- IRS forms
- Schedule I (Form 1041)
Schedule I (Form 1041): Alternative Minimum Tax – Estates
Download Schedule I (Form 1041)When it comes to filing taxes for an estate, there are various forms and schedules to navigate. One of these forms is Schedule I (Form 1041), which deals specifically with the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) for estates. The AMT is a parallel tax system that ensures individuals and entities with higher incomes or significant deductions pay a minimum amount of tax.
What is Schedule I (Form 1041)? Schedule I (Form 1041) is an attachment to Form 1041, U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts. It is used to calculate the Alternative Minimum Tax for estates. The Alternative Minimum Tax is a separate tax calculation designed to ensure that individuals and entities with substantial income and certain deductions still pay a minimum amount of tax, regardless of the regular tax rules. Schedule I helps estates calculate their AMT liability accurately.
In this blog post, we will delve into Schedule I (Form 1041) and explore the key aspects of the Alternative Minimum Tax for estates.
Purpose of Schedule I (Form 1041)
The purpose of Schedule I is to report income items, such as interest, dividends, rents, royalties, and capital gains or losses, that are specifically allocated to beneficiaries of the estate or trust. This schedule is used when the estate or trust distributes income to beneficiaries or retains income that is taxed at the trust level.
Some common reasons for using Schedule I include:
Allocation of income: Schedule I is used to allocate income items to beneficiaries based on their respective shares or interests in the estate or trust. This ensures that each beneficiary reports their share of the income on their individual tax returns.
**Income distribution deduction: **If the estate or trust distributes income to beneficiaries, it may be eligible for an income distribution deduction. Schedule I is used to calculate and report this deduction.
**Income taxable at trust level: **Certain types of income, such as income derived from trade or business activities conducted by the estate or trust, may be subject to taxation at the trust level. Schedule I is used to report such income.
Miscellaneous deductions: Schedule I allows for the reporting of miscellaneous deductions that are not directly attributable to the estate or trust but can be allocated to beneficiaries. These deductions may include expenses related to the administration of the estate or trust.
Benefits of Schedule I (Form 1041)
Here are some of the benefits of using Schedule I:
-
Comprehensive reporting: Schedule I provides a structured format for reporting various types of income, deductions, and tax calculations specific to estates and trusts. It ensures accurate reporting and helps fulfill the tax obligations of the estate or trust.
-
Income reporting: Schedule I allows estates and trusts to report different types of income, such as interest, dividends, capital gains, rental income, and business income. By reporting all income sources on Schedule I, the taxpayer can ensure compliance with tax laws and accurately determine their taxable income.
-
Deduction reporting: The form allows for the reporting of various deductions, such as administration expenses, attorney fees, trustee fees, charitable contributions, and certain taxes paid by the estate or trust. These deductions can help reduce the taxable income, resulting in potential tax savings.
-
Alternative minimum tax (AMT) calculation: Schedule I includes a section for calculating the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) for estates and trusts. The AMT is a separate tax calculation that ensures taxpayers with high deductions and certain types of income still pay a minimum amount of tax. By calculating the AMT, estates and trusts can determine if they owe any additional tax.
-
Foreign transactions reporting: If an estate or trust has foreign transactions or holds foreign assets, Schedule I provides sections to report these activities. It includes reporting requirements for foreign income, foreign taxes paid, and certain foreign financial accounts.
-
Tax computation: Schedule I provides a step-by-step computation of the taxable income and tax liability for the estate or trust. It helps ensure accurate tax calculations and helps determine the final tax owed.
-
Filing requirements: Using Schedule I ensures compliance with IRS regulations for estates and trusts. By completing the form correctly and submitting it along with the appropriate supporting documents, the taxpayer meets their filing requirements and avoids potential penalties or audits.
Who Is Eligible To File Schedule I (Form 1041)?
The following entities are eligible to file Schedule I:
Estates of decedents: When an individual passes away, their assets may be transferred to an estate, which is a legal entity responsible for managing and distributing those assets to beneficiaries or heirs.
Complex trusts: Complex trusts are trusts that do not meet the requirements of a simple trust. A complex trust may accumulate income, distribute income to beneficiaries, make charitable contributions, or have multiple beneficiaries with varying interests.
It's important to note that Schedule I (Form 1041) is an attachment to Form 1041, which is the U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts. Both estates and complex trusts must file Form 1041, and if they meet certain criteria, they may need to complete Schedule I.
How To Complete Schedule I (Form 1041): A Step-by-Step Guide
Here is a general outline of the steps involved in completing Schedule I (Form 1041):
Step 1: Gather necessary information
Collect all relevant financial and tax-related documents, including income statements, expense receipts, asset information, and any other supporting documents.
Step 2: Identify the estate or trust
Provide the basic identifying information about the estate or trust, including its name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN).

Step 3: Determine filing status
Determine the appropriate filing status for the estate or trust, such as "Simple Trust," "Complex Trust," or "Grantor Type Trust." This determination is based on the terms of the trust document and the nature of the income and deductions.
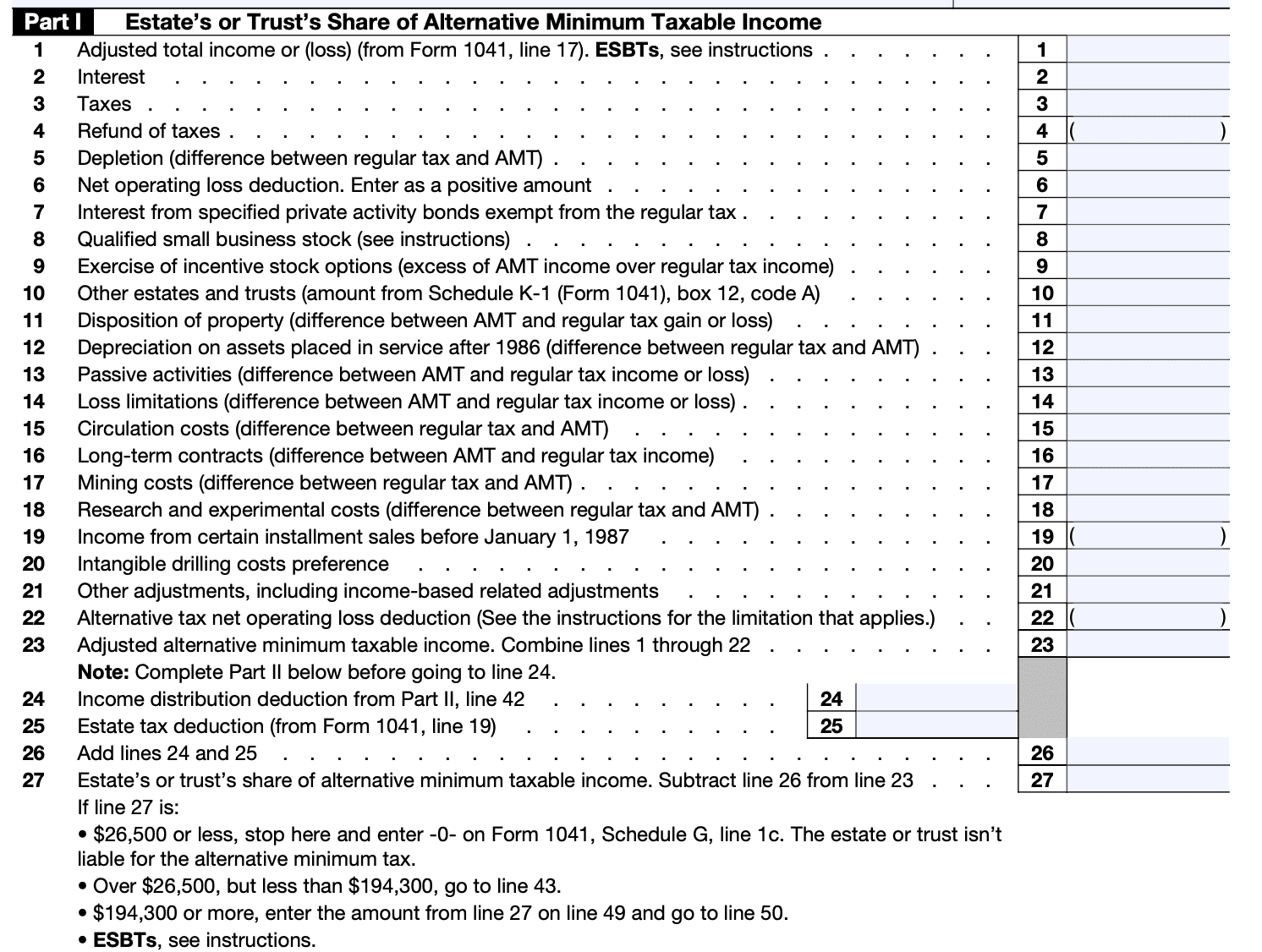
Step 4: Calculate income and deductions
- Determine the total income earned by the estate or trust during the tax year, including interest, dividends, rental income, capital gains, and any other applicable income sources.
- Subtract allowable deductions, such as trustee fees, attorney fees, administration expenses, charitable contributions, and any other eligible expenses.
- Calculate taxable income by subtracting deductions from the total income.
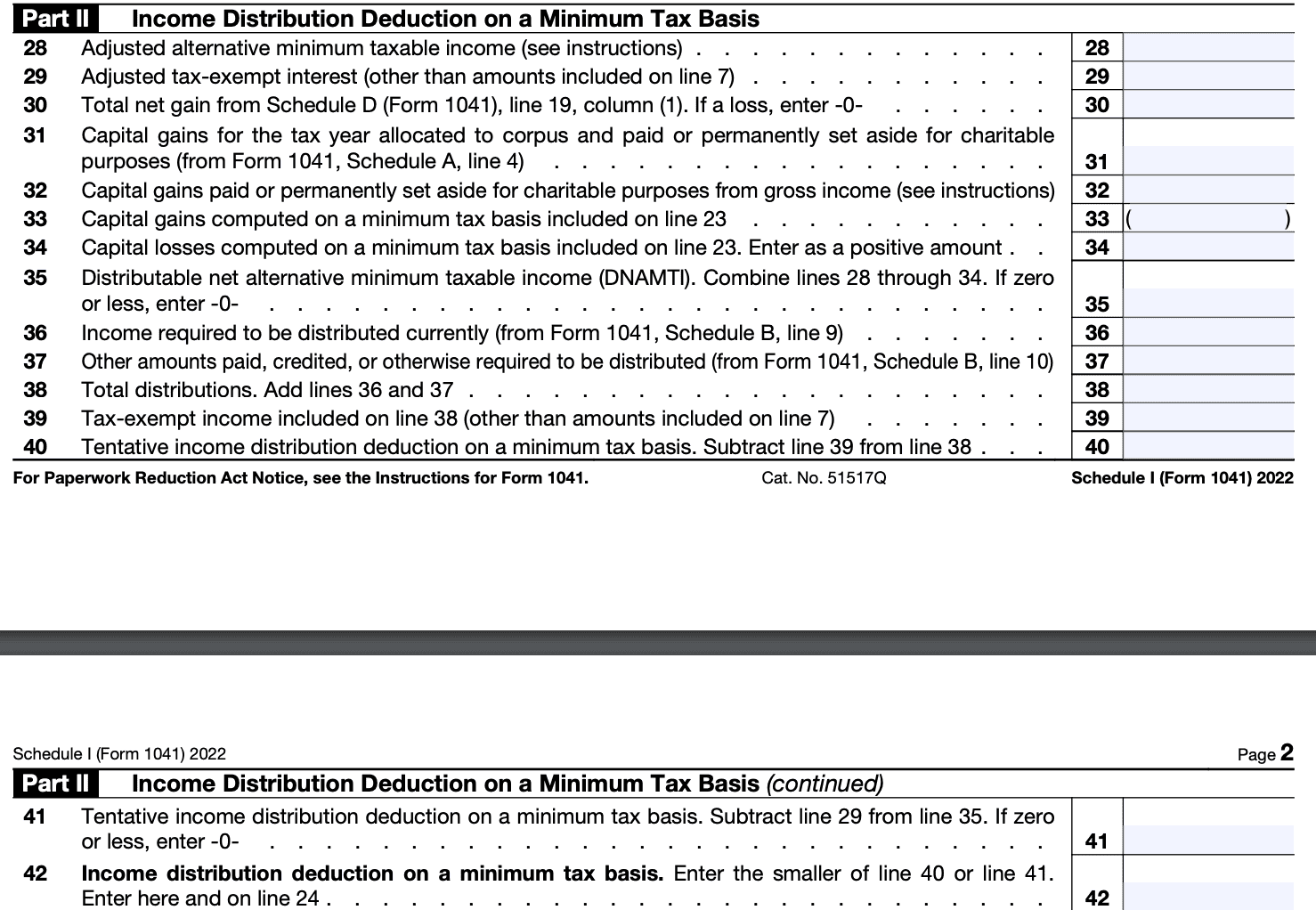
Step 5: Determine tax liability
Consult the tax rate schedules provided in the instructions to determine the applicable tax rate for the estate or trust's taxable income.
Calculate the tax liability by applying the appropriate tax rate to the taxable income.
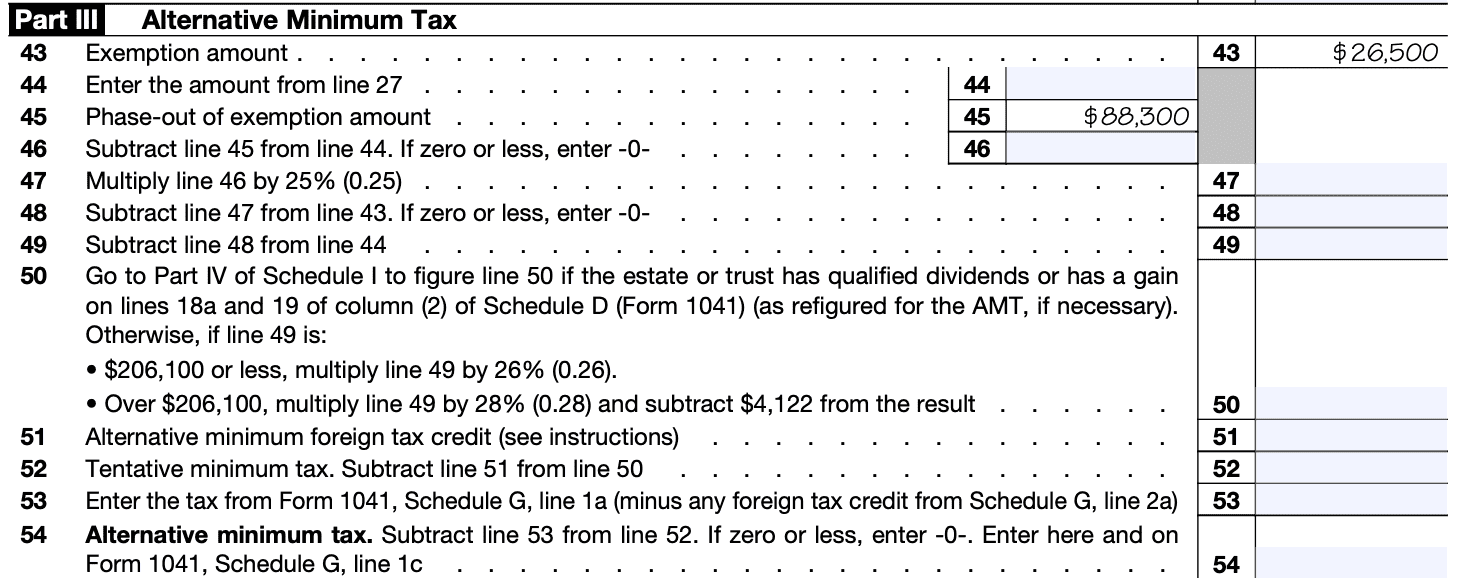
Step 6: Report income, deductions, and tax liability
Transfer the calculated income, deductions, and tax liability amounts to the corresponding sections of Schedule I (Form 1041).
Ensure accurate and complete reporting of all required information.
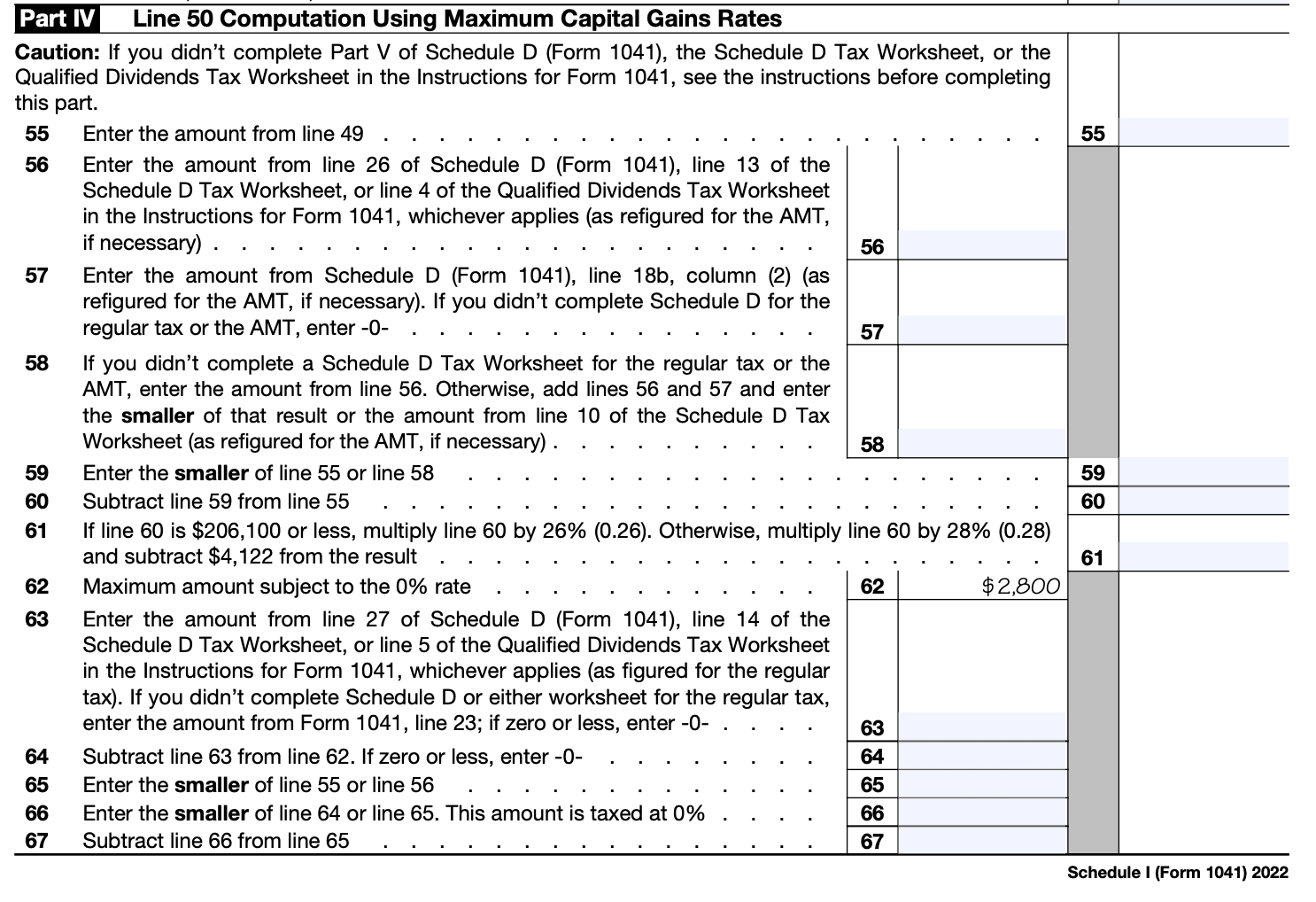
Step 7: Complete additional sections, if applicable
Schedule I may include additional sections for reporting specific types of income or deductions, such as rental real estate, royalties, or capital gains. Complete these sections if they apply to the estate or trust.
Step 8: Attach Schedule I to Form 1041
Once you have completed Schedule I, attach it to Form 1041, U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts.
Step 9: Review and file the forms
- Review the completed forms for accuracy and completeness.
- Sign the forms as required.
- Make copies of all the documents for your records.
- Submit the forms to the IRS by the due date, including any payments due.
Special Considerations When Filing Schedule I (Form 1041)
When filing Schedule I (Form 1041), there are several special considerations that you need to keep in mind. Schedule I is used to report the income distribution deduction and the income tax liability of an estate or trust. Here are some important points to consider:
**Income distribution deduction: **The income distribution deduction represents the amount distributed to beneficiaries of an estate or trust. It is important to accurately calculate this deduction by following the instructions provided by the IRS. The deduction is generally limited to the estate or trust's distributable net income (DNI), but certain deductions may be allowed in excess of DNI in certain situations.
Beneficiary information: When completing Schedule I, you must provide detailed information about each beneficiary, including their name, address, taxpayer identification number (TIN), and the amount distributed to them. Ensure that the information provided is accurate and matches the beneficiary's records.
**Income tax liability: **Schedule I is used to calculate the estate or trust's income tax liability. It is essential to accurately report all sources of income, deductions, and credits to determine the correct tax liability. You may need to attach additional schedules or forms, such as Schedule K-1 (Form 1041), to report specific types of income or deductions.
**Alternative minimum tax (AMT): **Estates and trusts are subject to the alternative minimum tax if their taxable income exceeds certain thresholds. If the estate or trust is subject to AMT, you will need to complete and attach Form 6251, Alternative Minimum Tax—Individuals, to the Form 1041.
Estimated tax payments: If the estate or trust is required to make estimated tax payments, you should report the total estimated payments made during the tax year on Schedule I. Make sure to keep accurate records of these payments to support your filing.
**Filing deadlines: **The filing deadline for Form 1041 is generally the 15th day of the fourth month following the end of the tax year (April 15 for calendar year estates or trusts). However, if you need additional time to file, you can request an extension using Form 7004, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns.
State and local considerations: In addition to federal tax obligations, estates and trusts may also have state and local tax obligations. It's important to be aware of the specific requirements in the jurisdiction where the estate or trust is located and comply with all filing and payment obligations.
How To File Schedule I (Form 1041): Offline/Online/E-filing
To file Schedule I (Form 1041), you have the option to file offline by mail or electronically through online or e-filing methods. Here's an overview of each filing method:
Offline filing (mail)
a. Obtain the necessary forms: Download Form 1041 and Schedule I from the IRS website or request them by mail by calling the IRS at 1-800-TAX-FORM (1-800-829-3676).
b. Fill out the forms: Complete the required information on Form 1041 and Schedule I, ensuring accuracy and legibility. Attach any additional schedules or forms as necessary.
c. Supporting documentation: Gather all supporting documents, such as statements, receipts, and other relevant records that support the information reported on the forms.
d. Sign and date: Sign and date the completed forms where required.
e. Make copies: Make copies of the completed forms and supporting documents for your records.
f. Mail the forms: Send the completed forms and copies of supporting documents to the appropriate IRS address for your area. Make sure to use certified mail or a delivery method that provides proof of mailing.
Online filing
a. Use tax preparation software: Utilize IRS-approved tax preparation software to electronically file Form 1041 and Schedule I. These software programs guide you through the process, perform necessary calculations, and help ensure accuracy.
b. Complete the forms: Enter the required information into the tax software following the prompts and instructions provided. The software will typically populate the necessary fields on Schedule I based on the information entered.
c. Review and verify: Double-check all entered information for accuracy and completeness. Review any automatically generated forms or schedules to ensure they reflect the correct data.
d. Submit electronically: When you are ready, follow the software's instructions to submit the completed forms electronically to the IRS. The software will provide confirmation of successful submission.
E-filing through a tax professional
a. Engage a tax professional: Seek the assistance of a tax professional or accountant experienced in handling estate or trust tax matters.
b. Provide necessary information: Furnish the tax professional with all relevant details and supporting documents required to complete Form 1041 and Schedule I accurately.
c. Tax professional's preparation: The tax professional will prepare the forms based on the provided information and perform necessary calculations.
d. Review and sign: Review the completed forms for accuracy and sign where required.
e. E-filing: The tax professional will electronically file the completed forms on your behalf using their authorized e-filing methods.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Filing Schedule I (Form 1041)
When filing Schedule I (Form 1041), it's important to be aware of common mistakes to avoid. Here are some errors to watch out for when completing Schedule I:
Incorrect reporting of income and deductions: Ensure that all income earned by the estate or trust is reported accurately, including interest, dividends, capital gains, rental income, and any other sources. Likewise, make sure to deduct eligible expenses and deductions correctly.
**Failure to report all beneficiaries: **Schedule I requires the reporting of all beneficiaries who received income or distributions from the estate or trust during the tax year. Make sure to list all beneficiaries accurately, along with their respective shares of income.
**Misclassification of income: **It's essential to correctly categorize income based on its nature, such as ordinary income, capital gains, or tax-exempt income. Misclassifying income may result in incorrect tax calculations.
Incorrect allocation of expenses and deductions: If the estate or trust has expenses or deductions that are attributable to specific beneficiaries, ensure that they are allocated correctly. Improper allocation can lead to inaccuracies in tax liability for both the estate or trust and the beneficiaries.
Inaccurate calculation of taxable income: Carefully calculate the taxable income for the estate or trust, taking into account applicable deductions, exemptions, and credits. Incorrect calculations may lead to errors in tax liability.
Failing to report estimated tax payments: If the estate or trust made estimated tax payments throughout the year, ensure they are properly reported on Schedule I. Neglecting to report these payments can result in underpayment penalties.
**Late or incorrect filing: **Make sure to file Schedule I and Form 1041 by the due date, which is typically April 15th. Late filing can lead to penalties and interest charges. Additionally, review your forms thoroughly to avoid any errors or omissions.
**Ignoring changes in tax laws: **Stay updated with current tax laws and regulations, as they can change from year to year. Failing to consider updated tax provisions may result in errors when filing Schedule I.
Conclusion
Navigating the tax requirements for estates can be complex, and the Alternative Minimum Tax adds an additional layer of complexity. Schedule I (Form 1041) plays a crucial role in calculating the AMT liability for estates, ensuring that they pay a minimum amount of tax regardless of regular tax rules.
Understanding the various components of Schedule I and the Alternative Minimum Tax helps estates comply with their tax obligations accurately. As always, it's advisable to consult with a tax professional or an estate planning attorney to ensure proper compliance with tax laws and to optimize tax planning strategies.


