- IRS forms
- Form 706-NA
Form 706-NA: United States Estate (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax Return
Download Form 706-NAManaging the affairs of a deceased individual can be a complex and emotionally challenging task. Apart from dealing with the personal loss, the executor or administrator of an estate may also need to navigate the intricate world of estate taxation. In the United States, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires the filing of Form 706-NA, the United States Estate (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax Return for Non-resident Not a Citizen of the United States.
Form 706-NA is a tax form used to report and calculate the estate tax and generation-skipping transfer (GST) tax liabilities of a nonresident who is not a citizen of the United States but owns property within the country. The form is applicable when a non-U.S. citizen's estate is subject to U.S. estate tax or when a non-U.S. citizen makes a generation-skipping transfer that triggers a GST tax. It serves as the tax return for these events, allowing the IRS to assess and collect the appropriate taxes.
This blog post aims to shed light on Form 706-NA, its purpose, and the key considerations involved.
Purpose of Form 706-NA
The purpose of Form 706-NA is to calculate and report the estate tax owed to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) when a nonresident alien decedent passes away and leaves behind assets located in the United States. This form is required to be filed if the total value of the decedent's U.S. assets exceeds the applicable threshold set by the IRS.
The form provides a comprehensive overview of the decedent's estate, including details about the assets owned, their values, deductions, exemptions, and any applicable tax credits. It also requires information about the decedent's beneficiaries and the distribution of the estate.
By completing and filing Form 706-NA, the executor or personal representative of the estate ensures compliance with U.S. tax laws and facilitates the determination of the estate tax liability for the decedent's U.S. assets. The IRS reviews the information provided on the form to assess and collect the appropriate estate tax amount.
Benefits of Form 706-NA
Here are some potential benefits of filing Form 706-NA:
Compliance with U.S. tax laws: Filing Form 706-NA ensures that nonresident aliens are compliant with U.S. tax laws. It allows individuals to fulfill their legal obligations and avoid potential penalties or legal issues that may arise from non-compliance.
Utilization of tax exemptions and deductions: The estate tax laws in the United States provide certain exemptions and deductions that can help reduce the overall estate tax liability. By filing Form 706-NA, nonresident aliens can take advantage of these exemptions and deductions, potentially reducing the tax burden on their estates.
**Planning for future generations: **The Generation-Skipping Transfer (GST) tax provisions on Form 706-NA allow nonresident aliens to transfer assets to future generations without incurring additional estate taxes. This can be beneficial for individuals who wish to pass on wealth to their heirs while minimizing the tax consequences.
Coordination with estate planning strategies: Filing Form 706-NA allows nonresident aliens to coordinate their estate planning strategies with U.S. tax laws. By understanding the implications of U.S. estate tax rules, individuals can structure their assets and transfers in a way that minimizes the tax burden and maximizes the benefits for their beneficiaries.
Access to potential tax credits and refunds: In some cases, nonresident aliens may be eligible for tax credits or refunds related to their estate tax liability. By filing Form 706-NA, individuals can determine if they qualify for any credits or refunds and take advantage of them, potentially reducing their overall tax liability.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 706-NA?
Eligibility to file Form 706-NA depends on the following criteria:
Non-resident alien status: The decedent must be a nonresident alien at the time of their death. A nonresident alien is someone who is not a U.S. citizen and does not meet the criteria to be classified as a U.S. resident for tax purposes.
Ownership of U.S. situs property: The decedent must have owned property located in the United States that is subject to U.S. estate tax. U.S. situs property typically includes real estate, tangible property, and certain financial assets located within the United States.
Threshold requirement: The total value of the decedent's U.S. situs assets must exceed the applicable exemption threshold for the year of the decedent's death. The exemption threshold is subject to change and should be checked with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for the specific year.
If a nonresident alien meets these criteria, they may be required to file Form 706-NA to report and pay estate taxes on their U.S. situs assets.
How To Complete Form 706-Na: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here's a step-by-step guide to completing Form 706-NA:
Step 1: Obtain the necessary forms and instructions
Visit the official website of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and download Form 706-NA along with the instructions. Ensure that you have the most recent version of the form.
Step 2: Gather required information
Before you begin filling out the form, gather all the relevant information you will need. This may include personal details of the deceased individual, information about the estate, and the fair market value of the assets.
Step 3: Start with Part 1 - General Information
Enter the decedent's personal information, including their name, Social Security number or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN), date of death, and place of death. Provide the executor's information as well.
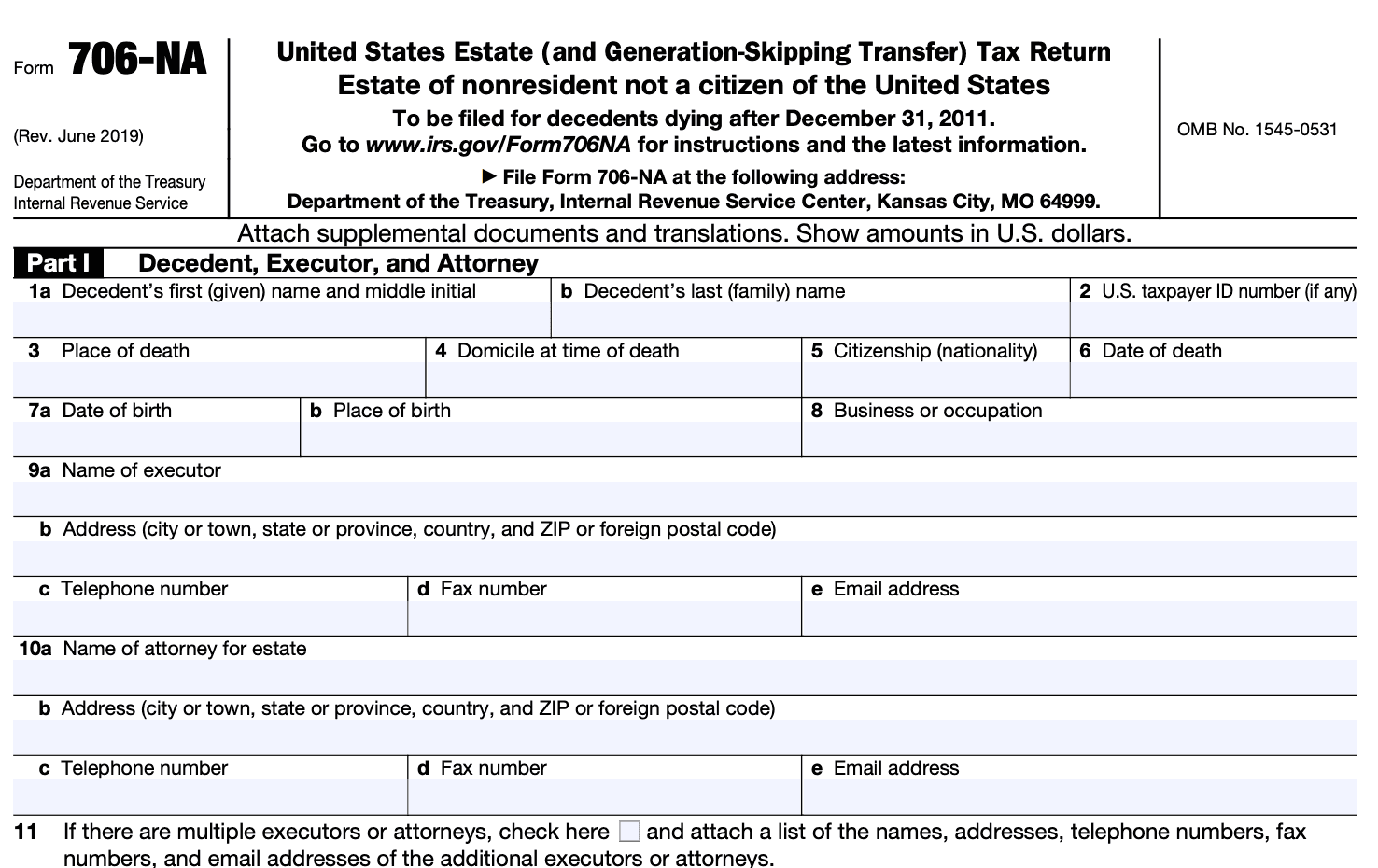
Step 4: Complete Part 2 - Elections by the Executor
In this section, the executor can make certain elections, such as the use of alternate valuation date or the allocation of the GST exemption. Follow the instructions and mark the appropriate boxes based on the choices made.
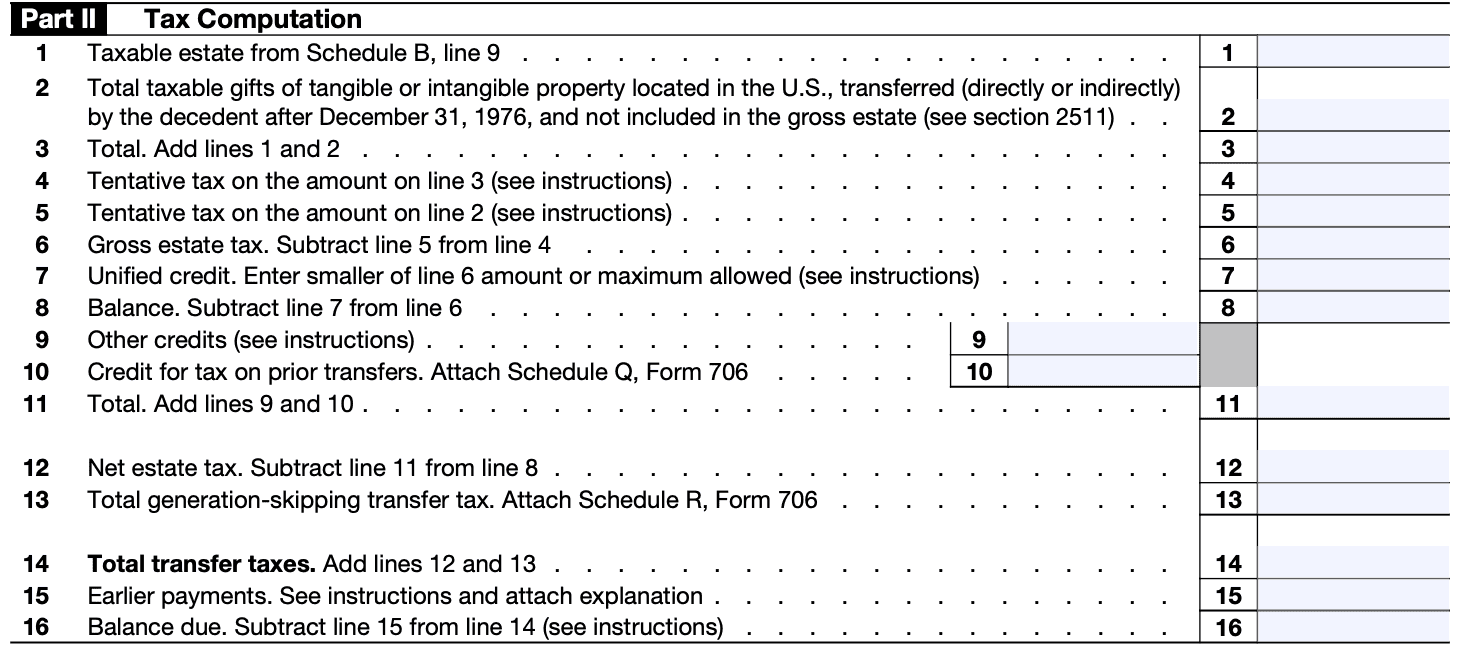
Step 5: Fill out Part 3 - Computation of Tax
This section requires you to calculate the estate tax owed. Provide the fair market value of the assets and calculate the gross estate. Subtract allowable deductions and arrive at the taxable estate. Apply the tax rates to determine the tentative tax.
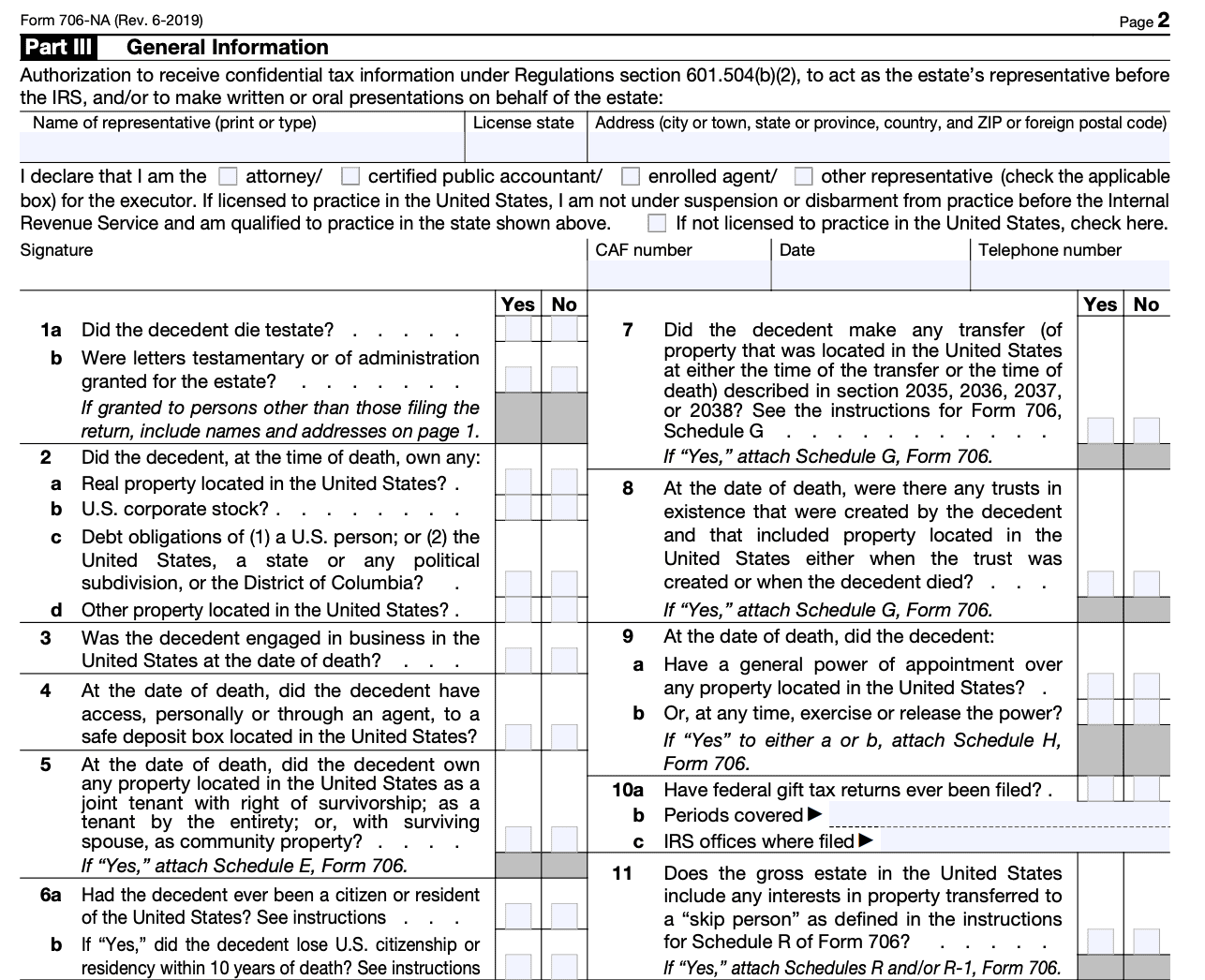
Step 6: Complete Part 4 - Credit for Tax on Prior Transfers
If there have been any previous taxable transfers, they may impact the estate tax calculation. Follow the instructions to determine the credit for tax on prior transfers, if applicable.
Step 7: Fill out Part 5 - Tax Computation and Payment
Using the information from Parts 3 and 4, compute the final estate tax amount owed. If any gift or GST tax is payable, include it as well. Provide details of any prior payments made. Calculate the net tax due and indicate the method of payment.

Step 8: Complete Part 6 - Consent to Extend the Time to Assess Tax
If you need additional time to gather information or if the estate is subject to litigation, you may need to request an extension of time to assess the tax. Follow the instructions in this section if applicable.
Step 9: Sign and date the form
Ensure that the form is signed and dated by the executor or authorized representative. If a paid preparer assisted in completing the form, they should also sign and include their information.
Step 10: Attach required documentation
Review the instructions to determine which supporting documents must be included with Form 706-NA. These may include an appraisal of the property, copies of wills and trusts, and any other relevant paperwork.
Step 11: Submit the form
Make a copy of the completed Form 706-NA and all supporting documents for your records. Mail the original to the address provided in the instructions. It is recommended to send it via certified mail to have proof of delivery.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 706-NA
When filing Form 706-NA, there are several special considerations to keep in mind. Here are some important points to consider:
**Non-resident alien status: **Form 706-NA is specifically for nonresident aliens, which means individuals who are not U.S. citizens and do not reside in the United States at the time of their death. Only estates of nonresident aliens should use this form.
**U.S. assets: **The estate tax only applies to the value of the decedent's assets that are situated in the United States. Non-U.S. assets are generally not subject to U.S. estate tax. Therefore, you should only report and value the assets located within the United States on Form 706-NA.
Determining the gross estate: The gross estate includes all assets subject to U.S. estate tax, such as real estate, tangible personal property, and certain intangible assets located in the United States. You need to carefully determine the fair market value of these assets as of the date of the decedent's death.
Applicable exclusion amount: Form 706-NA allows for an applicable exclusion amount that may reduce or eliminate the estate tax liability. The exclusion amount is subject to change each year, so it is essential to consult the most recent IRS instructions or a tax professional to determine the correct amount for the year of the decedent's death.
Filing deadline and extensions: Generally, Form 706-NA must be filed within nine months from the date of the decedent's death. However, you may request an automatic six-month extension by filing Form 4768. It's important to adhere to the filing deadlines to avoid penalties and interest.
Qualified domestic trust (QDOT): If the decedent's surviving spouse is a non-U.S. citizen, you may consider establishing a Qualified Domestic Trust (QDOT). A QDOT allows the deferral of estate tax on assets passing to the surviving spouse. Specific rules and requirements apply, so consult with a tax advisor to determine eligibility and establish a QDOT if needed.
Reporting and payment: Form 706-NA requires a detailed listing of all the assets, deductions, and credits claimed. Ensure accurate reporting of all required information. The estate tax owed, if any, must be paid in U.S. dollars.
**Professional assistance: **Given the complexity of U.S. estate tax laws and the unique circumstances of nonresident aliens, seeking professional assistance from a qualified tax advisor or estate attorney experienced in international tax matters is highly recommended. They can provide guidance, help with compliance, and ensure the accurate completion of Form 706-NA.
Filing Deadlines & Extensions on Form 706-NA
The filing deadlines and extensions for Form 706-NA are as follows:
**Initial filing deadline: **The initial filing deadline for Form 706-NA is nine months after the date of the decedent's death. For example, if the decedent passed away on January 1, the initial filing deadline would be September 30 of the same year.
**Extension of time to file: **If you need additional time to complete Form 706-NA, you can request an extension of time to file. The extension allows for an additional six months beyond the initial filing deadline. To request an extension, you must file Form 4768, "Application for Extension of Time To File a Return and/or Pay U.S. Estate (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Taxes," before the initial filing deadline.
Late filing and penalties: If you fail to file Form 706-NA by the initial deadline or the extended deadline, you may be subject to late filing penalties. The penalty is generally calculated based on the amount of tax due. It's important to note that the extension of time to file does not extend the time to pay any estate or GST taxes owed. Late payment penalties may apply if the taxes are not paid by the original due date.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 706-NA
When filing Form 706-NA (United States Estate (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax Return), it's important to be thorough and accurate to ensure compliance with tax laws. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when filing Form 706-NA:
Incorrect or incomplete information: Ensure that all required fields are filled out accurately. Double-check names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and other identifying information to avoid errors.
Failure to attach supporting documentation: Form 706-NA requires various supporting documents, such as appraisals, valuations, and copies of trust instruments. Failing to attach the necessary documents can delay processing and may result in penalties.
Incorrect valuation of assets: It's crucial to value the assets correctly. Use the appropriate valuation methods and provide adequate documentation to support the valuations. Errors in asset valuation can lead to underpayment or overpayment of estate tax.
Overlooking applicable deductions and credits: Be aware of the available deductions and credits specific to Form 706-NA. Common deductions include funeral expenses, debts, administration expenses, and charitable contributions. Failing to claim eligible deductions and credits can result in unnecessary tax liability.
Incorrect calculation of tax liability: Use the correct tax rates and formulas provided by the IRS to calculate the estate tax liability accurately. Mathematical errors can lead to incorrect tax payments.
Late or missing filing: Form 706-NA must be filed within nine months of the decedent's date of death, with a possible six-month extension. Failing to file on time or missing the deadline can result in penalties and interest charges.
**Lack of professional guidance: **If you're unfamiliar with the complexities of Form 706-NA, it's advisable to seek professional help from an estate tax attorney or a certified public accountant (CPA) who specializes in estate tax matters. They can guide you through the process, ensure accuracy, and help avoid costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Form 706-NA plays a vital role in calculating and reporting the estate tax and generation-skipping transfer tax liabilities of nonresident non-citizens who have assets within the United States.
Executors and administrators should familiarize themselves with the form's requirements, filing deadlines, and applicable deductions and exemptions to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with IRS regulations.
Seeking professional guidance from tax advisors or estate planning attorneys is highly recommended to navigate the complexities of estate taxation effectively.


