- IRS forms
- Form 1065
Form 1065: U.S. Return of Partnership Income
Download Form 1065The IRS requires all partnership firms to file their tax returns yearly by filling out Form 1065. It's imperative to file this tax form to report any gains, incomes, losses, deductions, etc., in time to avoid a penalty for late filing.
So, what is IRS Form 1065, how do you fill one, and who needs to fill it? Here are all the IRS Form 1065 instructions you need to know.
What Is IRS Form 1065?
All partnerships need to report their incomes and expenses by filing tax Form 1065 every year.
Income reported under Form 1065 is not taxed, but rather the income "flows through" to individual owners of the partnership. As a result, all profits and incomes are taxed on the personal tax returns of the owners.
Partnership tax return through Form 1065 is filed in two key phases.
To begin with, partnerships need to report all their incomes, expenses, and other financial data for the year using the tax Form 1065. Schedule K reports the net income along with special sections of incomes and losses over the period.
After this, all the owners need to report their individual share of profits and losses accumulated over the tax year using a personal Schedule K-1.
Who Files Form 1065?
As we mentioned earlier, Form 1065 doesn't tax the income mentioned in it. It works by indicating to the IRS that the owners in a partnership firm have paid their taxes accurately.
Here are the business entities that need to file tax Form 1065:
- Domestic partnerships: All partnerships in the US need to file Form 1065. The IRS describes partnerships as a business relationship between two or more individuals.
- Certain LLCs: LLCs with two or more members that do not file their tax returns as corporations will need to do so as a partnership and must file Form 1065.
- Section 501(d): These include non-profit organizations that are apostolic or religious.
- Foreign Partnerships: Foreign partnerships with a gross annual income of more than $20,000 derived from sources in the US or ones with more than 1% of their income generated in the US need to fill out Form 1065.
If you're confused about whether your business is structured as a partnership or not, check the partnership agreement.
This document details the business roles, registered location of operation, and the business structure. It can help you distinguish your business as a general partnership, limited partnership (LP), or limited liability partnership (LLP).
How To Complete Form 1065: Step-by-Step Instructions
The IRS Tax Form 1065 is one of the most important annual tax forms filed by partnerships and LLCs.
If you’re required to report your income, gains and losses, deductions, credits, and other information about the establishment through Form 1065, you’ll need to know where to find it and how to file it.
Partnerships with fewer than 100 partners can choose to file Form 1065 online or offline, but you’ll have to file online if you have more than 100 partners. The form is due three months and fifteen days after the end of the tax year.
Form 1065 can be completed with the instructions mentioned below.
Step 1: Gather all the relevant information
You’ll require information from all of your financial statements for the end of the year, so keep the following handy:
- Profit and loss statement
- Deductible expenses
- Balance sheet
- Cost of goods sold
- Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- Business code number
- The accounting method used by your business
Step 2: Fill the details in the first part of Form 1065
You can begin filling in the form by providing basic information about your partnership on the first page of the five-page form.
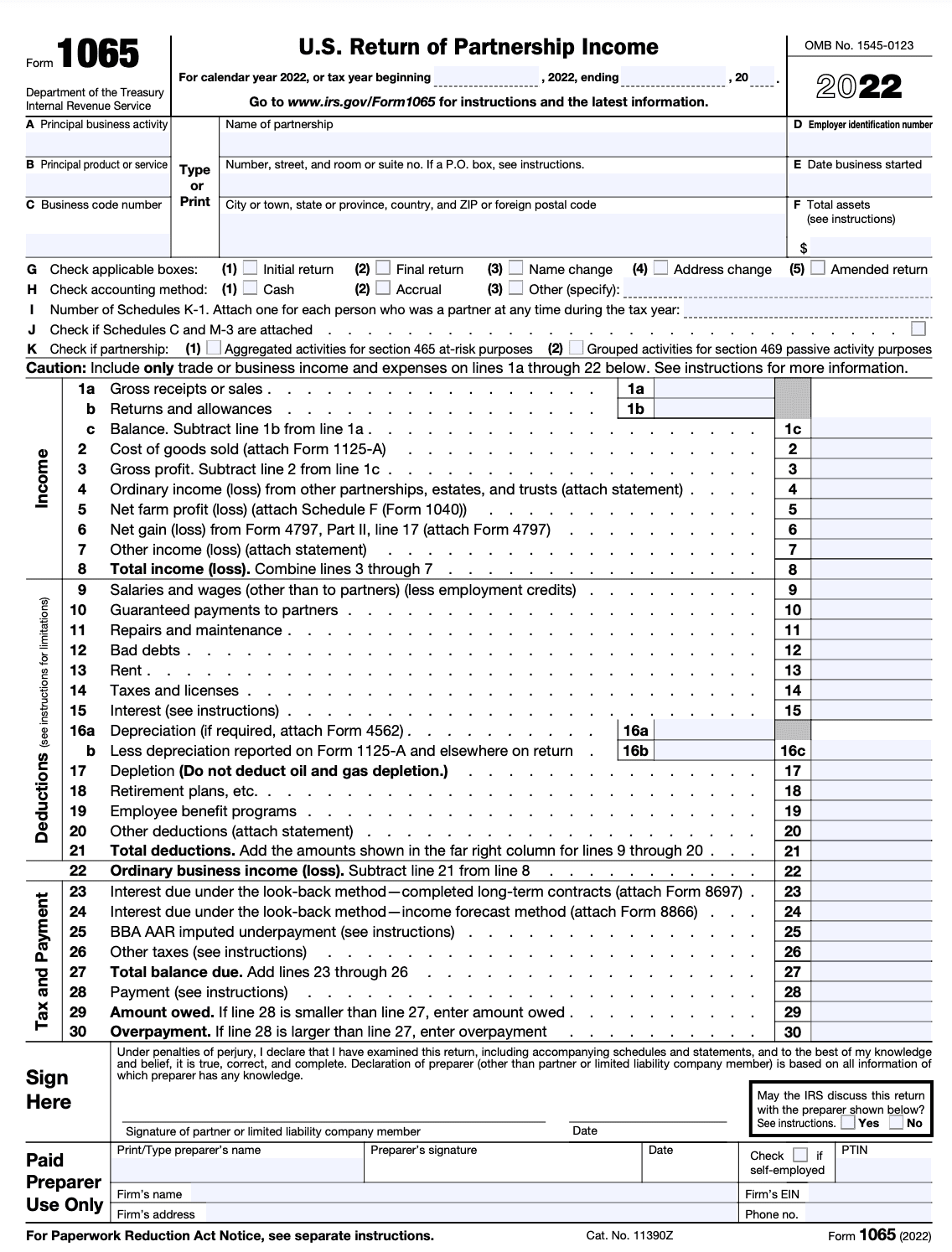
Step 3: Complete Schedule B
Schedule B is an important section that enquires about the percentage of holdings of each partner as well as any partnerships investments and debts.
If you answered no to all four of the questions in Part 4, you are not required to complete Schedules L, M-1, and M-2. Complete all relevant information in this schedule before moving to the next.
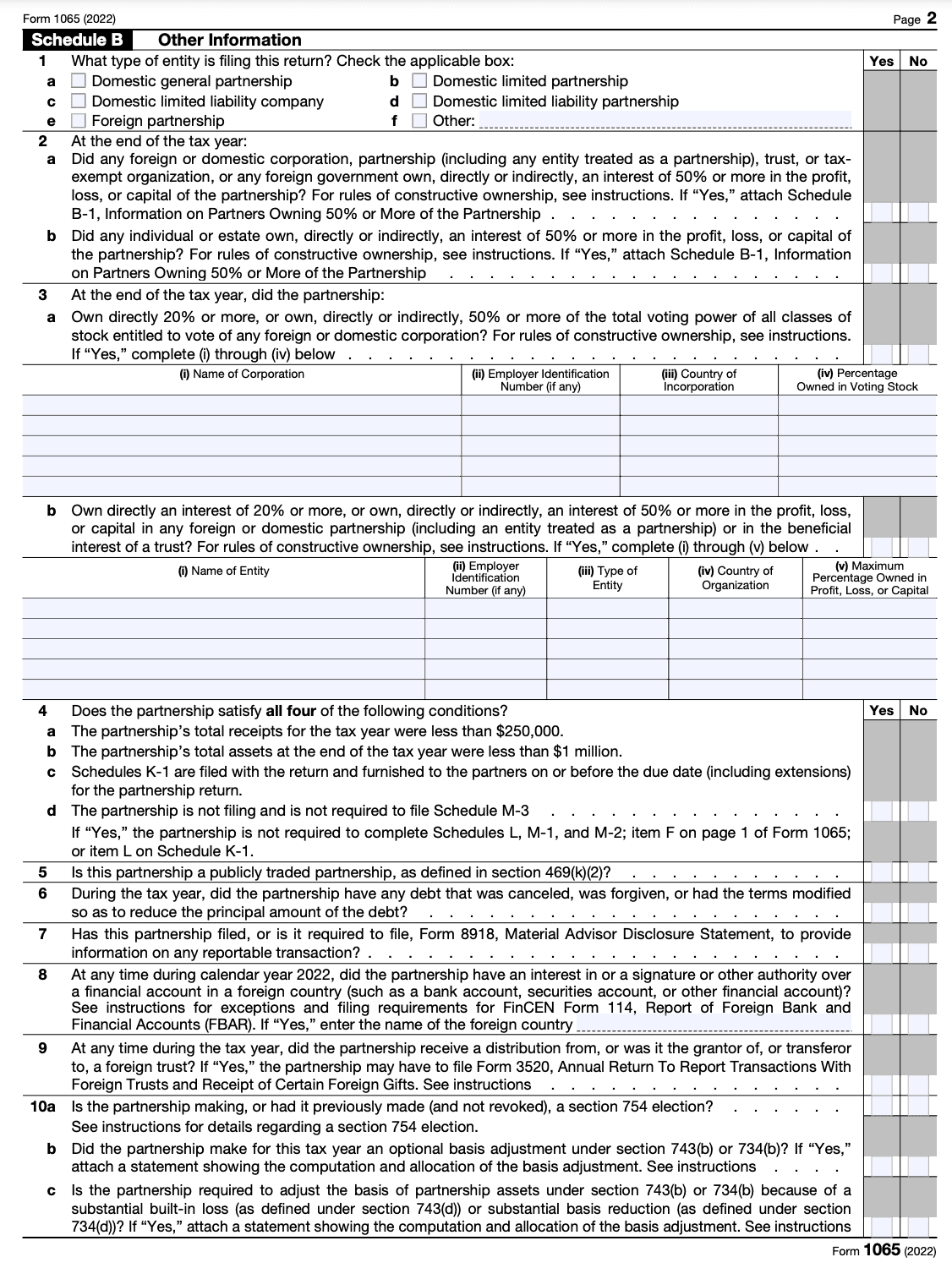
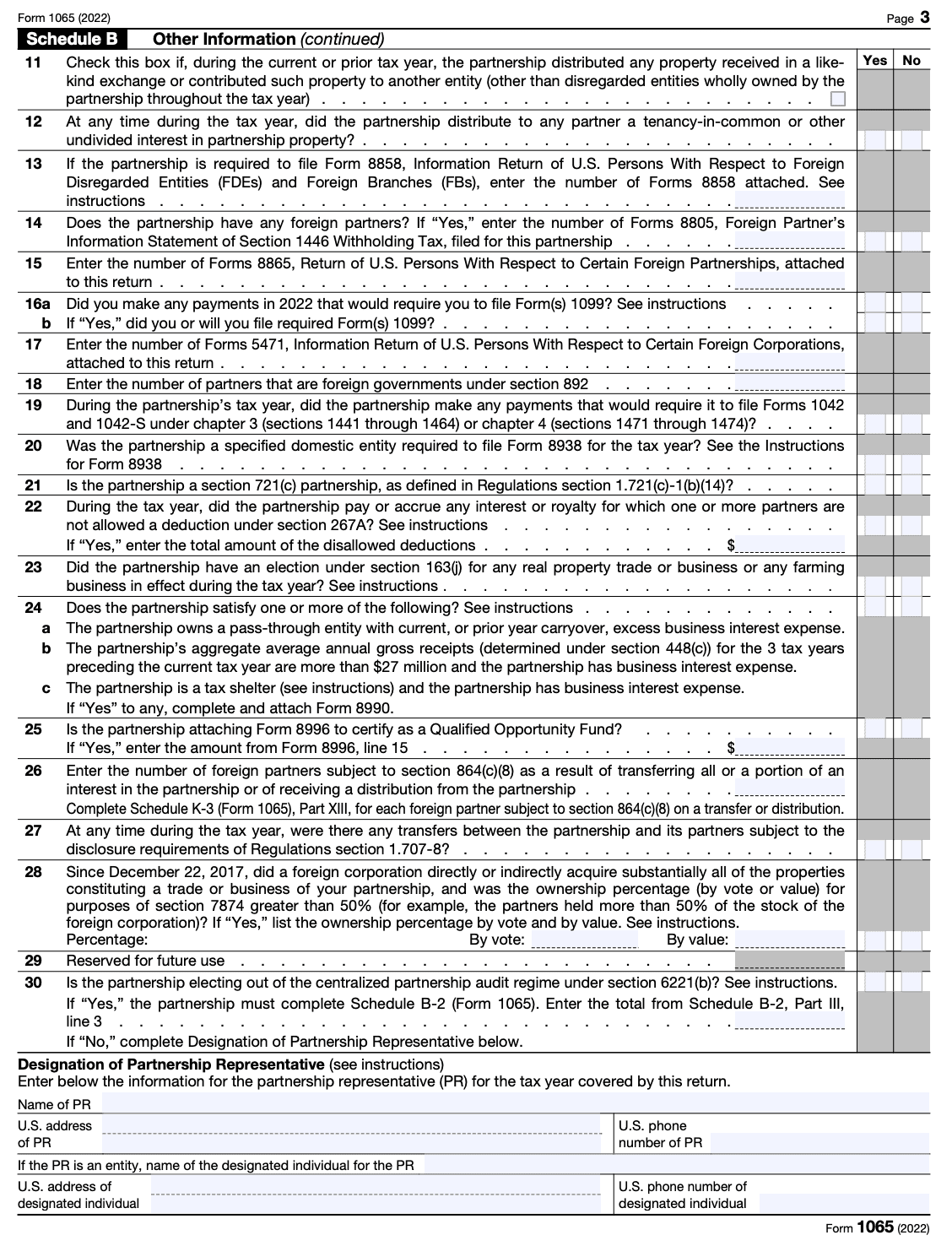
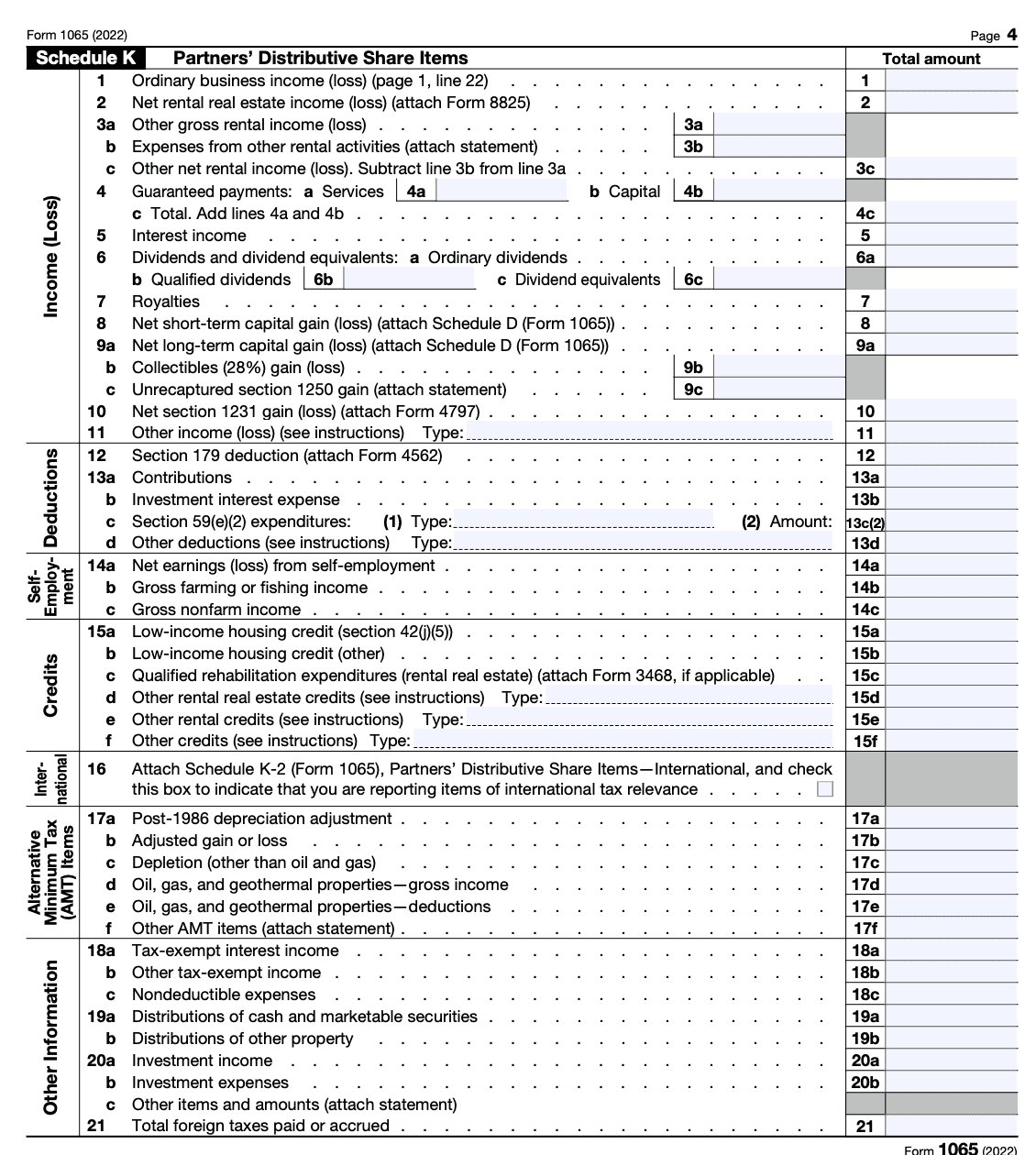
Step 4: Complete Schedules K and K-1
On page 4, you must complete Schedule K. This section of the form asks about the partnership’s income and other general information about holdings in the partnership.
Schedule K-1 is a supplement to Schedule K that allows partners to directly report their income, losses, dividends, and capital gains.
Every partner has to file an individual Schedule K-1 with the IRS. So you need to collect filled-out Schedule K-1s from each partner and attach them with Form 1965.
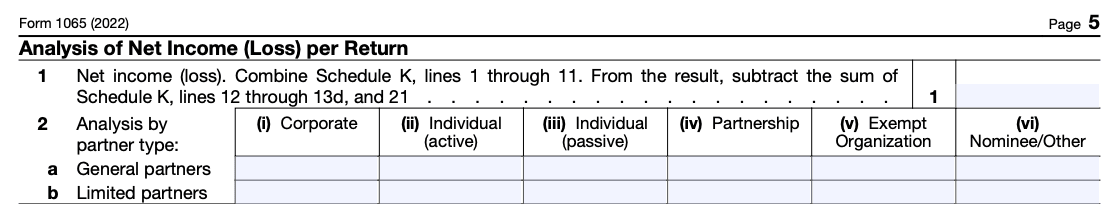
Step 5: Complete Schedule L
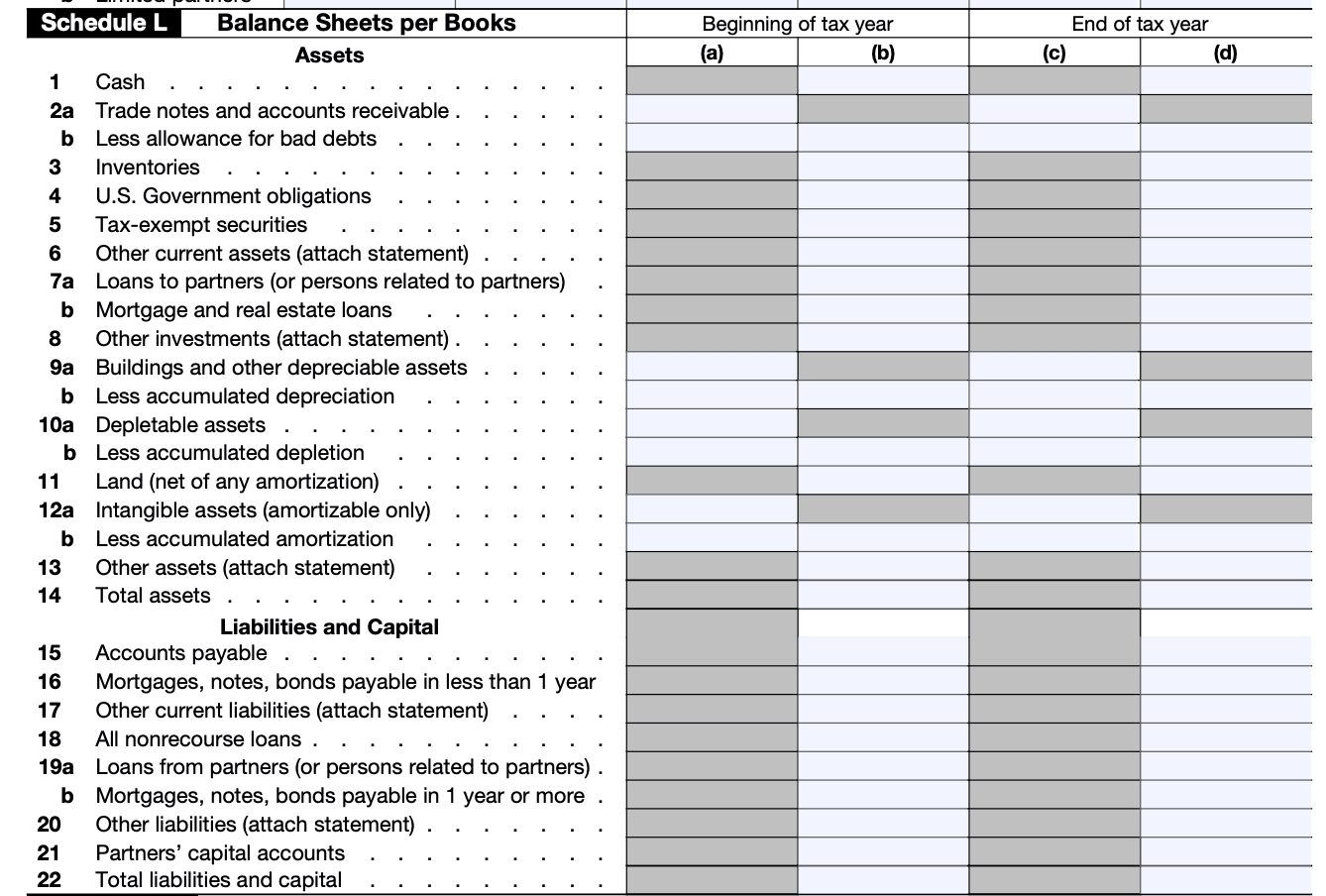
Pay close attention when filling out Schedule L of Form 1065. It’s a balance sheet that describes the financial health of your business. Complete the 22 questions to record your assets, liabilities, and capital.
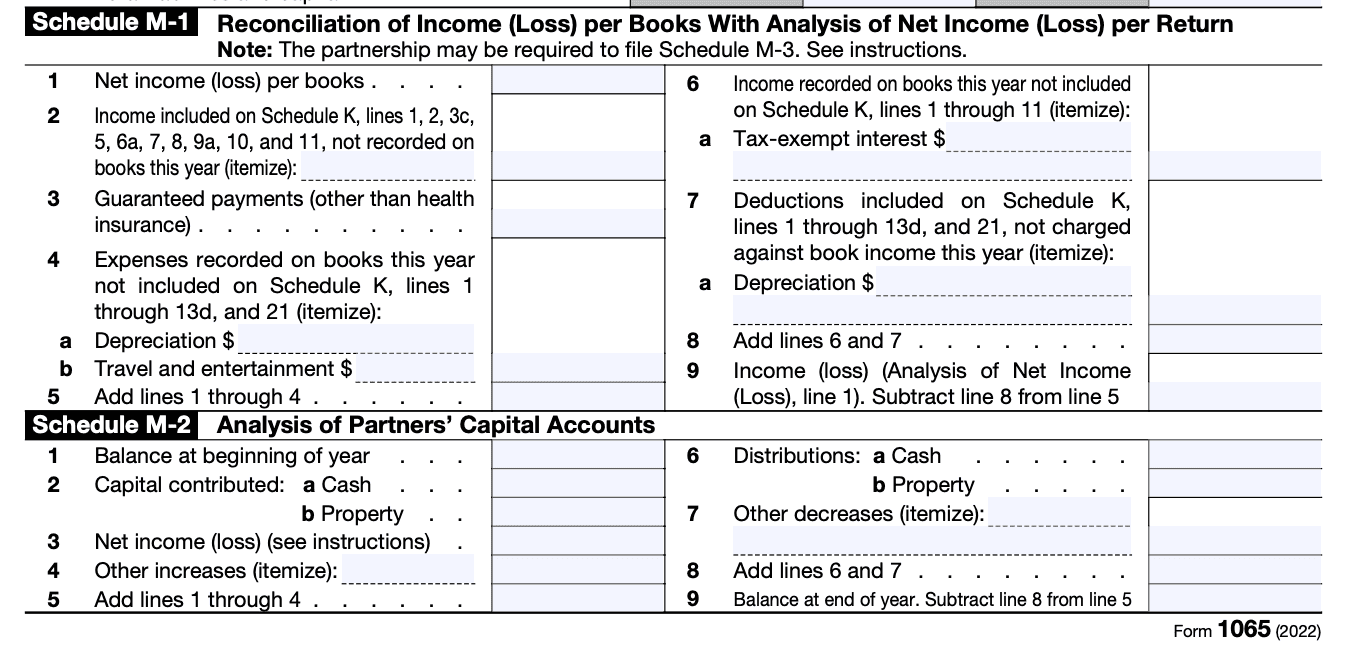
Step 6: Complete Schedule M-1 and M-2
Schedule M-1 helps describe and explain any bookkeeping discrepancies between the income on your records and the tax return income. If you meet the requirements, you’ll have to file this even if there are no such discrepancies.
The last section in Form 1065 is Schedule M-2 that notifies the IRS of any changes to the capital accounts of any partners. Make sure that any changes reported here tally with the information provided in the respective Schedule K-1s.
Step 7: Review and submit the form
Form 1065 is one of the most important tax information reporting documents. Make sure to take time to go through each item after filling it out to ensure there are no errors.
Using an IRS-approved tax filing system is the simplest way to file this form online. Many accounting and tax software programs provide support for Form 1065.
Ensure to read the 61-page instruction booklet that goes over how to fill in each item in Form 1065 for any questions that you may be confused about.
When Is the Deadline to File IRS Form 1065?
Partnerships using the calendar year as their tax year must file Form 1065 by March 15th of the coming year. You can also file for a 6-month extension which would make September 15th the new deadline.
For instance, if you close your books on December 31st, 2020, you must file your Form 1065 by March 15th, 2021. Likewise, if you have an extension, then you must do it by September 15th, 2021.
If you do not take calendar year as your tax year, you must file your form by the 15th day of the third month after your tax year-end date.
What if I miss the deadline?
The IRS imposes a penalty on partnerships that delay filing their Form 1065 accurately and in time. The penalty is $210 per month multiplied by the number of members that were a part of the partnership during the reporting period.
Conclusion
Filling in Form 1065 might seem complex and time-consuming, but it’s one of the most important documents for the tax compliance of partnerships. The five-page document is detailed and asks a plethora of questions.
So, while you can fill it out yourself, it's best to get a professional bookkeeping service like Fincent to assist you. Our expert bookkeepers can help you save time and money on bookkeeping so that you can get back to doing what you love.


