- IRS forms
- Form 4810
Form 4810: Request For Prompt Assessment Under Internal Revenue Code Section 6501(d)
Download Form 4810When it comes to taxes, prompt assessment plays a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in collecting taxes owed by individuals and businesses. The IRS has various mechanisms in place to assess and collect taxes, and one such mechanism is Form 4810, used for requesting prompt assessment under Internal Revenue Code (IRC) Section 6501(d).
Prompt assessment is essential for both taxpayers and the IRS. For taxpayers, it provides a resolution to tax-related issues in a timely manner, minimizing uncertainty and allowing them to plan accordingly. For the IRS, prompt assessment ensures the efficient collection of taxes owed, reduces the risk of tax evasion, and enables the allocation of resources to other areas of tax administration.
In this blog post, we will explore the purpose of Form 4810, its significance, and the process involved in requesting a prompt assessment.
Purpose of Form 4810
Internal Revenue Code Section 6501 establishes the statute of limitations for the IRS to assess and collect taxes. Generally, the statute of limitations is three years from the date a tax return is filed. However, there are certain situations where the statute of limitations can be extended or suspended.
Section 6501(d) specifically deals with situations where a taxpayer makes a written request to the IRS for prompt assessment. The taxpayer may have reasons for wanting the IRS to assess their taxes sooner rather than later, such as when they need to resolve their tax liabilities quickly for various purposes, including finalizing a business transaction or securing a loan.
By filing Form 4810, the taxpayer is formally requesting the IRS to expedite the assessment of their tax liability. The IRS will review the request and, if approved, will assess the taxpayer's taxes promptly. This allows the taxpayer to address their tax obligations more efficiently and proceed with their financial affairs.
Benefits of Form 4810
Form 4810 offers several benefits for taxpayers who need to expedite the assessment process. Here are some of the benefits associated with filing Form 4810:
**Timely resolution: **By filing Form 4810, taxpayers can request the IRS to assess their tax liability promptly. This can lead to a quicker resolution of any outstanding tax issues or disputes, allowing taxpayers to address their tax obligations more efficiently.
**Statute of limitations extension: **Under normal circumstances, the IRS has a limited time to assess additional taxes after a return is filed. However, by filing Form 4810, taxpayers can extend the statute of limitations for assessment. This can be particularly useful when taxpayers want to ensure that their tax liability is accurately determined and to avoid potential future tax assessments.
**Avoidance of penalties and interest: **By requesting a prompt assessment, taxpayers can reduce or avoid potential penalties and interest charges that may accrue over time. Timely assessment and payment can help minimize the additional costs associated with outstanding tax liabilities.
Certainty and peace of mind: When taxpayers file Form 4810, they initiate the assessment process and provide all necessary information to the IRS. This can bring a sense of certainty and peace of mind, knowing that their tax situation is being actively addressed and resolved.
Clarification of tax obligations: Prompt assessment can help taxpayers gain a clearer understanding of their tax obligations. By engaging in the assessment process, taxpayers may receive detailed explanations and calculations from the IRS, allowing them to better comprehend the factors contributing to their tax liability.
It's important to note that Form 4810 is subject to specific eligibility criteria and should be filed within the appropriate timeframes as outlined by the IRS.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 4810?
To be eligible to file Form 4810, you must meet certain criteria:
Expired or expiring assessment period: The normal assessment period for a tax return is generally three years from the filing date or the due date, whichever is later. If this assessment period is about to expire or has already expired, you may be eligible to file Form 4810.
Reasonable basis for assessment: You must have a reasonable basis to request the assessment. This means you should have valid reasons to believe that there is a tax liability or deficiency, and it should not be a frivolous or unfounded claim.
Compliance with other requirements: You should be in compliance with other IRS requirements, such as filing all required tax returns and paying any taxes owed.
It's important to note that the eligibility criteria and requirements for filing Form 4810 may vary, and the instructions provided with the form should be carefully reviewed to ensure accurate completion and submission.
How To Complete Form 4810: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here's a step-by-step guide to completing Form 4810:
Step 1: Obtain the form
You can obtain Form 4810 from the official IRS website (irs.gov) or by contacting the IRS directly. Make sure you have the most recent version of the form.
Step 2: Provide your personal information
Enter your name, address, Social Security number (or taxpayer identification number), and other requested personal information at the top of the form. If you are married and filing jointly, include your spouse's information as well.
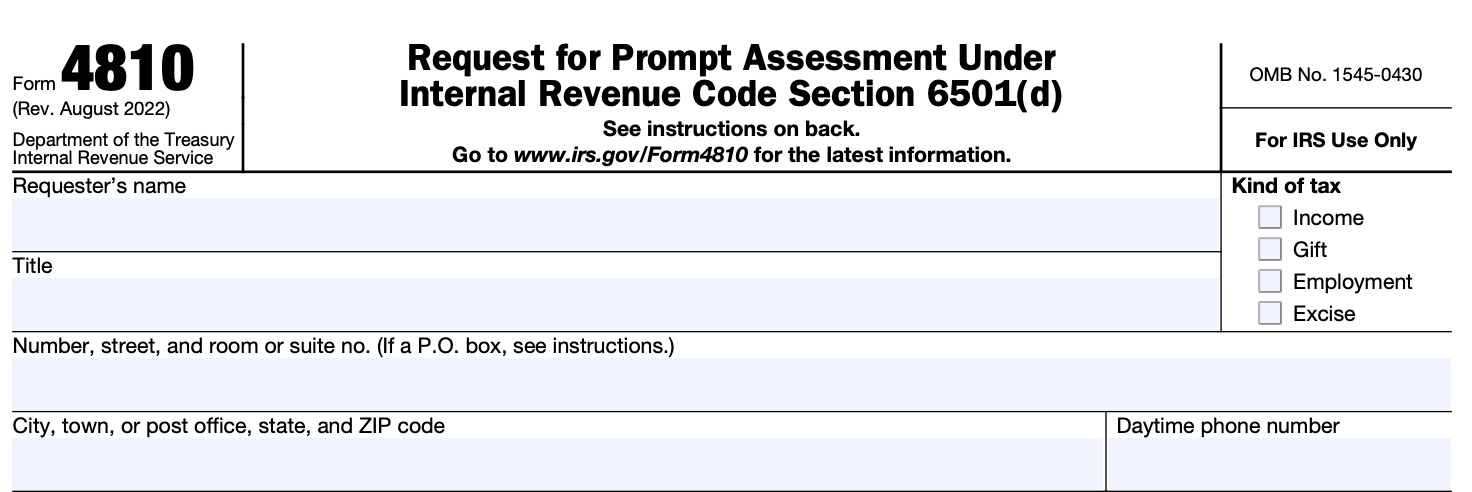
Step 3: Complete Part I - Taxpayer Information
In Part I, provide information about the tax year for which you are requesting prompt assessment. Include the tax return type (e.g., Form 1040), the tax year, and the date you filed your original return.
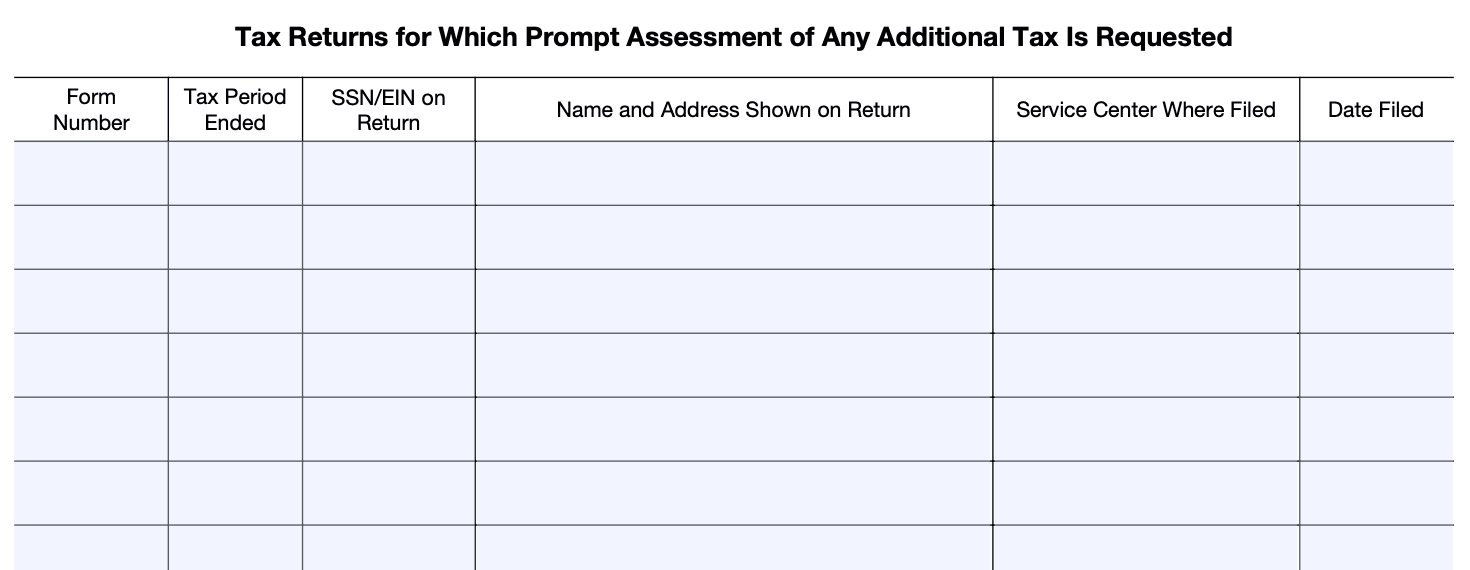
Step 4: Complete Part II - Reason for Request
In Part II, explain the reason for your request. Describe the specific issue or circumstances that led you to believe there might be additional taxes owed. Be clear and concise in your explanation.

Step 5: Attach supporting documents
If you have any supporting documentation that helps substantiate your claim, such as receipts, records, or calculations, attach them to the form. These documents can provide further clarification to the IRS regarding your request.


Step 6: Sign and date the form
Ensure that you and your spouse (if applicable) sign and date the form in the designated spaces. Unsigned forms may be rejected by the IRS.
Step 7: Submit the form
Make a copy of the completed form and all attached documents for your records. Then, mail the original form to the appropriate IRS address. Check the instructions on the form or the IRS website for the correct mailing address based on your location.
Step 8: Follow up with the IRS
After submitting Form 4810, it is advisable to follow up with the IRS to ensure they received your request. You can contact the IRS directly or consult with a tax professional for guidance on the next steps.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 4810
When filing Form 4810, there are a few special considerations to keep in mind. Here are some key points:
Purpose of Form 4810: Form 4810 is used to request the prompt assessment of a tax liability. It is typically used when there is concern about the statute of limitations expiring on a particular tax assessment.
Time limit: The request for prompt assessment must be filed within three years from the time the tax return was filed or within two years from the time the tax was paid, whichever is later.
**Supporting documentation: **It is essential to provide all necessary supporting documentation to substantiate the need for prompt assessment. This can include relevant tax returns, statements, receipts, or any other relevant evidence supporting your request.
Explanation of need: You should provide a clear and detailed explanation of why you believe a prompt assessment is necessary. This can include factors such as potential fraud, concerns about the taxpayer's ability to pay, or other circumstances that warrant expedited assessment.
**Contact information: **Ensure that your contact information, including your name, address, phone number, and taxpayer identification number (TIN), is accurate and up to date. This will help the IRS communicate with you regarding your request.
Professional assistance: Consider consulting with a tax professional or an experienced tax attorney to assist you in preparing and filing Form 4810. They can provide guidance on the specific requirements and help you present your case effectively.
**Follow-up: **After filing Form 4810, it is important to follow up with the IRS to confirm receipt of your request and to inquire about the status of your application. You can contact the IRS using the phone number or address provided on their official website or in the instructions for Form 4810.
Filing Deadlines & Extensions Form 4810
Regarding filing deadlines and extensions for Form 4810, here are some general points to consider:
Deadline: The filing deadline for Form 4810 is typically determined based on the specific circumstances and requirements of the taxpayer. It is best to consult the IRS instructions for Form 4810 or seek professional tax advice to determine the applicable deadline for your situation.
**Extensions: **In general, the IRS allows extensions for various tax forms, but it's important to note that Form 4810 may have specific rules regarding extensions. It is recommended to review the instructions for Form 4810 or consult a tax professional to understand the options for requesting an extension, if available.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Filing Form 4810
When filing Form 4810, it's important to avoid common mistakes to ensure accurate and timely processing. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
Incorrect or incomplete information: Ensure that you provide accurate and complete information on the form. Double-check all the details, including your name, address, Social Security Number (SSN), tax year, and tax type.
Missing or inaccurate taxpayer identification number (TIN): Use the correct TIN, which is typically your SSN or Employer Identification Number (EIN). Providing an incorrect or missing TIN can lead to processing delays or rejection of the form.
Improper selection of tax type: Make sure you select the correct tax type for which you are requesting a prompt assessment. Check the instructions or consult a tax professional if you're unsure about the applicable tax type.
Failure to attach supporting documents: Depending on the circumstances, you may need to attach supporting documents to your Form 4810. These could include copies of tax returns, schedules, or other relevant documents. Ensure you include all the necessary attachments as specified in the instructions.
**Late filing: **The request for prompt assessment must be filed within three years after the due date of the return or the date the return was filed, whichever is later. Filing the form after the deadline may result in the rejection of your request.
Lack of explanation or reasoning: Clearly explain the reason for your request for a prompt assessment. Provide sufficient details and supporting information to justify why you believe an accelerated assessment is necessary. Vague or incomplete explanations may lead to rejection.
Failure to sign and date: Sign and date the form where indicated. Unsigned forms will not be processed. Ensure that you have the authority to sign on behalf of the taxpayer if applicable.
**Incorrect mailing address: **Use the correct mailing address as provided in the form instructions. Sending the form to the wrong address may cause delays in processing or non-delivery of your request.
Failure to keep copies: Before submitting the form, make copies of all the documents for your records. This will help you keep track of your submission and serve as evidence of your request if needed.
**Ignoring communication: **If the IRS requests additional information or clarification regarding your request, promptly respond to their inquiries. Ignoring or delaying responses may lead to complications or denial of your request.
Conclusion
Form 4810, Request for Prompt Assessment Under Internal Revenue Code Section 6501(d), is a valuable tool for taxpayers seeking a prompt resolution to their outstanding tax liabilities. By expediting the assessment process, this form helps individuals and businesses mitigate uncertainty, plan accordingly, and resolve tax-related issues efficiently.
If you find yourself in a situation where you believe prompt assessment is warranted, consult with a qualified tax professional or reach out to the IRS for guidance. Understanding your rights and responsibilities as a taxpayer is crucial when dealing with the IRS, and utilizing Form 4810 can be an effective way to expedite the assessment of taxes owed.


