- IRS forms
- Form 8937
Form 8937: Report of Organizational Actions Affecting Basis of Securities
Download Form 8937When it comes to navigating the complexities of the financial world, taxpayers and investors often encounter various forms and reports. One such form that plays a crucial role in determining the tax implications of organizational actions is Form 8937.
Form 8937, also known as the "Report of Organizational Actions Affecting Basis of Securities," is a document filed with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). The purpose of this form is to report any corporate actions that affect the basis of securities held by shareholders or investors.
In this blog post, we will delve into the details of Form 8937 and explore its significance in reporting the basis of securities affected by organizational actions.
Purpose of Form 8937
The purpose of Form 8937 is to provide information to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and to holders of specified securities about the actions taken by the issuer that may result in an adjustment to the tax basis of those securities.
Organizational actions that may trigger the requirement to file Form 8937 include mergers, acquisitions, stock splits, stock dividends, and certain other changes that affect the basis of the securities. When these actions occur, the issuer must file Form 8937 to report the details of the action, including the date of the action, the description of the securities involved, and the impact on the tax basis of the securities.
The purpose of this form is to ensure that both the IRS and the holders of the specified securities have accurate information about the organizational actions and any resulting changes to the basis of the securities. This information is essential for the accurate calculation of capital gains or losses when the securities are sold or otherwise disposed of by the holders.
Benefits of Form 8937
While the primary purpose of Form 8937 is to provide information to investors for tax reporting purposes, there are several benefits associated with filing this form:
-
Compliance: Filing Form 8937 ensures compliance with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) regulations. By accurately reporting the organizational actions that affect the basis of securities, the company or issuer demonstrates its adherence to tax laws and requirements.
-
Transparency: Form 8937 provides transparency to investors by disclosing the details of organizational actions that may impact their tax obligations. This allows investors to accurately calculate their gains or losses and properly report them on their tax returns.
-
Tax reporting simplification: By providing clear and concise information on the organizational actions, Form 8937 simplifies tax reporting for investors. It helps in determining the adjusted basis of the securities and the holding period, which are essential for calculating the taxable gain or loss upon a subsequent sale or disposition of the securities.
-
Avoiding tax penalties: Filing Form 8937 in a timely and accurate manner helps companies and issuers avoid potential tax penalties. Failure to file the form or providing incorrect information may result in penalties imposed by the IRS.
-
Investor confidence: Transparent and compliant reporting through Form 8937 enhances investor confidence in the company or issuer. By providing accurate information on organizational actions and their tax implications, the company demonstrates its commitment to transparency and good corporate governance practices.
-
Legal requirement: In certain cases, filing Form 8937 is a legal requirement. For example, if a company undergoes a significant organizational action such as a merger, acquisition, spin-off, or stock split, they are obligated to file Form 8937 to disclose the tax consequences of these actions to investors.
-
Consistency and Standardization: The use of Form 8937 promotes consistency and standardization in reporting organizational actions. By following the prescribed format and providing specific details, companies and issuers ensure that the information is presented uniformly, making it easier for investors and tax authorities to understand and process the data.
It's important to note that while Form 8937 offers benefits in terms of compliance, transparency, and tax reporting simplification, it is primarily designed to fulfill tax obligations and provide information to investors.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 8937?
Generally, the issuer of the securities is responsible for filing Form 8937. This includes corporations, mutual funds, real estate investment trusts (REITs), regulated investment companies (RICs), and other entities that issue specified securities.
The form is filed when certain organizational actions occur, such as:
- Stock splits or stock dividends
- Mergers or acquisitions
- Recapitalizations or reorganizations
- Conversions or exchanges of securities
- Other similar transactions that affect the basis of securities
Individual taxpayers who hold the specified securities should consult the information provided in Form 8937 to determine the appropriate tax treatment of these actions.
How To Complete Form 8937: A Step-by-Step Guide
However, here is a general overview of the process:
Step 1: Obtain the form
Visit the official website of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and search for Form 8937. Download the form and also obtain the accompanying instructions.
Step 2: Understand the requirements
Read through the instructions carefully to understand the requirements for completing Form 8937. This will help you gather the necessary information and ensure accurate reporting.
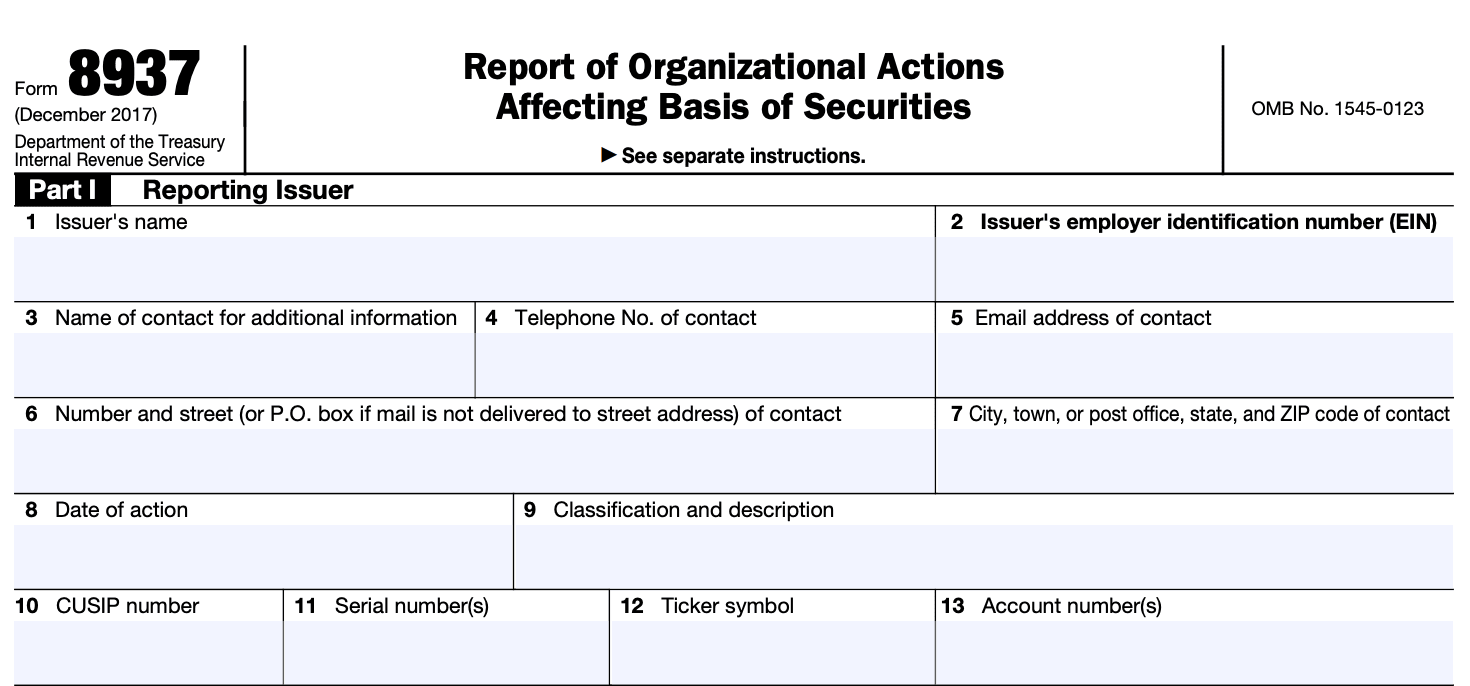
Step 3: Provide general information
At the top of the form, provide the required general information, including the name of the issuer, employer identification number (EIN), contact information, and the date of the organizational action.
Step 4: Describe the organizational action
In Part I of the form, provide a detailed description of the organizational action that affects the basis of the securities. This could include actions such as mergers, acquisitions, stock splits, or other events that impact the basis of securities.
Step 5: Determine and report the changes to basis
In Part II of the form, report the changes to the basis of the affected securities resulting from the organizational action. This typically involves providing the date of the action, the fair market value of the securities before and after the action, and any adjustments made to the basis.
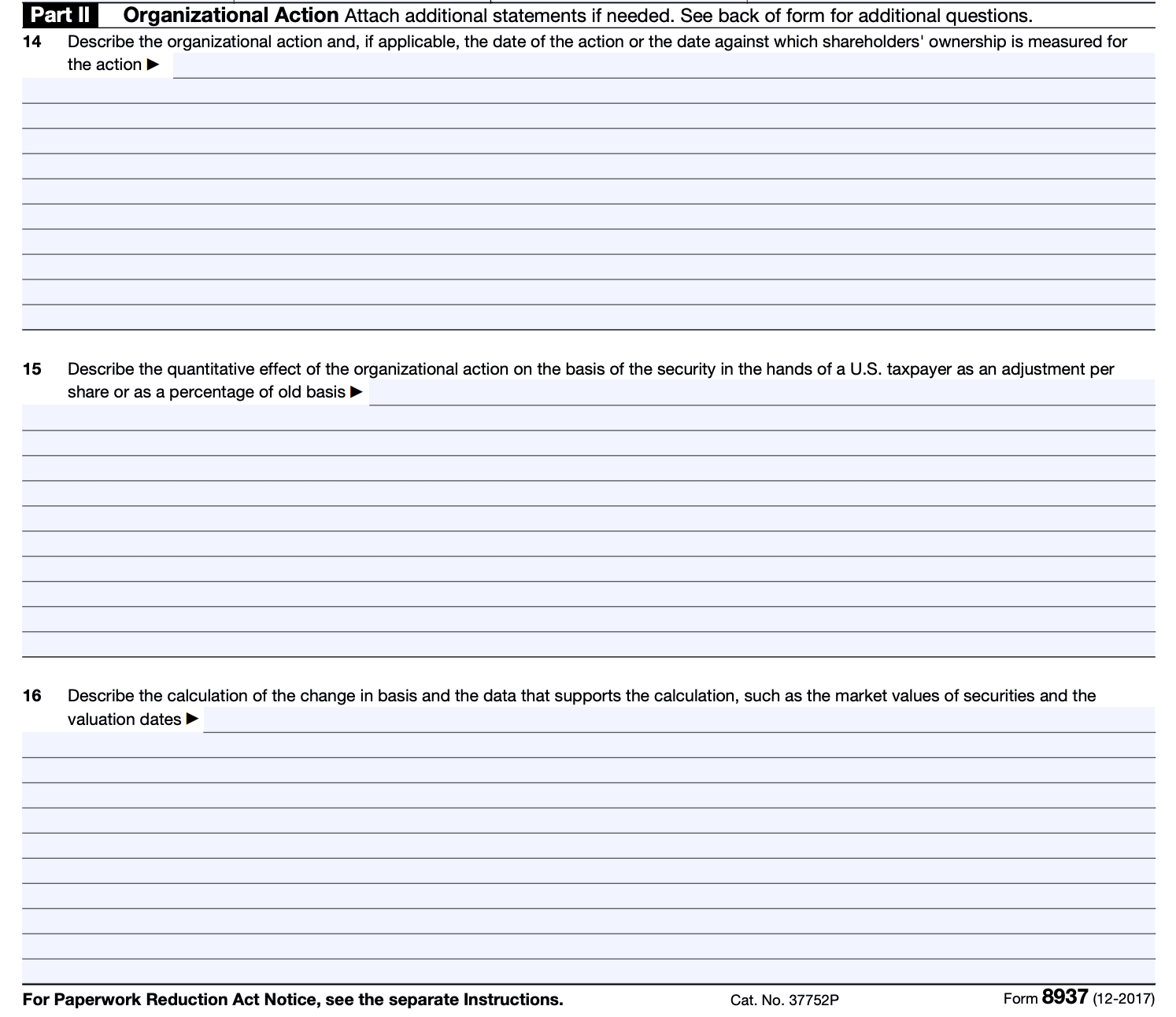
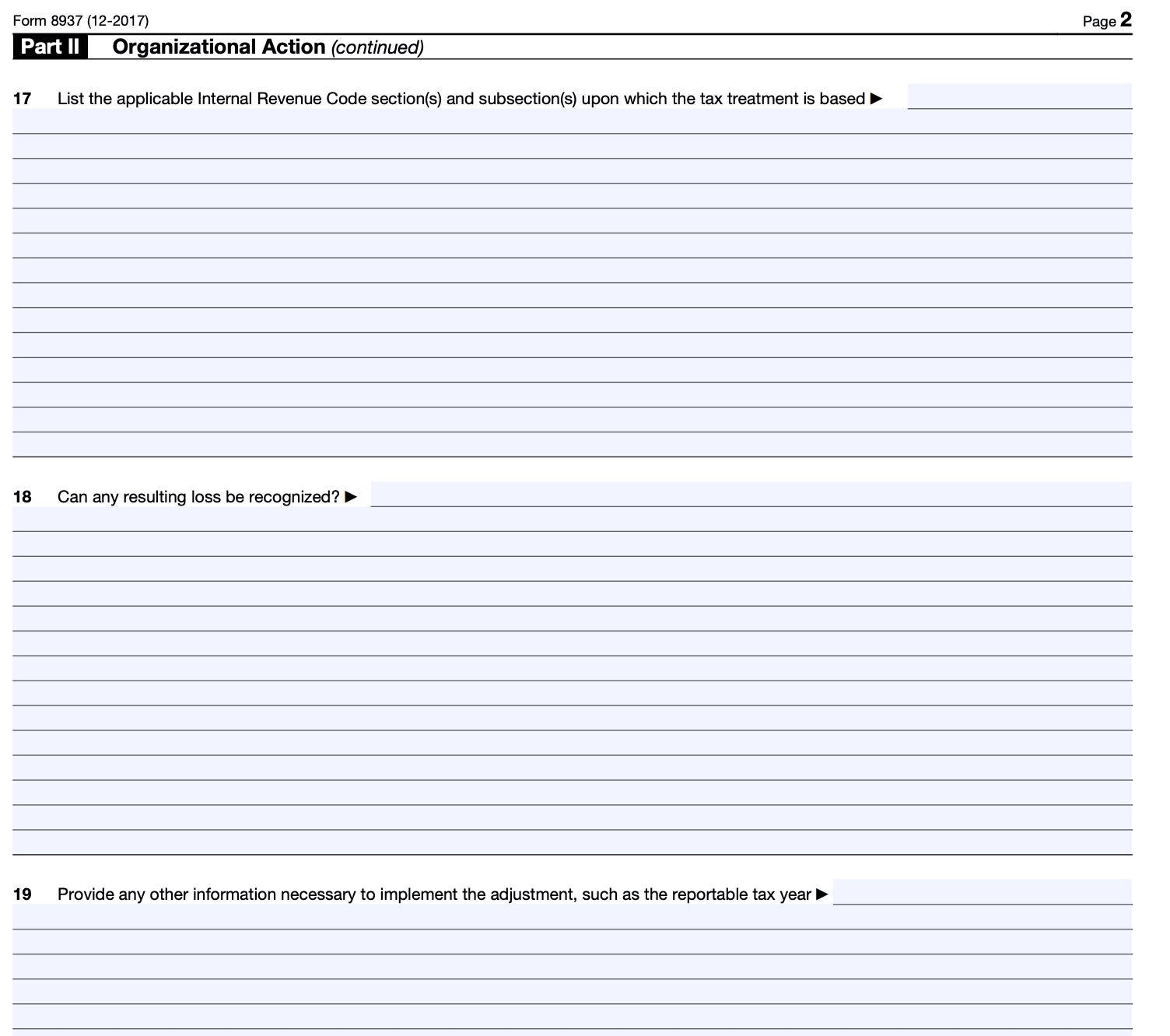
Step 6: Attach additional information
If necessary, you may need to attach additional information or supporting documentation to substantiate the reported changes to the basis of securities. Follow the instructions to ensure you provide all required documentation.
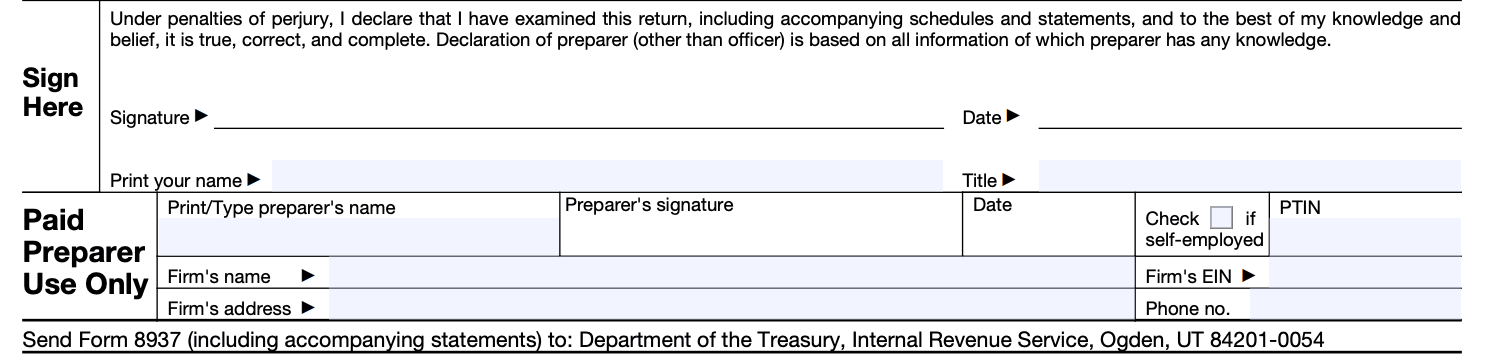
Step 7: Sign and date the form
The issuer or authorized representative should sign and date the form at the bottom to certify the accuracy of the information provided.
Step 8: Submit the form
Once you have completed Form 8937, make a copy for your records and submit the original form to the IRS according to the instructions provided. Be sure to retain a copy of the form, along with any supporting documentation, for your own records.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 8937
When filing Form 8937, there are several special considerations to keep in mind. Here are some important points to consider:
Purpose of Form 8937: Form 8937 is used to report organizational actions that may affect the basis of securities, such as stock splits, mergers, acquisitions, spin-offs, and other similar transactions. The form provides information to both the issuer of the securities and the holder or recipient of the securities.
Timely filing: Form 8937 must be filed with the IRS by the issuer of the securities no later than 45 days after the organizational action affecting the basis of the securities occurs. The form should also be made available to the public on the issuer's website or at a designated location.
Information to be included: The form requires specific information to be provided, including the issuer's name, address, taxpayer identification number (TIN), the type of organizational action, the date of the action, and a description of how the basis of the securities is affected. The form should also include a statement explaining how the issuer calculated the adjustments to the basis of the securities.
**Reporting multiple actions: **If multiple organizational actions occur during the same calendar year that affect the basis of the same security, the issuer may report them on a single Form 8937 or file separate forms for each action. However, it is important to clearly identify each action and provide the required information for each.
**Availability to holders or recipients: **The issuer must make the Form 8937 available to holders or recipients of the securities by either providing a copy of the form or publishing it on the issuer's website. The information must be provided or made available no later than 30 days after the form is filed with the IRS.
Consistency with other forms: The information reported on Form 8937 should be consistent with the information reported on other tax forms, such as Form 1099-B (for brokers) and Form 8949 (for taxpayers reporting the sale or exchange of securities).
Penalties for non-compliance: Failure to timely file Form 8937 or provide it to holders or recipients of the securities may result in penalties imposed by the IRS. It is important to ensure compliance with the filing requirements to avoid potential penalties.
How To File Form 8937: Offline/Online/E-filing
To file Form 8937, which is used to report organizational actions that affect the basis of securities, you have a few options: offline filing, online filing, or e-filing. Here's an overview of each method:
Offline filing
To file Form 8937 offline, you need to download the form from the official IRS website. Once you have the form, you can fill it out manually or using a typewriter. Make sure to complete all the required fields accurately. Afterward, you can print and mail the form to the address provided in the instructions of Form 8937.
Online filing
Online filing typically refers to using tax software or online platforms that support electronic filing of tax forms. You can check if your preferred tax software or online platform supports the filing of Form 8937. If it does, you can enter the required information into the software or platform, and it will generate and file the form electronically on your behalf.
E-filing
E-filing involves directly submitting your Form 8937 electronically to the IRS through their designated electronic filing system. The IRS offers several options for e-filing, including the Modernized e-File (MeF) system. However, it's important to note that the availability of e-filing for Form 8937 may vary depending on the specific circumstances.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Filing Form 8937
When filing Form 8937, which is used to report organizational actions that affect the basis of securities, it's important to be thorough and accurate. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when filing Form 8937:
**Incomplete or incorrect information: **Ensure that you provide all the required information accurately. This includes details such as the issuer's name, CUSIP number, and description of the organizational action.
Failing to report all relevant organizational actions: Form 8937 should be filed for each organizational action that affects the basis of securities. Examples of such actions include stock splits, mergers, acquisitions, spin-offs, and debt-for-equity exchanges. Be sure to report all applicable actions.
Incorrect calculations: When reporting the tax basis adjustments resulting from the organizational action, make sure your calculations are accurate. Double-check your math to avoid errors that could lead to incorrect reporting.
**Failure to provide supporting documentation: **Form 8937 may require attachments, such as a description of the organizational action and any relevant stockholder notices. Ensure that you include all necessary supporting documentation with your filing.
Late or missed deadlines: Form 8937 must be filed with the IRS by the due date, which is generally within 45 days after the organizational action. Missing the deadline or filing late can result in penalties and unnecessary complications.
Inconsistent reporting: If you have multiple series or classes of securities affected by the same organizational action, make sure the information reported on Form 8937 is consistent across all affected securities. Inconsistencies can lead to confusion and potential IRS inquiries.
**Failing to distribute the form to shareholders: **Along with filing Form 8937 with the IRS, it is generally required to provide a copy of the form to affected shareholders or investors within a specified timeframe. Ensure that you comply with the distribution requirements.
**Neglecting to retain records: **Keep a copy of the filed Form 8937 and all supporting documentation for your records. Retaining these records will be helpful for future reference and potential audits.
Key Takeaways
Form 8937 plays a vital role in ensuring accurate tax reporting and providing transparency to shareholders and investors regarding the tax consequences of organizational actions. By disclosing the changes in the basis of securities resulting from these actions, the form enables taxpayers to calculate gains or losses correctly and comply with IRS regulations.
While Form 8937 may seem daunting at first glance, understanding its purpose and components can help taxpayers navigate the complexities of reporting organizational actions. As always, seeking the advice of a tax professional is highly recommended to ensure compliance and maximize tax efficiency.


