- IRS forms
- Form 8038-G
Form 8038-G: Information Return for Government Purpose Tax-Exempt Bond Issues
Download Form 8038-GAs citizens, we often hear about government projects that aim to improve infrastructure, schools, and other public facilities. These projects are frequently funded through bonds issued by local and state governments. To ensure transparency and compliance with tax regulations, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires governmental issuers of tax exempt bonds to file Form 8038-G - the Information Return for Government Purpose tax exempt bond Issues.
Before we delve into Form 8038-G, let's briefly understand what tax exempt bonds are and why they are relevant. Tax exempt bonds are debt instruments issued by state and local governments, as well as certain governmental entities, to raise funds for public projects.
These bonds are considered tax exempt because the interest earned by bondholders is not subject to federal income tax, and in some cases, it may be exempt from state and local taxes as well. This tax advantage makes tax exempt bonds an attractive investment option for individuals and institutions seeking tax-free income.
Purpose of Form 8038-G
The purpose of Form 8038-G is to provide information about the issuance of these bonds and to comply with federal tax regulations.
Here are some key points regarding the purpose of Form 8038-G:
**1. Disclosure: **The form serves as a disclosure document that provides essential details about the issuance of tax exempt governmental bonds to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
**2. Identification: **It helps the IRS identify the issuer of the bonds, which is usually a state or local government entity or a related agency.
**3. Tax compliance: **By filing this form, the issuer ensures that they are in compliance with the tax requirements associated with issuing tax exempt bonds.
4. Bond characteristics: The form provides information about the type of bonds issued, their purpose, the date of issue, maturity date, and other characteristics.
5. Use in IRS audits: Form 8038-G becomes a reference document for the IRS during audits or examinations of tax exempt bond issuers to verify compliance with tax regulations.
6. Availability to the public: Once filed with the IRS, these forms become public records, allowing interested parties to access information about the tax exempt bonds issued by various governmental entities.
Benefits of Form 8038-G
The form serves as an important tool for gathering necessary information for compliance and regulatory purposes. The benefits of Form 8038-G include:
Compliance with tax laws: Form 8038-G ensures that state and local governments issuing tax exempt bonds comply with the relevant tax laws and regulations. It provides the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) with essential information to monitor the issuance and use of tax exempt bonds.
Monitoring tax exempt bond usage: The form helps the IRS keep track of how tax exempt bond proceeds are used. There are specific requirements for how these funds can be used, and reporting on Form 8038-G helps ensure that they are being utilized appropriately, typically for projects that serve public purposes, such as infrastructure development or public service improvements.
**Transparency and accountability: **By requiring governmental entities to submit Form 8038-G, it promotes transparency and accountability in the use of tax exempt bond proceeds. This information is publicly available and can be accessed by investors and other stakeholders.
Preventing abusive practices: The reporting requirements on Form 8038-G help prevent abusive practices, such as arbitrage, where the proceeds from tax exempt bonds are invested in higher-yield investments with the intent of generating a profit at the taxpayers' expense.
Ensuring tax exempt status: Filing Form 8038-G is essential to maintaining the tax exempt status of the bonds. Failure to comply with reporting requirements could result in the loss of tax exempt status, leading to higher borrowing costs for the issuing government.
Facilitating audits and reviews: The information provided on Form 8038-G makes it easier for the IRS to conduct audits and reviews of tax exempt governmental bonds. This helps ensure that the tax exempt status was properly claimed and maintained.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 8038-G?
Eligibility to file Form 8038-G is typically limited to the issuer of tax exempt governmental bonds. In this context, the issuer refers to the state or local government or other governmental entity that is responsible for issuing the bonds to raise funds for various public projects and infrastructure.
Here are some examples of entities that may be eligible to file Form 8038-G:
- State governments
- Local governments (e.g., counties, cities, municipalities)
- Governmental agencies and authorities (e.g., transportation authorities, housing authorities)
- Special districts (e.g., school districts, water districts)
How To Complete Form 8038-G: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here’s a general step-by-step guide to help you understand how to complete Form 8038-G.
Step 1: Obtain the form and instructions
Download Form 8038-G and its accompanying instructions from the IRS website. The form and instructions should be available under the "Forms and Publications" section.
Step 2: Gather the necessary information
Before starting to fill out the form, ensure you have all the required information readily available. This may include details about the bond issuer, issue date, bond amount, the purpose of the bond, and other relevant financial data.
Step 3: Complete Part I - provide general information
Begin by completing Part I of the form. This section requires basic information about the issuer, the type of bond, the purpose of the issue, the issue date, and other essential details. Ensure all information is accurate and up-to-date.
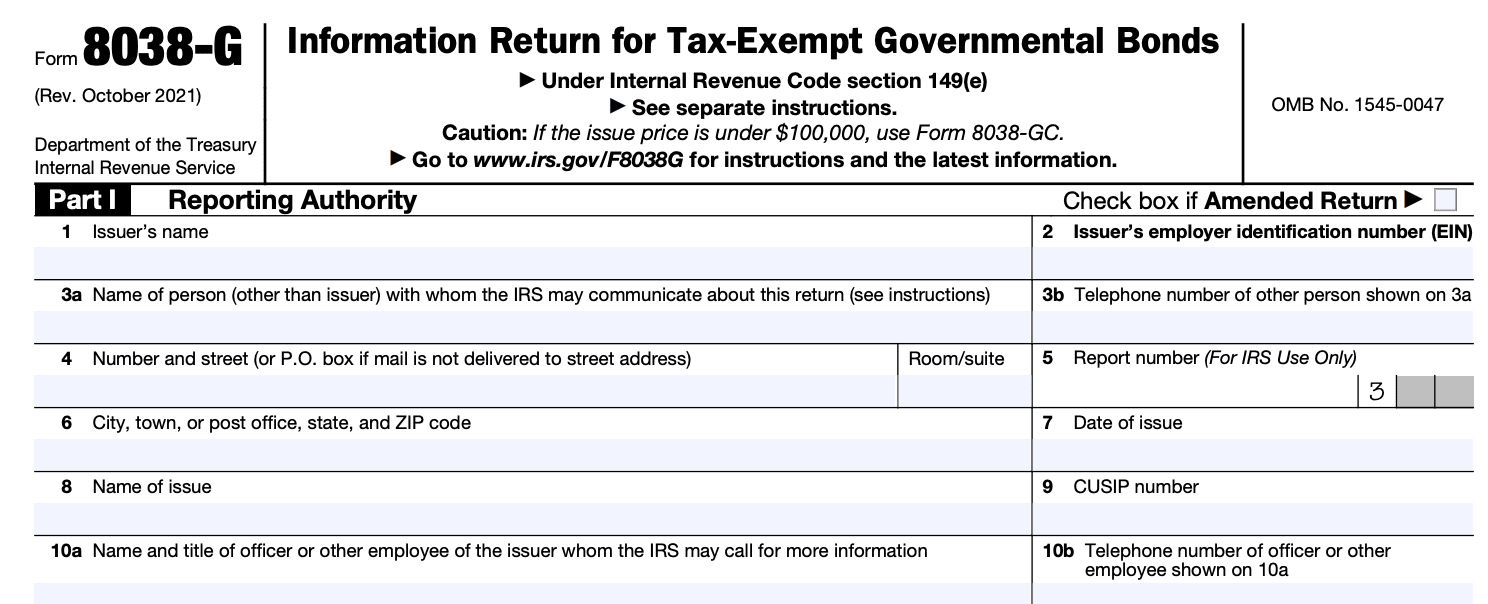
Step 4: Complete Part II
Part II of Form 8038-G requires information about the issue price and the purpose of the issue. Provide a detailed description of the purpose for which the bond proceeds will be used.
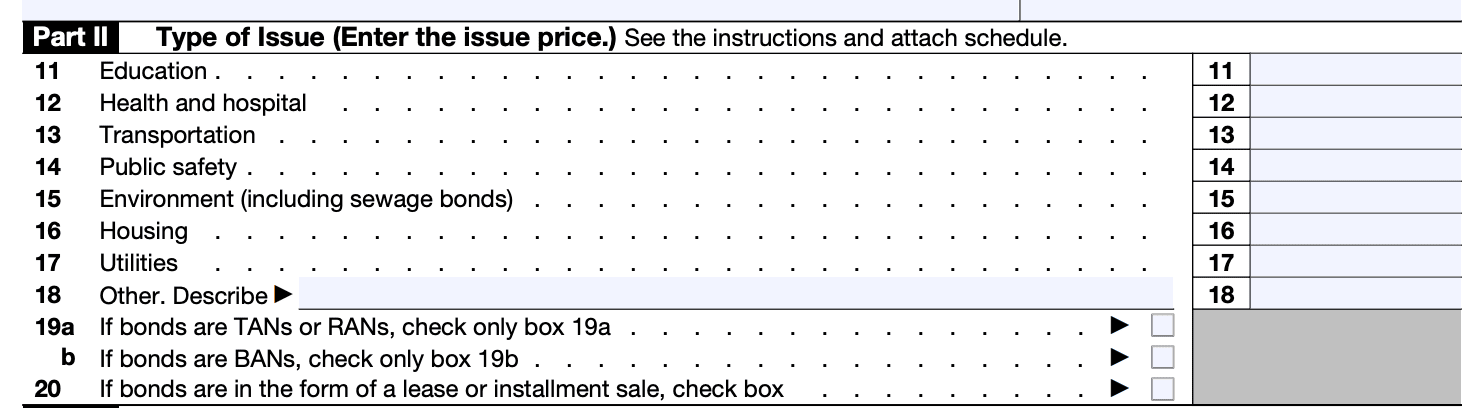
Step 5: Fill out Part III
In Part III, you will need to specify if the bond is a private activity bond, and if so, provide details about the facility used, location, and ownership.

Step 6: Complete Part IV
Part IV is dedicated to providing information about the private business use of the bond proceeds. This section is essential for determining compliance with tax exempt status requirements.
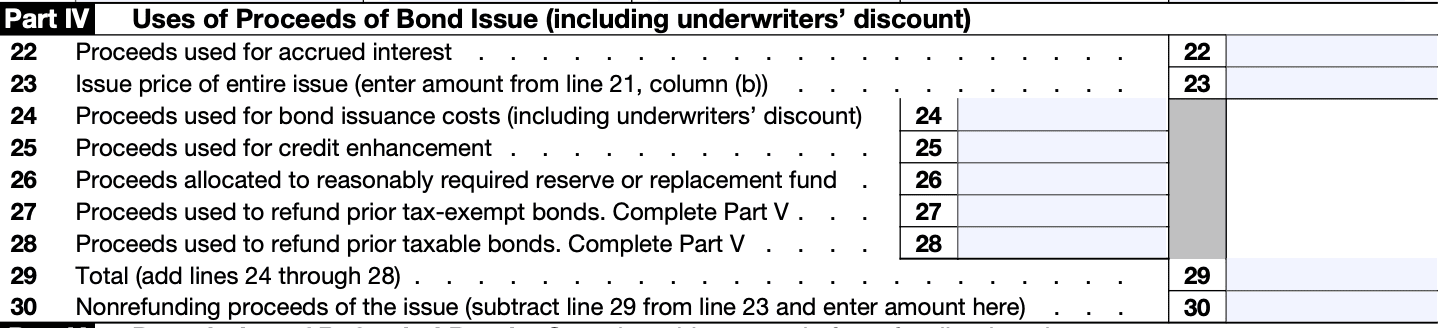
Step 7: Fill out Part V
Part V requires information about arbitrage, rebate, yield reduction payments, and other related matters. Be prepared to provide specific financial data regarding investment earnings on the bond proceeds.

Step 8: Complete Part VI
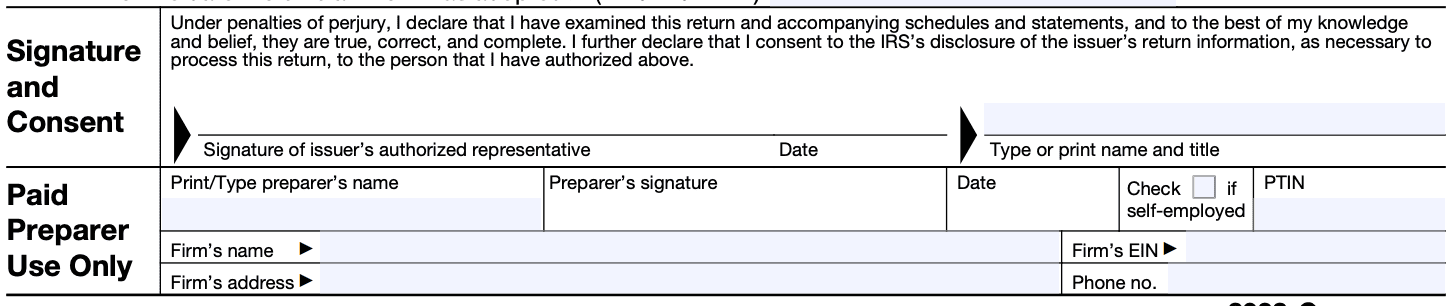
In Part VI, you will need to certify that the information provided is true, correct, and complete to the best of your knowledge. Review the entire form and ensure all necessary fields are filled accurately.

Step 9: Sign and submit the form
Once you have completed the form, attach any required schedules or supporting documentation. Make a copy for your records, and then submit the original form to the IRS. The submission address should be mentioned in the form instructions.
Step 10: Review the latest instructions
Always double-check the latest instructions provided by the IRS for Form 8038-G to ensure you are following the most up-to-date guidelines.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 8038-G
When filing Form 8038-G, there are some special considerations that issuers should be aware of:
Accurate and timely filing: It is crucial to ensure the form is filed accurately and on time. Missing the filing deadline or providing incorrect information can result in (link: https://fincent.com/blog/irs-tax-penalty-identification text: penalties) and interest charges.
Record-keeping: Maintain proper records of the issuance and compliance of tax exempt bonds. This includes documentation related to the bond issuance, use of proceeds, arbitrage compliance, and any other relevant financial information.
**Arbitrage compliance: **Governments issuing tax exempt bonds need to comply with arbitrage rules to avoid potential penalties and to maintain the tax exempt status of the bonds. These rules govern the investment of bond proceeds to ensure that any investment earnings do not exceed certain limits.
**Private business use: **If tax exempt bonds are used to finance facilities or projects that involve private business use, certain restrictions may apply. The issuer needs to identify and report any private business use to maintain the tax exempt status of the bonds.
**Continuing disclosure requirements: **In some cases, issuers may have continuing disclosure obligations related to their tax exempt bonds. These obligations may require providing ongoing information about the bond issue and the financial health of the issuer.
Compliance with tax law changes: Stay updated on any changes to tax laws that may affect the reporting requirements for tax exempt governmental obligations. Tax laws can change over time, so it's essential to remain informed.
Qualified opinion: If the issuer receives a "qualified opinion" from a tax professional regarding the tax exempt status of the bonds, the issuer may be required to provide additional information to the IRS.
**Use of electronic filing: **The IRS encourages electronic filing of Form 8038-G for faster processing and acknowledgment.
Filing Deadlines & Extensions Form 8038-G
General guidelines that were applicable as of September 2021 are as follows
Filing deadline: The standard deadline for filing Form 8038-G is 15 days after the issue date of the bonds.
**Extensions: **The IRS may grant extensions on a case-by-case basis if the issuer requests additional time to file the form. The extension request should be made in writing and sent to the IRS office where the form would typically be filed. The request should provide a valid reason for the extension.
Late filing penalties: If the form is not filed by the original or extended due date, the issuer may be subject to penalties based on the number of days the filing is late.
Since the tax laws and regulations can change, it's crucial to check the IRS website or consult with a tax professional for the most up-to-date information on filing deadlines and extensions for Form 8038-G.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Filing Form 8038-G
When filing Form 8038-G, it's essential to be accurate and thorough to avoid potential issues and delays. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Incorrect identification information: Ensure that the correct name, address, and identification number of the issuer are provided. Double-check these details to avoid any confusion.
**Errors in bond information: **Accurately report the details of the bonds issued, such as the issue date, maturity date, and CUSIP number. Any mistakes in these details can lead to discrepancies in the tax calculation.
Incomplete or missing information: Fill out all required fields on the form. Leaving any relevant sections blank or incomplete can result in processing delays or even rejection of the form.
Incorrect bond classification: Private activity bonds are subject to specific tax rules. Make sure you correctly classify the bonds to ensure they are treated appropriately for tax purposes.
Inaccurate use of codes: The form may require certain codes to be used for specific purposes. Be sure to use the correct codes as instructed in the form's guidelines.
Failure to attach necessary schedules: Depending on the complexity of the bond issue, additional schedules may be required to be attached to Form 8038-G. Ensure you include all the necessary supporting documents.
**Missing signatures: **Make sure the form is signed by the authorized parties as required. Missing signatures can invalidate the form.
Late filing: Be mindful of the filing deadline. Missing the deadline could result in (link: https://fincent.com/irs-tax-forms/form-1098-f text: penalties) and interest charges.
Incorrect calculations: Double-check all calculations to ensure accuracy. Any errors in the calculations may lead to discrepancies in the tax liability.
Not seeking professional assistance: If you are unsure about how to fill out Form 8038-G correctly, it's best to seek guidance from a tax professional or advisor with experience in handling tax exempt bonds.
Conclusion
Form 8038-G plays a vital role in promoting transparency and accountability in the issuance of tax exempt bonds for government projects.
By requiring governmental issuers to provide comprehensive information, the IRS ensures that these bonds are used for their intended public purposes and that they comply with applicable tax laws.
As taxpayers, understanding the importance of this form can help us appreciate the measures in place to manage public funds and contribute to the development of our communities.


