- IRS forms
- Form W-8BEN-E
Form W-8BEN-E: Certificate of Status of Beneficial Owner for United States Tax Withholding and Reporting (Entities)
Download Form W-8BEN-EFor entities engaging in business or investments in the United States, understanding and complying with the tax regulations is crucial. One important document in this context is Form W-8BEN-E, which is used by foreign entities to establish their status as beneficial owners and claim beneficial tax treaty rates, exemptions, or reductions on income subject to U.S. withholding tax.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Form W-8BEN-E, providing a detailed overview, discussing its purpose, instructions, and implications for entities seeking to navigate the U.S. tax landscape.
Understanding Form W-8BEN-E
Overview of Form W-8BEN-E
To determine the status of foreign entities for U.S. tax withholding and reporting, the IRS requires Form W-8BEN-E, Certificate of Status of Beneficial Owner for United States Tax Withholding and Reporting (Entities). It serves as a declaration of the entity's eligibility for treaty benefits or exemptions from withholding tax under the Internal Revenue Code.
The form is typically used by foreign entities such as corporations, partnerships, and other entities that earn income from U.S. sources. It allows these entities to claim reduced or exempted tax rates as per applicable tax treaties between the United States and their home countries.
Purpose of Form W-8BEN-E
The primary purpose of Form W-8BEN-E is to collect essential information from foreign entities to determine their eligibility for preferential tax treaty rates, exemptions, or reductions. By submitting this form, entities certify their beneficial ownership status and claim the benefits provided by relevant tax treaties.
Form W-8BEN-E enables the IRS to identify the foreign entity, ascertain its eligibility for treaty benefits, and establish the appropriate withholding tax rate. It also aids in ensuring compliance with tax regulations and reporting requirements, thereby facilitating accurate tax withholding and reporting on income derived from U.S. sources.
Filling out Form W-8BEN-E
General instructions
To complete Form W-8BEN-E accurately, it is essential to carefully follow the instructions provided by the IRS. The form consists of four parts, each requiring specific information. Following are some general instructions to consider when filling out the form:
a) Use the most recent version of Form W-8BEN-E available on the IRS website, and ensure it is properly downloaded and printed.
b) Complete the form using black ink and print legibly to avoid misinterpretation of the information provided.
c) Provide accurate and up-to-date information, including legal names, addresses, and taxpayer identification numbers (TINs), to avoid delays or errors in processing.
d) If certain sections of the form do not apply, mark them as "N/A" to indicate non-applicability.
e) When providing an address, use the official postal system format of the foreign country, including the country name in uppercase letters.
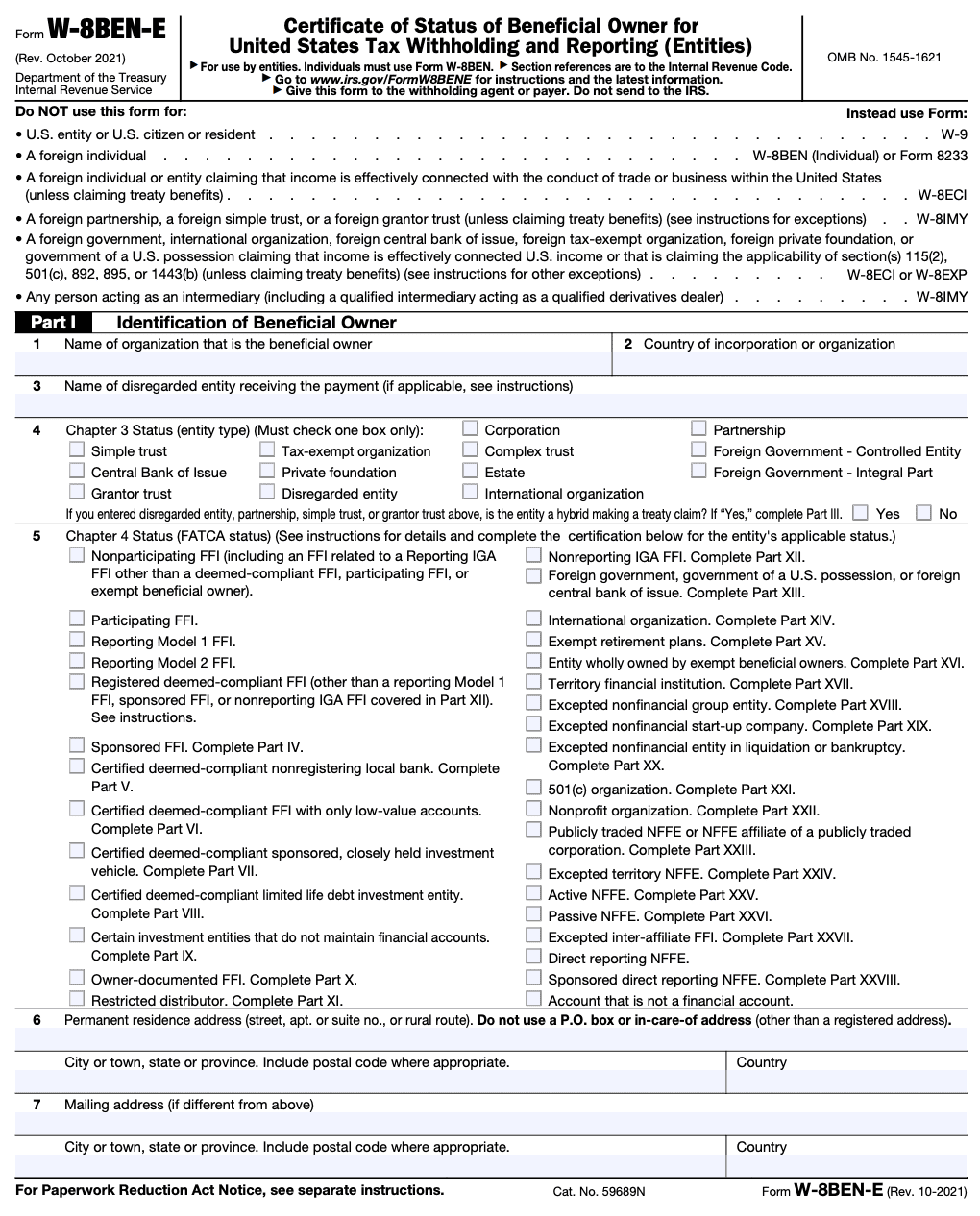
Part I: Identification of beneficial owner
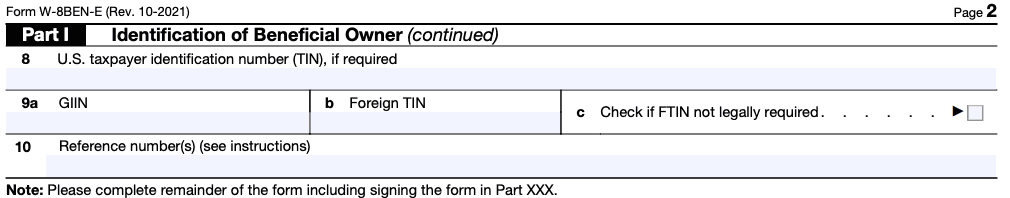
Part I of Form W-8BEN-E focuses on gathering information about the beneficial owner of the income. This section requires the entity to provide details such as its name, country of organization, legal entity type, and permanent residence address.
The form also requests the entity's taxpayer identification number (TIN) issued by the country of residence. If the entity is not issued a TIN, it should provide the reason for non-issuance and any applicable reference numbers or certifications.
Additionally, Part I seeks information regarding the entity's controlling persons, which includes individuals who exercise control over the entity or have a significant interest in it. This information assists the IRS in determining the entity's ultimate beneficial ownership.
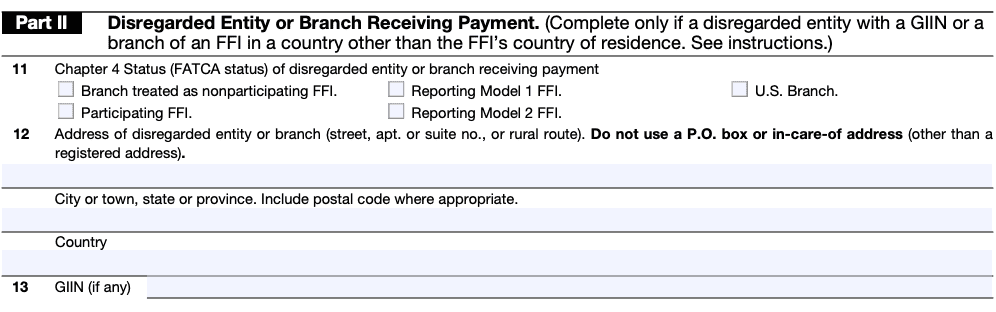
Part II: Disregarded entity or branch receiving payment
Part II of Form W-8BEN-E is relevant only for disregarded entities and branches receiving payments. Disregarded entities are single-member entities for U.S. tax purposes, while branches refer to parts of foreign entities that operate in the United States.
This section requires the disregarded entity or branch to provide details such as its name, EIN (Employer Identification Number) if applicable, and address. It also includes a checkbox to indicate whether the disregarded entity is owned by an entity that is not a foreign person.
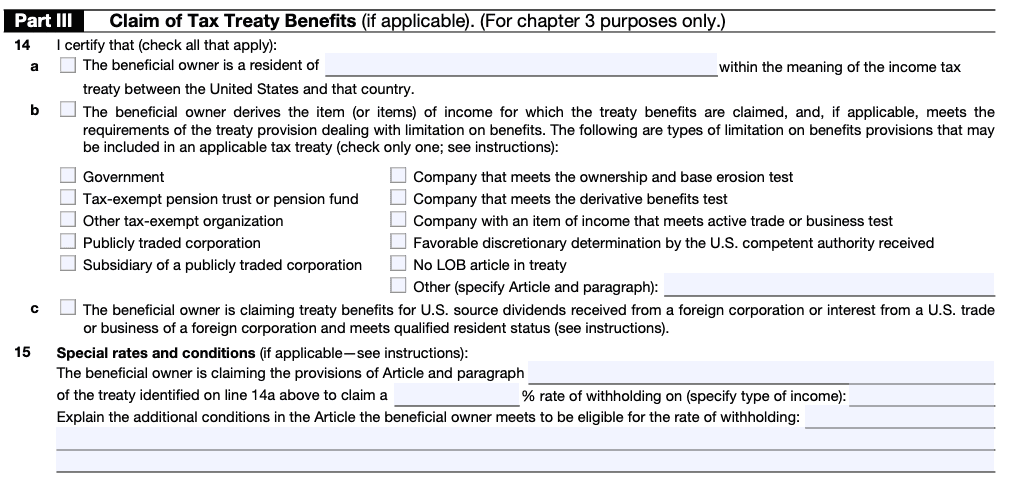
Part III: Claim of tax treaty benefits
Part III of Form W-8BEN-E is crucial for entities seeking to claim tax treaty benefits. This section requires the entity to specify the tax treaty article and country that allows for the benefits claimed. The entity must also provide details of any limitations or special conditions associated with the tax treaty benefits.
It is essential to consult the relevant tax treaty between the entity's country of residence and the United States to accurately determine the eligible benefits and ensure compliance with the treaty's provisions.
Part IV: Certification
Part IV serves as a certification by the entity that the information provided on the form is accurate and that the entity is the beneficial owner of the income for which the form is submitted. By signing the certification, the entity acknowledges its responsibility to notify the withholding agent if any information provided on the form changes in the future.
Additionally, the certification declares that the entity is not a U.S. person and that it has provided a correct TIN (if applicable) or a valid reason for not providing one.

Supporting documentation
Depending on the circumstances, you may need to attach additional documentation to support your claim, such as a tax residency certificate or other required forms.
Remember to review the instructions provided with Form W-8BEN-E for detailed guidance and any additional requirements that may apply to your specific situation. It is also recommended to consult with a tax professional or advisor to ensure accurate completion of the form.
Implications and Considerations
Tax treaty benefits
By completing Form W-8BEN-E and claiming tax treaty benefits, foreign entities can potentially reduce or eliminate the amount of U.S. withholding tax imposed on their income from U.S. sources. Tax treaties often establish lower withholding rates on specific types of income, such as dividends, interest, and royalties.
However, to claim tax treaty benefits, entities must meet the eligibility criteria outlined in the applicable tax treaty and provide accurate information on Form W-8BEN-E. It is crucial to review the specific provisions of the relevant tax treaty and consult with tax advisors to ensure compliance and maximize the benefits available.
Reporting requirements
While Form W-8BEN-E helps establish eligibility for reduced withholding rates, it does not eliminate reporting obligations. Foreign entities that receive U.S. income and claim tax treaty benefits are generally required to file annual tax returns with the IRS.
The reporting requirements may vary depending on the nature of the income and the tax treaty provisions. It is crucial for entities to understand their reporting obligations, maintain proper documentation, and comply with any additional filing requirements imposed by the IRS or their home country.
Validity and renewal
Unless a change in circumstances makes the information on the form erroneous, Form W-8BEN-E is typically valid from the date it is signed until the last day of the third subsequent calendar year.
Entities should review and renew their Form W-8BEN-E within 30 days of any change in circumstances that affects their eligibility for treaty benefits or the accuracy of the information previously provided. Failure to update or renew the form may result in the withholding agent treating the entity as a nonresident alien subject to higher withholding tax rates.
Deadlines & Due Dates for Submitting Form W-8BEN
For submitting Form W-8BEN-The deadlines for submitting Form W-8BEN-E can vary depending on the circumstances. Here are a few scenarios:
- Initial submission: Foreign entities that are subject to withholding and are not yet documented typically submit Form W-8BEN-E to the withholding agent before the first payment subject to withholding.
- Expiration: The validity of Form W-8BEN-E generally expires after three years. The entity must provide an updated form to the withholding agent before the expiration date to continue claiming the reduced or exempt withholding rates.
- Change in circumstances: If there is a change in circumstances that makes any information on the previously submitted form incorrect, the entity must provide an updated form within 30 days of the change.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls
Inaccurate or incomplete information
One common mistake made when completing Form W-8BEN-E is providing inaccurate or incomplete information. It is crucial to ensure that all the required fields are filled out correctly and that the information provided aligns with official records and supporting documentation.
Inaccurate or incomplete information can lead to delays in processing, rejection of the form, or imposition of higher withholding tax rates. To avoid these issues, entities should carefully review the instructions and seek professional advice when necessary.
Failure to update or renew
Entities must promptly update their Form W-8BEN-E in the event of any changes that affect their eligibility or the accuracy of the information provided. Failure to update the form within the required timeframe can result in adverse consequences, including the withholding agent applying a higher withholding tax rate or rejecting the claim for tax treaty benefits.
Entities should establish internal processes to monitor changes in circumstances and implement procedures to ensure timely updates or renewal of Form W-8BEN-E.
Best Practices for Collecting W-8BEN-E Forms
Managing the flow of incoming and departing international payments plays a significant part in contemporary accounts payable. Making sure all of those foreign entities have the necessary tax documentation and IRS filings on file is another crucial duty.
As the payer and withholding agent, a U.S. person or business has the onus of accuracy. Any international commerce handled must be closely supervised by AP to prevent confusion and any legal dangers.
The collecting of these crucial documents can be streamlined in the following methods, which will ensure that all foreign organizations are covered:
- The potential of legal issues is increased and accuracy can suffer with manual collecting.
- The W-8BEN-E is a complicated document with numerous sections, so a business should use online quizzes and other technological tools to make sure that payees accurately complete all forms.
- Use automated technologies to check all tax forms and data.
- Use software that automatically keeps track of any new rules, legislation, or limits as well as the most recent updates to tax laws.
Automating the W-8BEN-E Process
Any AP process that is automated today reaps significant benefits. Financial technology guarantees that tax-related papers won't be rejected during an audit in addition to increasing speed and accuracy.
Several manual W8 form gathering processes would be improved by automation, including:
- Conducting due diligence on each supplier to establish the correct W8 information,
- Accurately gathering all necessary data without requiring manual entry,
- Determining the precise withholding obligations based on the entity status, and
- Making sure all W8 forms are completed completely and accurately.
Benefits of W-8BEN-E automation
Everything here has the potential to turn into an AP nightmare with just a little carelessness. The following advantages are possible with an automated solution for workers who are time-constrained:
- Use cloud-based communications to improve visibility and streamline workflow while dealing with vendors. Better supplier connections and the potential for early payment reductions result from this.
- Reduce the amount of time and resources wasted so that they can be put to better use.
- Make sure that each W-8BEN-E form is correctly completed to eliminate any concerns about audit risk or IRS penalties.
- Prevent vendor payment delays brought on by incorrect W8 forms.
- When making payments, automatically deduct the 30% tax rate to avoid the need for incorrect withholdings, erroneous corrections, or last-minute adjustments.
Conclusion
Complying with U.S. tax regulations is essential for foreign entities conducting business or investments in the United States. Form W-8BEN-E serves as a crucial document for establishing beneficial ownership status and claiming tax treaty benefits, exemptions, or reductions on income subject to U.S. withholding tax.
By understanding the purpose, instructions, and implications of Form W-8BEN-E, entities can navigate the U.S. tax landscape more effectively, ensure compliance, and optimize their tax position. Consulting with tax professionals and staying informed about changes in tax regulations and treaty provisions are essential to maximize the benefits and avoid potential pitfalls associated with Form W-8BEN-E.


