- IRS forms
- Form 5884-D
Form 5884-D: Employee Retention Credit for Certain Tax-Exempt Organizations Affected by Qualified Disasters
Download Form 5884-DIn times of economic hardship or qualified disasters, it becomes crucial for organizations to retain their employees. To support tax-exempt organizations in this endeavor, the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) was introduced. The ERC provides eligible organizations with a (link: https://fincent.com/glossary/tax-credits text: tax credit) to help them retain their workforce. Form 5884-D is the specific form used by tax-exempt organizations to claim the ERC for qualified disasters.
In this blog post, we will delve into the details of Form 5884-D, its purpose, eligibility requirements, credit calculation, and the overall benefits it offers to tax-exempt organizations affected by qualified disasters.
Understanding Form 5884-D
Form 5884-D is an IRS tax form used to claim the work opportunity credit. The work opportunity credit is a tax incentive provided to employers who hire individuals from targeted groups that face barriers to employment. The form helps employers calculate and report the credit amount they are eligible for based on the wages paid to qualifying employees.
The targeted groups eligible for the work opportunity credit include, but are not limited to, qualified veterans, ex-felons, designated community residents, vocational rehabilitation referrals, and Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) recipients. Each targeted group has specific eligibility criteria outlined in the instructions accompanying the form.
Form 5884-D consists of several parts that guide employers through the credit calculation process. It includes sections to enter employer information, calculate the credit for qualified first-year wages paid to employees in targeted groups, claim additional credits for long-term family assistance recipients, determine any credit carryforward to future years, and arrive at the total work opportunity credit amount.
Employers must attach Form 5884-D to their business tax return, such as Form 3800, Form 1120, or Form 1065, and include the calculated credit amount on the appropriate line of the tax return.
It's important to note that the instructions and requirements for Form 5884-D can change, so it's advisable to refer to the most recent version of the form and consult with a tax professional or the IRS for the latest guidance and regulations.
Benefits of Form 5884-D
Form 5884-D, also known as the "Disabled Access Credit," has several benefits associated with it. The following are some of them:
**Tax credit: **The primary benefit of Form 5884-D is that it allows businesses to claim a tax credit for expenses related to providing accessibility to individuals with disabilities. The credit can be used to offset the business's tax liability, potentially resulting in reduced tax payments or even a refund.
**Financial assistance: **By claiming the Disabled Access Credit, businesses can receive financial assistance for the costs associated with making their premises more accessible. This can help offset the expenses of renovations, installations, or equipment purchases necessary to accommodate individuals with disabilities.
Inclusive business environment: Making a business accessible to individuals with disabilities not only ensures compliance with legal requirements but also promotes inclusivity. By removing physical barriers and providing accommodations, businesses can welcome a broader customer base, leading to increased patronage and improved customer satisfaction.
Compliance with accessibility laws: In many jurisdictions, businesses are required to meet certain accessibility standards as mandated by the law. By claiming the Disabled Access Credit and utilizing it to improve accessibility, businesses can ensure compliance with these legal requirements and avoid potential penalties or litigation.
Enhanced reputation: Businesses that prioritize accessibility and inclusivity often enjoy an enhanced reputation within their community. By proactively investing in accessibility improvements, businesses demonstrate their commitment to social responsibility and equal access for all individuals, which can attract positive attention and loyalty from customers.
**Long-term cost savings: **While making accessibility modifications may initially incur expenses, they can lead to (link: https://fincent.com/blog/proven-ways-to-reduce-costs-increase-profit-for-your-business text: long-term cost savings). For example, installing ramps, wider doorways, or accessible restrooms may reduce the need for future renovations or costly retrofits. Additionally, by accommodating individuals with disabilities, businesses can tap into an underserved market segment, potentially generating increased revenue.
Who is eligible to file Form 5884-D?
To be eligible to file Form 5884-D, you must meet the following criteria:
Small business status: You must be a qualified small business. A qualified small business is defined as a business with either:
a. Gross receipts of $1 million or less for the preceding tax year, and no more than 30 full-time employees during that year.
b. Gross receipts of more than $1 million for the preceding tax year but less than $1.5 million, and you can certify that you have incurred expenses for the removal of architectural, transportation, communication, or other barriers to accessibility.
Eligible expenses: You must have incurred expenses for the purpose of providing access to individuals with disabilities. This includes expenses related to making physical modifications to your business premises or acquiring adaptive equipment or technology to accommodate disabled individuals.
**Barrier removal: **The expenses must be incurred for the removal of architectural and transportation barriers. This includes making changes to entrances, parking lots, bathrooms, signage, and other physical aspects of the business that facilitate access for individuals with disabilities.
ADA compliance: The expenses must be incurred to comply with the requirements of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). The ADA sets standards for accessibility in public accommodations, employment, transportation, and other areas, and businesses must adhere to these standards to be eligible for the credit.
How To Complete Form 5884-D: A Step-by-Step Guide
Form 5884-D is used by employers to claim the work opportunity credit for qualified first-year wages paid to eligible employees who are members of targeted groups. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to complete Form 5884-D:
Step 1: Obtain the necessary forms
Download Form 5884-D from the official website of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). You may also refer to the instructions for Form 5884-D for additional guidance.
Step 2: Provide general information
Enter the required information at the top of the form, including your employer identification number (EIN), your name, and address. Make sure all the information is accurate and up to date.
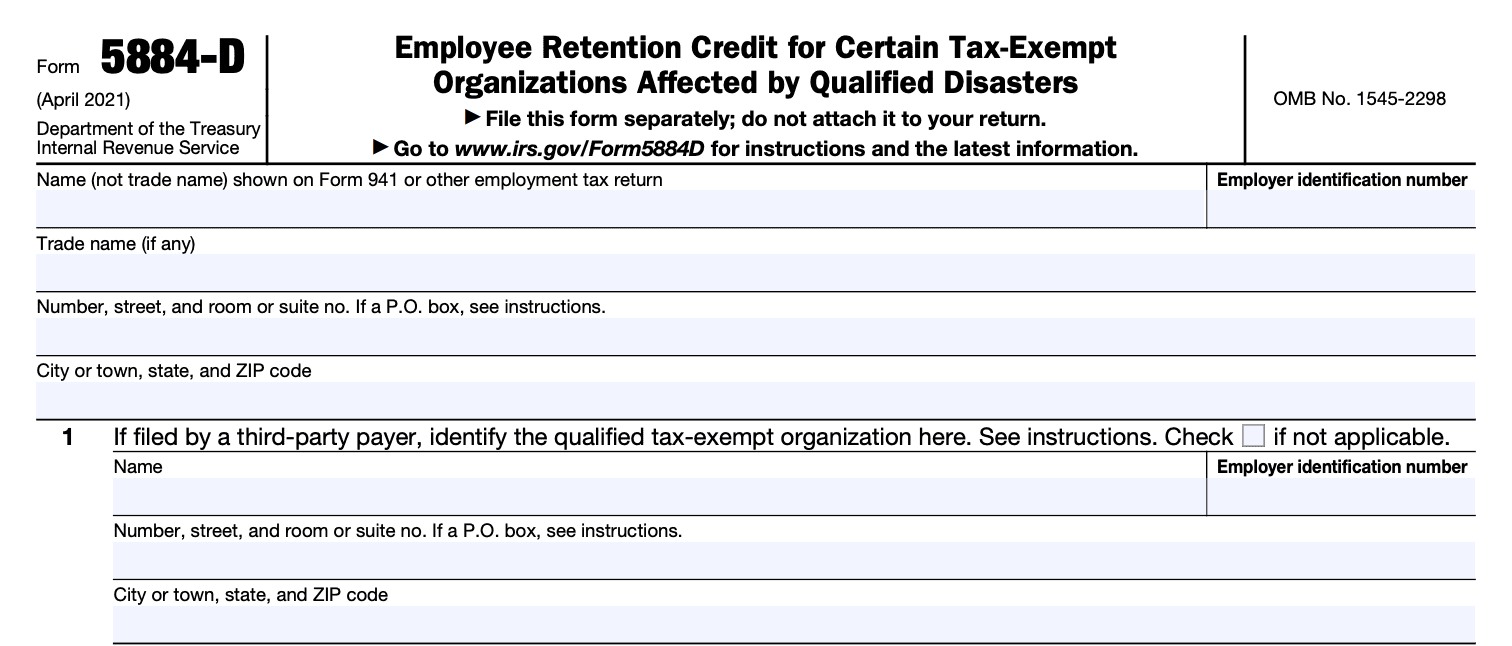
Step 3: Identify the targeted group
In Part I of Form 5884-D, you will identify the targeted group that applies to the eligible employees for whom you are claiming the credit. There are various targeted groups, such as qualified IV-A recipients, qualified veterans, ex-felons, designated community residents, vocational rehabilitation referrals, summer youth employees, Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) recipients, and SSI recipients. Check the appropriate box or boxes that apply.
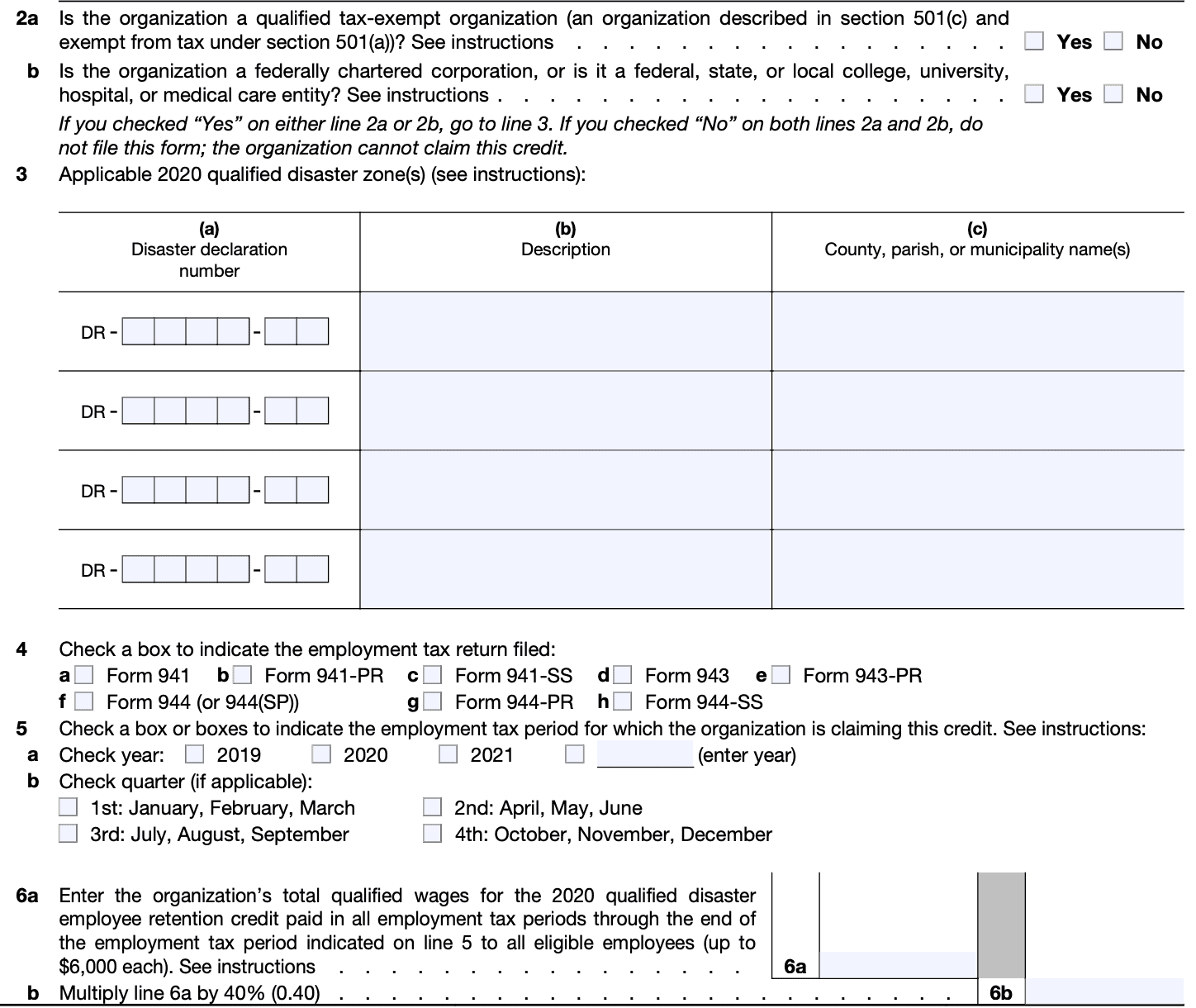
Step 4: Determine the number of hours and wages
In Part II, you will need to provide the number of hours and wages paid to each employee who qualifies for the credit. You must separately calculate the qualified first-year wages for each employee and enter the total amount in the appropriate section.
Step 5: Calculate the credit
In Part III, you will calculate the credit for each targeted group. Follow the instructions provided on the form to determine the amount of credit you are eligible to claim for each employee and targeted group. Ensure that you accurately perform all the calculations.

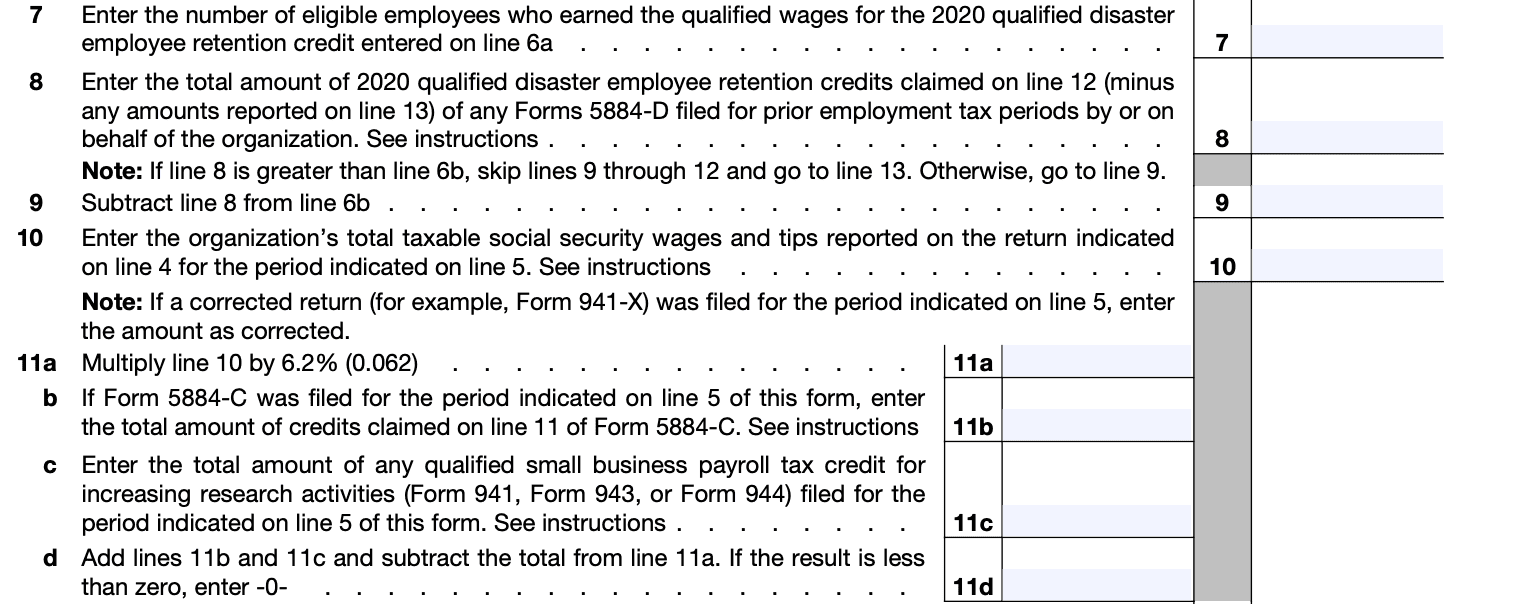
Step 6: Complete the summary section
In Part IV, you will summarize the total credit calculated for all targeted groups. Add up the credits from Part III and enter the totals in the appropriate fields.
Step 7: Attach supporting documents
If required, attach any necessary documentation to support your claim for the work opportunity credit. This may include completed Form 8850, Pre-Screening Notice and Certification Request for the Work Opportunity Credit, or other relevant documentation.
Step 8: Review and sign the form
Carefully review the completed Form 5884-D to ensure accuracy and completeness. Sign and date the form in the designated section.
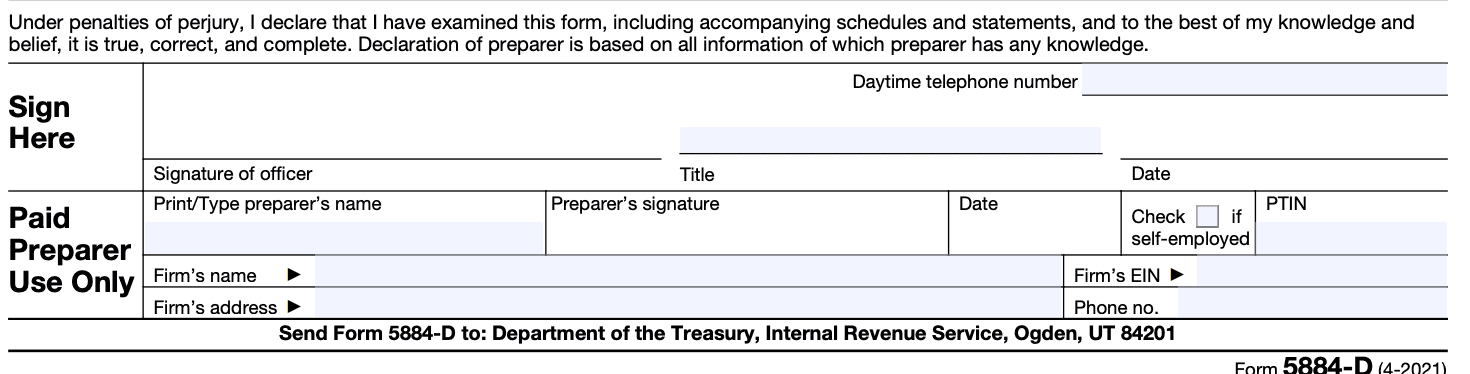
Step 9: Retain a copy for your records
Make a copy of the completed Form 5884-D and all supporting documents for your records. Keep them in a secure place as part of your tax records.
Step 10: Submit the form
Submit the original Form 5884-D to the IRS according to the instructions provided. Retain proof of submission, such as certified mail or electronic filing confirmation, for your records.
It's important to note that this guide provides a general overview of completing Form 5884-D. For specific and detailed instructions, refer to the official IRS instructions or consult a tax professional for guidance tailored to your situation.
Filing deadlines & extensions for Form 5884-D
As of September 2021, the regular tax filing deadline for most individuals and businesses is April 15 of the year following the tax year. However, please note that tax deadlines can change, and it's always advisable to consult the latest IRS guidelines or consult with a tax professional for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
If you need an extension to file Form 5884-D, you can request an automatic six-month extension by filing Form 7004, "Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns." This form must be filed by the original due date of the tax return (April 15) or the extended due date if already granted an extension.
Keep in mind that an extension to file the tax return does not extend the time to pay any taxes owed. If you anticipate owing taxes, you should estimate the amount and make a payment by the original due date to avoid penalties and interest.
How To File Form 5884-D: Offline/Online/E-filing
The method for filing Form 5884-D can vary depending on the options provided by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and your preference. Here are the three common methods you can use:
Offline filing:
If you prefer to file your tax forms manually by mail, follow these steps:
a. Obtain a physical copy of Form 5884-D from the IRS. You can visit the IRS website at www.irs.gov or call their toll-free number at 1-800-829-3676 to request the form.
b. Fill out the form accurately and legibly using black ink or type it using a typewriter.
c. Gather any required documentation or supporting materials as outlined in the form's instructions.
d. Make a copy of the completed form and all attachments for your records.
e. Mail the original form and attachments to the appropriate IRS address provided in the form's instructions. It's recommended to send it via certified mail to have proof of delivery.
Online filing
The IRS provides an online platform called the modernized e-File (MeF) system that allows businesses to file certain tax forms electronically. As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, Form 5884-D was not available for electronic filing. However, it's always a good idea to check the IRS website or consult with a tax professional to determine if online filing options have been updated since then.
E-filing with authorized software
Another option for electronic filing is to use authorized tax preparation software. Check with the software provider to confirm if Form 5884-D is supported for e-filing. If it is, follow the software's instructions to complete and submit the form electronically.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 5884-D
When filing Form 5884-D, which is used to claim the "Qualified Disaster Recovery Assistance" credit, it's important to be accurate and thorough to avoid making mistakes that could delay or jeopardize your claim. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
**Incorrect or incomplete information: **Ensure that all the required fields on Form 5884-D are filled out accurately and completely. Double-check your name, address, and Social Security Number or Employer Identification Number (EIN) for accuracy.
**Using outdated forms or instructions: **Always use the most recent version of Form 5884-D and follow the instructions provided by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Using outdated forms or instructions may lead to errors or delays in processing your claim.
Failing to meet eligibility criteria: The Qualified Disaster Recovery Assistance credit is available to businesses and tax-exempt organizations that meet certain criteria related to federally declared disasters. Make sure you meet all the eligibility requirements before claiming the credit.
Incorrect calculation of the credit amount: The credit amount is determined based on qualified wages paid to eligible employees during the applicable period. Ensure that you accurately calculate the credit amount by referring to the instructions provided by the IRS. Double-check your calculations to avoid errors.
**Lack of supporting documentation: **It's crucial to maintain adequate documentation to support your claim. This may include records of qualified wages paid, disaster declarations, and other relevant documents. Failure to provide supporting documentation or maintaining incomplete records may result in the denial or reduction of your claim.
Missing the deadline: Ensure that you file Form 5884-D within the specified deadline. The deadline can vary depending on the disaster declaration and can be extended in certain cases. Stay informed about the specific deadline for your situation to avoid missing it.
Neglecting to review the form: Before submitting Form 5884-D, carefully review all the information entered to identify any errors or omissions. It's a good practice to double-check your entries, calculations, and supporting documentation to minimize mistakes.
Key Takeaways
Form 5884-D plays a pivotal role in facilitating the "Work Opportunity Credit" and encouraging employers to hire individuals from targeted groups who may face employment barriers.
By leveraging this tax credit, businesses can make a positive impact on society while enjoying potential financial benefits. However, it is crucial to stay up to date with the latest guidelines and consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance and accurate reporting.
Remember, the information provided in this blog is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace professional advice. Always consult with a tax professional or refer to the most recent IRS publications and instructions for Form 5884-D to understand and comply with the latest regulations and requirements.


