- IRS forms
- Form W-4R
Form W-4R: Withholding Certificate for Non-Periodic Payments and Eligible Rollover Distributions
Download Form W-4RForm W-4R, also known as the withholding certificate for non-periodic payments and eligible rollover
distributions, is an essential document used by individuals to determine the amount of federal income tax to be withheld from certain nonperiodic payments and eligible rollover distributions. This form is specifically designed for taxpayers who receive distributions from retirement plans, annuities, or other similar sources.
In this post, we will delve into the details of Form W-4R, exploring its purpose, when it is required, how to fill it out correctly, and other important considerations. Understanding this form is crucial for ensuring accurate tax withholding and avoiding any potential penalties or surprises when it comes to your tax obligations.
Overview of Form W-4R
Form W-4R is a document issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. It allows recipients of nonperiodic payments and eligible rollover distributions to specify the amount of federal income tax they want to have withheld from these distributions. Nonperiodic payments refer to one-time or occasional distributions from sources such as retirement plans or annuities.
The primary purpose of Form W-4R is to provide individuals with greater control over their tax withholding. By filling out this form, taxpayers can ensure that an appropriate amount of federal income tax is withheld from their nonperiodic payments, helping them avoid any underpayment issues when they file their tax returns.
It is important to note that Form W-4R is distinct from Form W-4, which is commonly used by employees to adjust withholding from their regular paychecks. Form W-4R specifically addresses the withholding requirements for nonperiodic payments and eligible rollover distributions.
When Is Form W-4R Required?
Form W-4R is typically required when a taxpayer receives a nonperiodic payment or an eligible rollover distribution. Here are some common situations where this form may be necessary:
Retirement plan distributions
When individuals receive distributions from their retirement plans, such as a 401(k) plan, they may need to complete Form W-4R. This form helps determine the appropriate amount of federal income tax to be withheld from the distribution.
Annuity payments
If you receive annuity payments, whether from a private annuity or an employer-sponsored pension plan, you may need to submit Form W-4R to indicate the desired amount of federal income tax withholding.
Individual retirement account (IRA) distributions
When individuals take distributions from their traditional IRAs, they may be required to complete Form W-4R to specify the federal income tax withholding amount.
Other non-periodic payments
Form W-4R may also be necessary for other nonperiodic payments that do not fall into the retirement plan or annuity categories. Examples include distributions from nonqualified deferred compensation plans or distributions from life insurance contracts.
It's important to consult the specific instructions provided by the IRS or seek professional advice to determine whether Form W-4R is required in your particular situation.
Completing Form W-4R
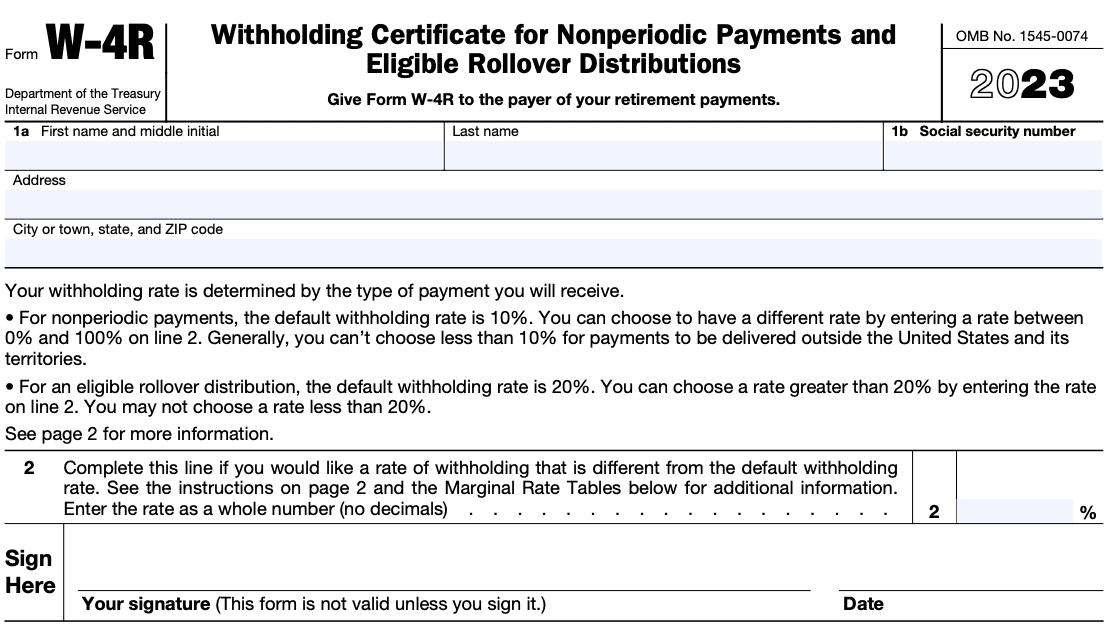
To correctly complete Form W-4R, follow these step-by-step instructions:
- **Personal information: **Begin by entering your full name, Social Security number, and address in the designated sections. Ensure that the information is accurate and matches your records with the IRS.
- **Filing status: **Check the appropriate box to indicate your filing status (e.g., single, married filing jointly, head of household, etc.). Your filing status determines the applicable tax rates and standard deduction amount.
- **Multiple jobs or employed spouse: **If you have multiple jobs or your spouse works, refer to the two-earners/multiple jobs worksheet provided with Form W-4R instructions to adjust your withholding accurately. This step accounts for potential under-withholding due to multiple income sources.
- **Claiming dependents: **If you have dependents and are eligible to claim them for tax purposes, indicate the total number of allowances you are claiming. Each allowance reduces the amount of federal income tax withheld.
- **Additional withholding: **If you anticipate owing more taxes than what will be withheld based on your filing status and allowances, you can specify an additional amount to be withheld from each payment. This helps avoid underpayment penalties and ensures closer adherence to your estimated tax liability.
- **Signed and dated form: **After completing the necessary sections, sign and date the form. Unsigned or undated forms may be considered invalid.
Telephonic Submissions of Form W-4R
Stakeholders have questioned whether telephone submissions of Form W-4R are acceptable because it is a new form. Payers may allow Form W-4R submissions by phone. Depending on the circumstances of the payee, the IRS anticipates advising that one of the following three scripts be used for telephonic submissions of Form W-4R.
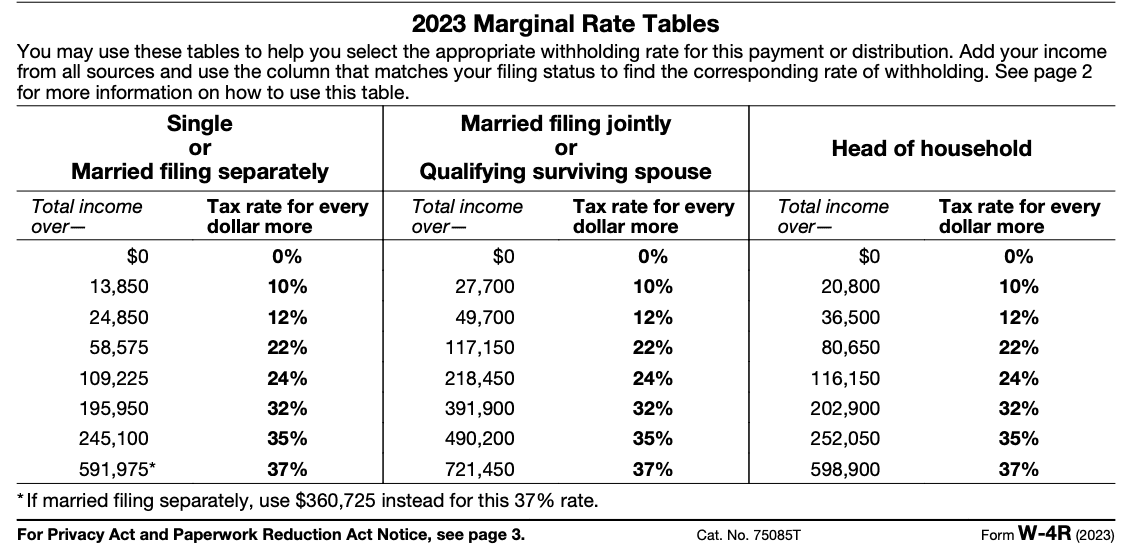
Form W-4R Marginal Rate Tables
According to 2022 Publication 15-A, electronic forms that replace Form W-4R must exactly match the Marginal Rate Tables (together with any pertinent material that appears above and within the tables) as they do on the paper Form W-4R. Some payers have inquired as to whether electronic alternatives to the Form W-4R can connect to a new website that contains the Marginal Rate Tables rather than giving the tables themselves.
A link to a web page containing the Marginal Rate Tables, along with all pertinent text on the first page of the W-4R beginning with the text "2022 Marginal Rate Tables," as well as the applicable specific instructions beginning with "Suggestion for determining withholding," may be provided as an electronic substitute for the Form W-4R. This can be done in place of providing the tables themselves.
Important Considerations and Tips
When dealing with Form W-4R, consider the following factors:
Changes in personal circumstances
Review your withholding status annually or whenever there are significant changes in your personal or financial circumstances. Life events such as marriage, divorce, birth, or adoption of a child may necessitate adjustments to your withholding.
Consult a tax professional
If you are unsure about how to complete Form W-4R or the appropriate withholding amount, consider consulting a tax professional. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation and help ensure accurate compliance with tax laws.
State income tax withholding
Remember that Form W-4R only addresses federal income tax withholding. Some states may require separate withholding forms for state income taxes. Check your state's requirements to ensure compliance.
Regular review of withholding amounts
Periodically review your withholding amounts to ensure they align with your tax obligations. Over- or under withholding can result in unexpected tax liabilities or unnecessarily large refunds. Adjust your withholding as needed to achieve a balanced outcome.
Key Highlights
Form W-4R plays a critical role in determining the federal income tax withholding for nonperiodic payments and eligible rollover distributions. By accurately completing this form, individuals can avoid underpayment issues and ensure that the appropriate amount of tax is withheld from their distributions.
Understanding the purpose of Form W-4R and its requirements is essential for effectively managing your tax obligations and avoiding any surprises when it comes time to file your tax return. If you have any questions or concerns about Form W-4R, consult the IRS resources or seek professional tax advice.
By staying informed and proactive, you can navigate the complexities of tax withholding and maintain compliance with the relevant regulations.


