- IRS forms
- I-9 Tax Form
I-9 Tax Form: Employment Eligibility Verification
Download I-9 Tax FormIn the realm of hiring and employment, ensuring legal compliance and verifying the eligibility of employees is of paramount importance. The I-9 Tax Form, also known as the Employment Eligibility Verification form, is a critical document used by employers in the United States to establish the eligibility of their employees to work in the country.
In this blog post, we will dive into the details of the I-9 form, its purpose, and the obligations it places on employers. By understanding the significance and requirements of the I-9 form, employers can ensure compliance and mitigate potential legal risks.
Purpose of I-9 Tax Form
When a person is hired, both the employee and employer must complete the I-9 form. The employee is required to provide certain documents that establish their identity and employment eligibility, such as a passport, driver's license, or Social Security card. The employer must examine the documents and determine whether they reasonably appear to be genuine and relate to the employee presenting them.
By completing the I-9 form, employers are fulfilling their responsibility to verify the eligibility of their employees to work in the United States. This helps to prevent the hiring of unauthorized workers and ensures compliance with federal immigration laws. The information provided on the I-9 form is also used to maintain records of employment eligibility verification.
It is important for employers to properly complete and retain the I-9 forms for each employee as failure to comply with these requirements can result in penalties, including fines and potential legal consequences. The form must be kept on file for a specific period of time, and employers may be subject to audits by the USCIS to verify compliance with employment eligibility verification regulations.
Who Must Complete the I-9 Tax Form?
I-9 is a must to verify identity and employment authorization of individuals hired for employment. Both employees and employers have responsibilities related to the completion of the I-9 form.
Employees: All employees hired in the United States must complete Section 1 of the I-9 form. This includes U.S. citizens, non-citizen nationals, lawful permanent residents (green card holders), and certain nonimmigrants authorized to work in the U.S.
Employers: Employers are responsible for completing Section 2 of the I-9 form. This section involves reviewing the employee's documents to verify their identity and employment authorization. Employers must examine the original documents in the presence of the employee and attest to their authenticity.
It's important to note that not all individuals are required to complete the I-9 form. Independent contractors and volunteers who are not considered employees for immigration and tax purposes typically do not need to complete the form. However, employers must be careful in correctly classifying individuals to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Understanding the Sections of the I-9 Form
The form is administered by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). The I-9 form consists of three sections, each with its own purpose and requirements. Let's go through them.
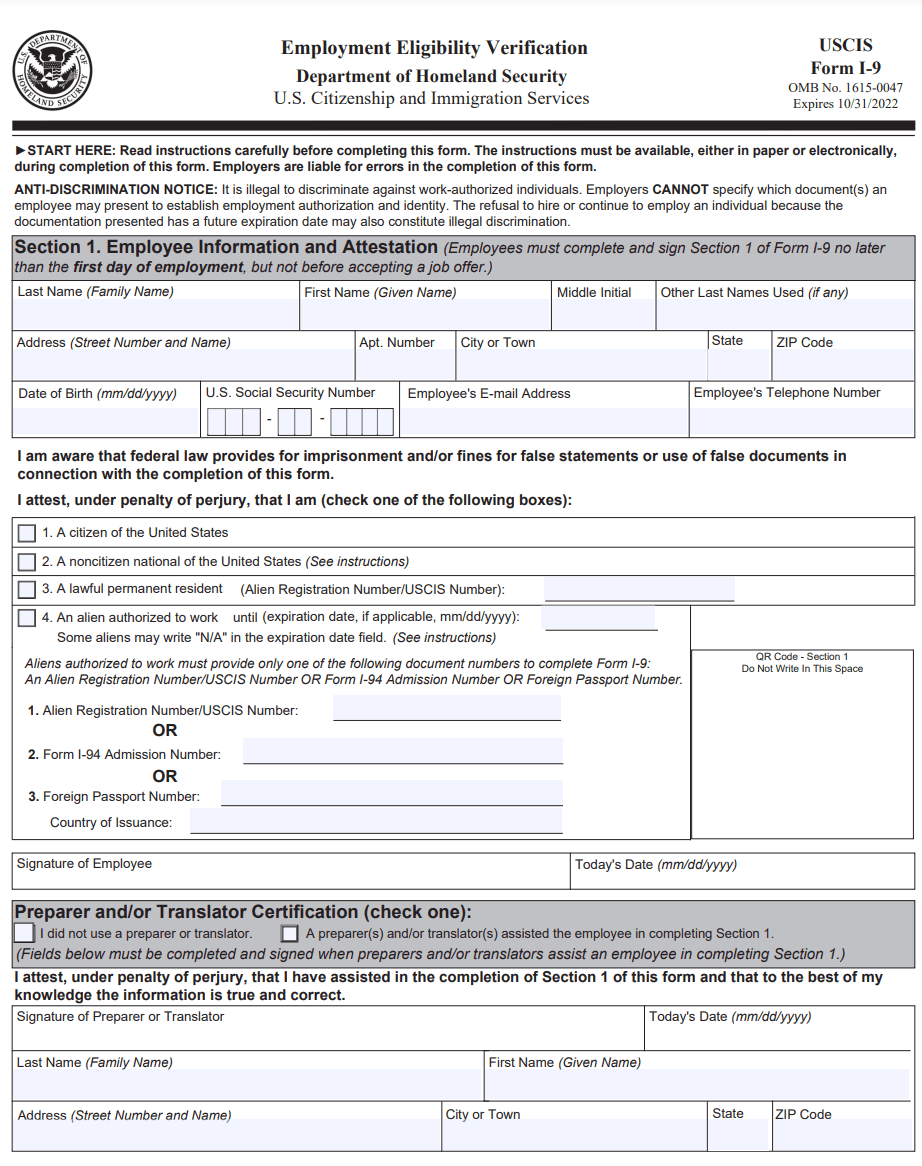
Section 1: Employee information and attestation
In this section, the employee is required to complete personal information and attest to their employment eligibility status. The employee must provide their full name, address, date of birth, Social Security number (optional unless the employer participates in E-Verify), and immigration status (if applicable).
The employee must also indicate their citizenship or immigration status and, if necessary, provide additional information such as Alien Registration Number/USCIS Number, Form I-94 admission number, or foreign passport number and country of issuance. The employee must sign and date this section.
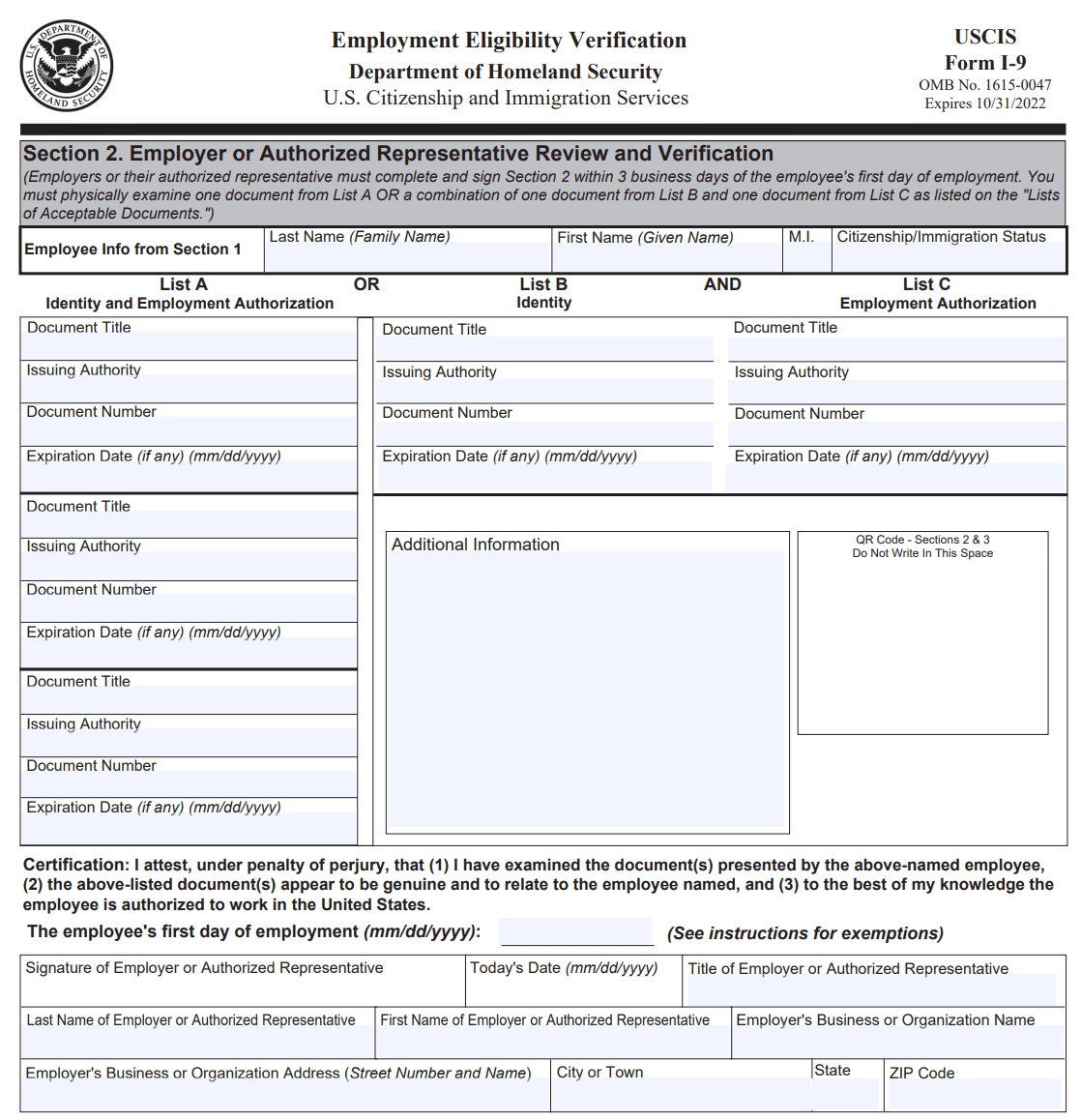
Section 2: Employer or authorized representative review and verification
In Section 2, the employer or an authorized representative of the employer reviews the employee's documentation to verify their identity and work eligibility. The employer must examine original documents from the Lists of Acceptable Documents provided by the USCIS.
These documents may include a U.S. passport, permanent resident card, Employment Authorization Document, or a combination of other acceptable documents. The employer must record the document title, issuing authority, document number, and expiration date (if applicable) on the form. The employer or representative must also sign and date this section, indicating that they have reviewed the documents and they appear to be genuine and relate to the employee.
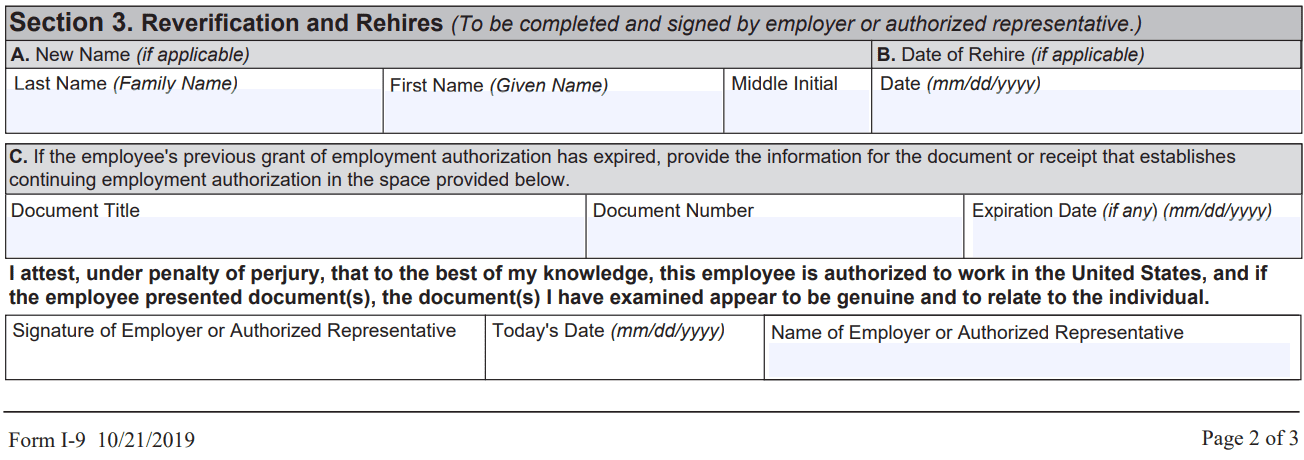
Section 3: Reverification and rehires (if applicable)
Section 3 is used in certain situations, such as when an employee's work authorization has expired, when an employee is rehired within three years of the date the original I-9 was completed, or when an employee's name has changed. The employer must complete this section by examining the new or updated documents provided by the employee, recording the information in the appropriate fields, and signing and dating the form.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing the I-9 Form
When filing the I-9 form, which is used to verify the identity and employment eligibility of individuals hired for employment in the United States, it's important to be aware of common mistakes to avoid. Here are some common errors to watch out for when completing the I-9 form:
Failure to complete all sections: Make sure to fill out all sections of the I-9 form accurately and completely. Leaving any section blank or incomplete can result in errors and potential penalties.
Using an outdated version of the form: USCIS occasionally updates the I-9 form, so it's crucial to use the current version. Check the USCIS website (uscis.gov) to ensure you have the most recent version available.
Incorrect or missing information: Ensure that all information provided on the form is accurate and matches the supporting documents. Mistakes such as misspelled names, incorrect dates of birth, or mismatched identification numbers can lead to discrepancies and complications.
Late completion of the form: The I-9 form must be completed within three business days of the employee's hire date. Failing to complete it within the designated time frame can result in penalties for non-compliance.
Accepting invalid or insufficient documents: It is crucial to review the list of acceptable documents provided on the I-9 form and ensure that the employee presents valid and unexpired documents to establish their identity and work authorization. Accepting invalid or insufficient documents can lead to compliance issues.
Failure to re-verify work authorization: For employees with temporary work authorization, such as those with limited-term employment authorization documents or certain nonimmigrant statuses, it's essential to monitor their expiration dates and reverify their work authorization before it expires.
Inadequate recordkeeping: Employers are required to retain completed I-9 forms for a specific period. Failing to maintain proper records or losing track of the forms can lead to compliance issues during audits.
Discrimination during the verification process: It's important to treat all employees fairly and consistently during the I-9 verification process. Avoid singling out specific individuals based on their appearance, ethnicity, or citizenship status. All individuals hired for employment in the United States must complete the I-9 form, regardless of their immigration status.
To ensure compliance and minimize errors, consider familiarizing yourself with the USCIS Handbook for Employers (Form M-274), which provides detailed guidance on completing the I-9 form correctly. Additionally, seeking legal advice or consulting with a human resources professional can be beneficial for understanding the specific requirements and best practices for your organization.
Retention and Storage of I-9 Forms
The retention and storage of I-9 forms, which are used for verifying the identity and employment authorization of individuals hired for employment in the United States, are subject to specific guidelines set forth by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
Here are some key points regarding the retention and storage of I-9 forms:
Retention period
Employers must retain a completed Form I-9 for each employee for a specific period. As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, the retention period for I-9 forms is as follows:
- **For employees who are still working for the employer: **The I-9 forms should be retained until the individual's employment is terminated. Once the employment ends, the retention period is either three years from the date of hire or one year from the date of termination, whichever is later.
- For former employees: If an individual's employment is terminated within three years of the date of hire, the I-9 form must be retained for one year from the date of termination or three years from the date of hire, whichever is later.
Storage format
Employers have the flexibility to store I-9 forms in either paper or electronic format. However, whichever format is chosen, the employer must ensure that the storage system provides reasonable controls to prevent unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction of the forms.
Accessibility: Employers must make the stored I-9 forms available for inspection upon request by authorized government agencies such as the USCIS, the Immigrant and Employee Rights Section (IER) of the Department of Justice, and the Department of Labor. These agencies may conduct audits and investigations to ensure compliance with employment eligibility verification laws.
Proper destruction: When the retention period for an I-9 form expires, employers must properly destroy and dispose of the forms to protect sensitive personal information. The destruction process should ensure that the information cannot be reconstructed or accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Electronic I-9 Systems
Electronic I-9 systems, also known as electronic employment eligibility verification systems, are digital tools designed to assist employers in verifying the identity and employment eligibility of their employees in the United States.
The I-9 form, issued by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), is used to document an individual's eligibility to work in the country. Traditional paper-based I-9 processes can be time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to manage, leading many employers to adopt electronic systems for greater efficiency and compliance.
Electronic I-9 systems streamline the process of verifying an employee's identity and work authorization by digitizing the documentation and storage procedures. These systems typically include features such as automatic form validation, real-time error checking, and integrated data validation with government databases. This helps ensure that the information provided by employees is accurate and complete, minimizing the risk of errors or fraudulent documents.
Deadlines & Due Dates for I-9 Tax Form
While there is no specific due date for submitting the I-9 form to the government, employers must be prepared to present the forms for inspection upon request by authorized government agencies, such as the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, the U.S. Department of Labor, or the U.S. Department of Justice.
Here are the important deadlines and timeframes related to the I-9 form:
Completing the form: The employee must complete Section 1 of the I-9 form no later than the first day of employment.
Verifying documents: The employer must review the employee's original identity and employment authorization documents and complete Section 2 of the I-9 form within three business days of the employee's start date.
Retaining the form: Employers must retain the completed I-9 forms for each employee for a specific period. The general rule is to keep the forms for either three years after the date of hire or one year after the date of employment ends, whichever is later. However, it's important to note that different rules apply to certain situations, such as when an employee is rehired within three years of their initial start date.
Audits and Penalties
Audits and penalties can be imposed on employers who fail to comply with the requirements of Form I-9. Here's an overview of audits and penalties related to Form I-9:
Audits
The U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), which is a part of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), is responsible for conducting audits of employers' Form I-9 records. These audits are typically referred to as I-9 audits or worksite enforcement investigations. The purpose of an audit is to ensure that employers have properly completed and maintained Form I-9 for their employees.
During an audit, ICE may request to review an employer's Form I-9 records, including the forms and any supporting documentation. They may also conduct on-site inspections to verify the authenticity of the documents provided by the employees. The audit process involves a review of the forms for technical and substantive errors, and the identification of potential unauthorized workers.
Penalties
If an employer is found to have violated the Form I-9 requirements, they may face civil and/or criminal penalties. The penalties can vary depending on the severity and frequency of the violations. The following are the potential penalties:
a. Civil penalties: Civil penalties may be imposed for various violations related to Form I-9, including failure to produce a Form I-9, failure to properly complete sections of the form, or engaging in document abuse or discrimination. As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, the civil penalties for Form I-9 violations were as follows:
- Minimum penalty per violation: $234
- Maximum penalty per violation: $2,332
- Repeat offender maximum penalty: $11,676
b. Criminal penalties: In cases of knowingly hiring or continuing to employ unauthorized workers, employers may face criminal penalties. These penalties can include fines and, in some cases, imprisonment. The severity of the penalties depends on the circumstances of the violation.
Conclusion
The I-9 Tax Form serves as a crucial tool for employers to verify the eligibility of their employees to work in the United States.
Compliance with the I-9 requirements is vital to avoid legal complications and penalties.
By understanding the purpose, sections, and common mistakes associated with the I-9 form, employers can take proactive steps to ensure accurate completion and retention of these forms.
Embracing electronic I-9 systems can further enhance efficiency and compliance. As employment eligibility verification remains a critical aspect of hiring, employers should stay up to date with the latest guidelines and regulations provided by USCIS.
Prioritizing the accurate completion and retention of I-9 forms will help create a workforce that is both legally compliant and authorized to work in the United States.


