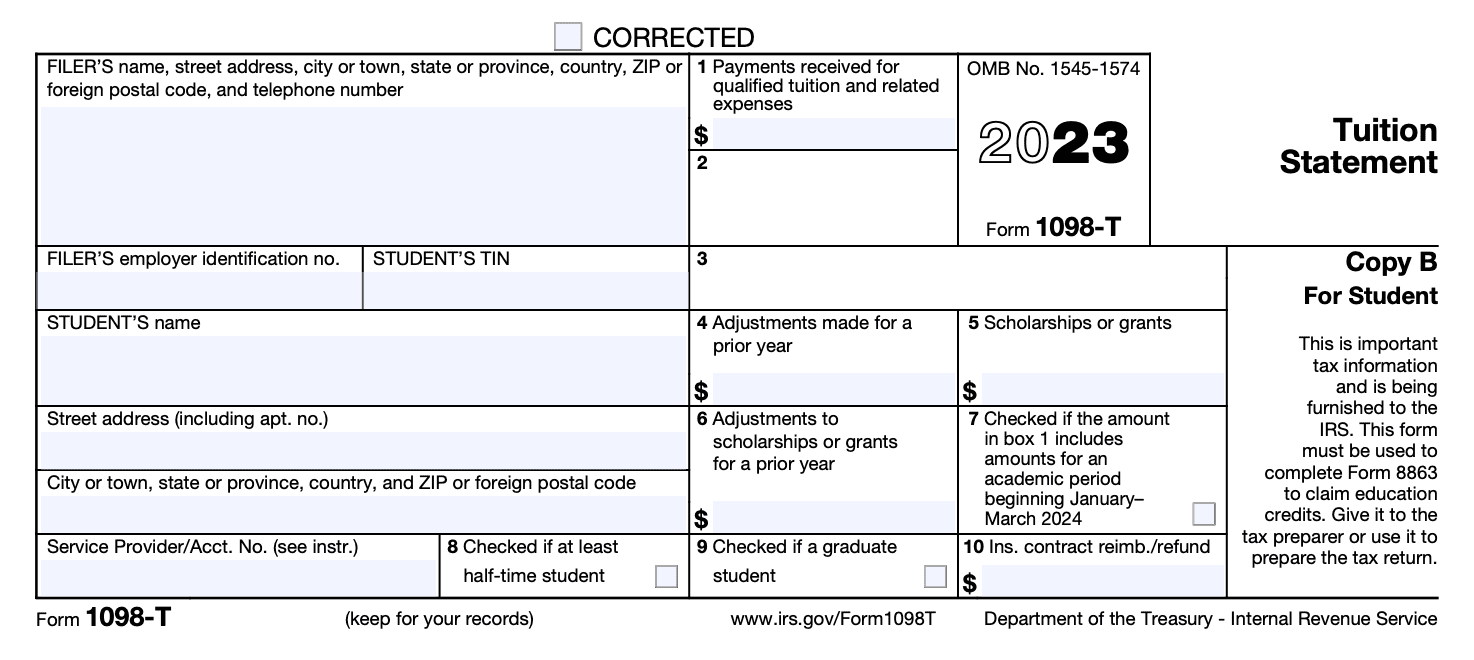
Instructions for Students:
- You may be eligible to claim an education credit on Form 1040 or 1040-SR.
- This statement has been provided to you by your educational institution or insurer and is required to support your education credit claim.
- Retain this statement for your records.
- Your institution must include its name, address, and contact information on the statement.
- Do not contact the filer or service provider for explanations on education credit requirements or how to calculate it.
- Your TIN may show only the last four digits for your protection. If not shown, contact your school.
- Box 1 shows total payments received by the educational institution for qualified tuition and related expenses.
- Box 5 shows the total of all scholarships or grants administered and processed by the institution.
- Box 10 shows the total amount of reimbursements or refunds of qualified tuition and related expenses made by an insurer.
- Box 7 shows whether amounts for an academic period beginning January–March 2024 are included in Box 1.
- Box 8 shows whether you are carrying at least half the normal full-time workload.
- Box 9 shows whether you are enrolled in a program leading to a graduate degree or other recognized graduate-level educational credential.
- Box 4 shows any adjustments made by the educational institution for prior year qualified tuition and related expenses.
- Box 6 shows any adjustments to scholarships or grants for a prior year that may affect your education credit.
- For the latest updates on Form 1098-T, visit www.irs.gov/Form1098T.
- Check www.irs.gov/FreeFile to see if you qualify for no-cost filing.
Copy C: This copy is intended for the institution's records. The institution must keep a copy of Form 1098-T for their records.
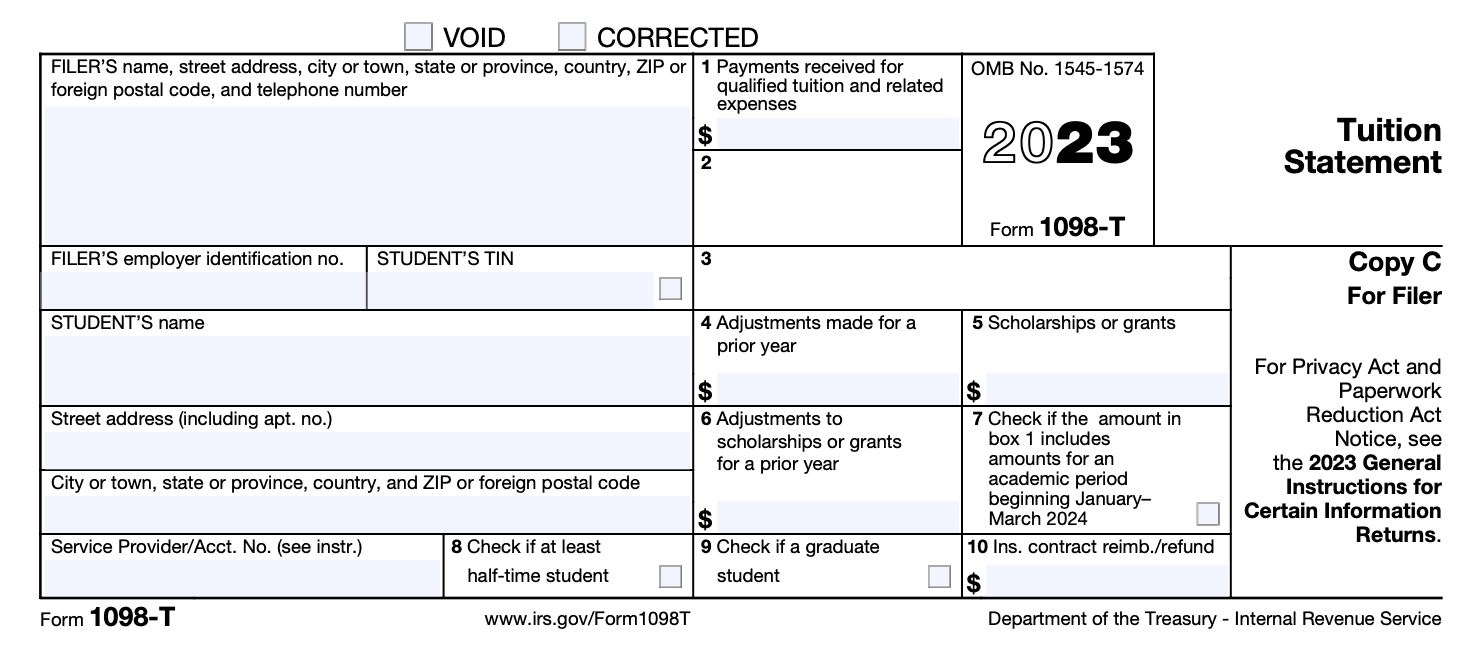
It is important to note that Copy A must be filed with the IRS, and failure to do so can result in penalties and interest. Additionally, the student must receive Copy B by January 31st of the following year to assist them in preparing their tax return. The institution must keep Copy C for their records for at least four years.
When to File Form 1098-T?
Form 1098-T must be sent to the student by January 31st of the following year. The institution must also submit the form to the IRS by the end of February, using either paper or electronic filing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing
When filing Form 1098-T, there are some common mistakes that institutions should avoid. These include:
- Failing to report all qualified tuition and related expenses paid by the student.
- Failing to report scholarships and grants received by the student.
- Failing to send a copy of Form 1098-T to the student by January 31st of the following year.
- Failing to submit Form 1098-T to the IRS by the end of February.
- Failing to obtain the correct TIN for the student.
What to Do if You Encounter An Issue?
If you encounter any mistakes with Form 1098-T, it is important to take the necessary steps to correct them as soon as possible. Here's what you can do:
- Identify the mistake: Before you can take any corrective action, you must first identify the mistake. Review the information on the form carefully to determine what information is incorrect.
- Contact the school: If the mistake is related to information provided by the school, contact the school's financial aid or registrar's office. They may be able to correct the mistake and issue a corrected Form 1098-T.
- Request a corrected form: If the school cannot or will not correct the mistake, you can request a corrected Form 1098-T. Contact the school and ask them to issue a corrected form with the correct information.
- Amend your tax return: If you have already filed your tax return and later discover a mistake on your Form 1098-T, you may need to amend your tax return. Use Form 1040X to amend your tax return and include the corrected information from the corrected Form 1098-T.
- Keep documentation: Make sure to keep all documentation related to the mistake and any corrective action taken. This includes any correspondence with the school or the IRS, the corrected Form 1098-T, and any amended tax returns.
Remember, it is important to correct any mistakes on your Form 1098-T as soon as possible to avoid any potential issues with your tax return. If you are unsure about how to correct a mistake, consider consulting with a tax professional or contacting the IRS for guidance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Form 1098-T is an important tax document that helps students and their families claim education-related tax credits and deductions. It is essential to review the form carefully to ensure that it is accurate and complete. Any mistakes or discrepancies should be addressed promptly to avoid potential penalties or delays in receiving tax refunds.
By following the steps outlined in this article, you can take proactive measures to correct any errors and ensure that your tax filing process goes smoothly. Make sure you keep all relevant documentation, communicate clearly with the educational institution and the IRS, and seek professional assistance if needed. With these steps in mind, you can confidently navigate the process of correcting mistakes with Form 1098-T and optimize your tax benefits.


