- IRS forms
- Form 2848
Form 2848: Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative
Download Form 2848Form 2848 is an official document issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. Its primary purpose is to grant authority to an appointed representative to act on behalf of a taxpayer in tax-related matters. The person authorized to act on behalf of the taxpayer is referred to as the "representative," and the taxpayer is known as the "principal."
This form essentially establishes a legal relationship between the principal and the representative, allowing the representative to handle various tax-related tasks and communicate with the IRS on behalf of the principal.
Whether you're an individual taxpayer or a business owner, understanding the purpose, significance, and proper utilization of Form 2848 is essential for effective tax management. In this blog, we'll delve into the details of Form 2848, exploring its key components, reasons to use it, and the process for completing and filing the form accurately.
Importance of Form 2848
Form 2848 grants the representative the authority to perform various tasks, such as signing documents, accessing tax information, and representing the taxpayer in discussions or proceedings with the IRS. The importance and benefits of Form 2848 include:
Delegation of authority: Form 2848 enables taxpayers to delegate their authority to a representative, allowing them to handle tax-related matters efficiently. This is particularly useful when the taxpayer is unable to personally attend to tax affairs due to illness, absence, or other reasons.
Convenience and flexibility: Using Form 2848, taxpayers can authorize someone else, such as a tax professional, to handle their tax matters. This saves time and effort for the taxpayer, as the representative can interact directly with the IRS on their behalf, reducing the need for the taxpayer's direct involvement.
Expertise and knowledge: Taxpayers often appoint representatives who possess specialized knowledge and expertise in tax law and regulations. This ensures that their tax matters are handled by individuals who are well-versed in the complexities of the tax system, potentially minimizing errors and maximizing opportunities for tax planning and savings.
Representation in IRS interactions: When a representative is authorized through Form 2848, they can represent the taxpayer in dealings with the IRS, such as responding to notices, providing additional information, or attending meetings or hearings. This allows the taxpayer to have a knowledgeable advocate who can navigate the complexities of the tax system and effectively communicate with the IRS on their behalf.
Confidentiality and privacy: The representative appointed through Form 2848 is required to adhere to strict confidentiality rules regarding the taxpayer's tax information. This ensures that sensitive financial and personal details remain confidential and are not disclosed without the taxpayer's consent.
Streamlined communication: Using Form 2848 establishes a clear line of communication between the IRS and the authorized representative. This facilitates efficient and effective communication, reducing the chances of miscommunication or delays in resolving tax matters.
Compliance with IRS requirements: When taxpayers engage in certain transactions or face specific tax issues, they may be required to provide the IRS with a power of attorney to authorize a representative. Form 2848 fulfills this requirement, ensuring compliance with IRS rules and regulations.
Representation across various tax periods: The authorization granted through Form 2848 generally covers all tax periods, unless specifically limited or revoked. This means that the representative can act on behalf of the taxpayer for past, present, and future tax matters, providing continuity and consistency in dealing with the IRS.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 2848?
The following individuals or entities are generally eligible to file Form 2848:
Taxpayers: Any individual or entity that has a tax-related matter before the IRS can file Form 2848 to authorize a representative to act on their behalf.
Individuals: This includes individuals who are filing their personal income tax returns, such as individuals filing Form 1040.
**Businesses: **Business entities, such as corporations, partnerships, (link: https://fincent.com/blog/your-how-to-guide-to-llcs-steps-to-launch-pros-cons text: limited liability companies (LLCs)), and trusts, can file Form 2848 to designate a representative to handle tax matters related to their business.
Fiduciaries: Individuals serving as fiduciaries for estates, trusts, or other entities can file Form 2848 on behalf of those entities.
**Tax professionals: **Attorneys, (link: https://fincent.com/glossary/american-institute-of-certified-public-accountants text: certified public accountants (CPAs)), enrolled agents, and other tax professionals can file Form 2848 if they have been authorized by the taxpayer to represent them before the IRS.
How To Complete Form 2848: A Step-by-Step Guide
Form 2848, also known as the Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative, is a form used by individuals or businesses to authorize someone to represent them before the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Here's a step-by-step guide to completing Form 2848:
Step 1: Obtain the form
You can download Form 2848 from the IRS website.
Step 2: Provide taxpayer information
Enter the taxpayer's personal information in Part I, including their name, address, Social Security Number (SSN), and daytime telephone number. If the form is being filed on behalf of a business, provide the Employer Identification Number (EIN) instead of an SSN.
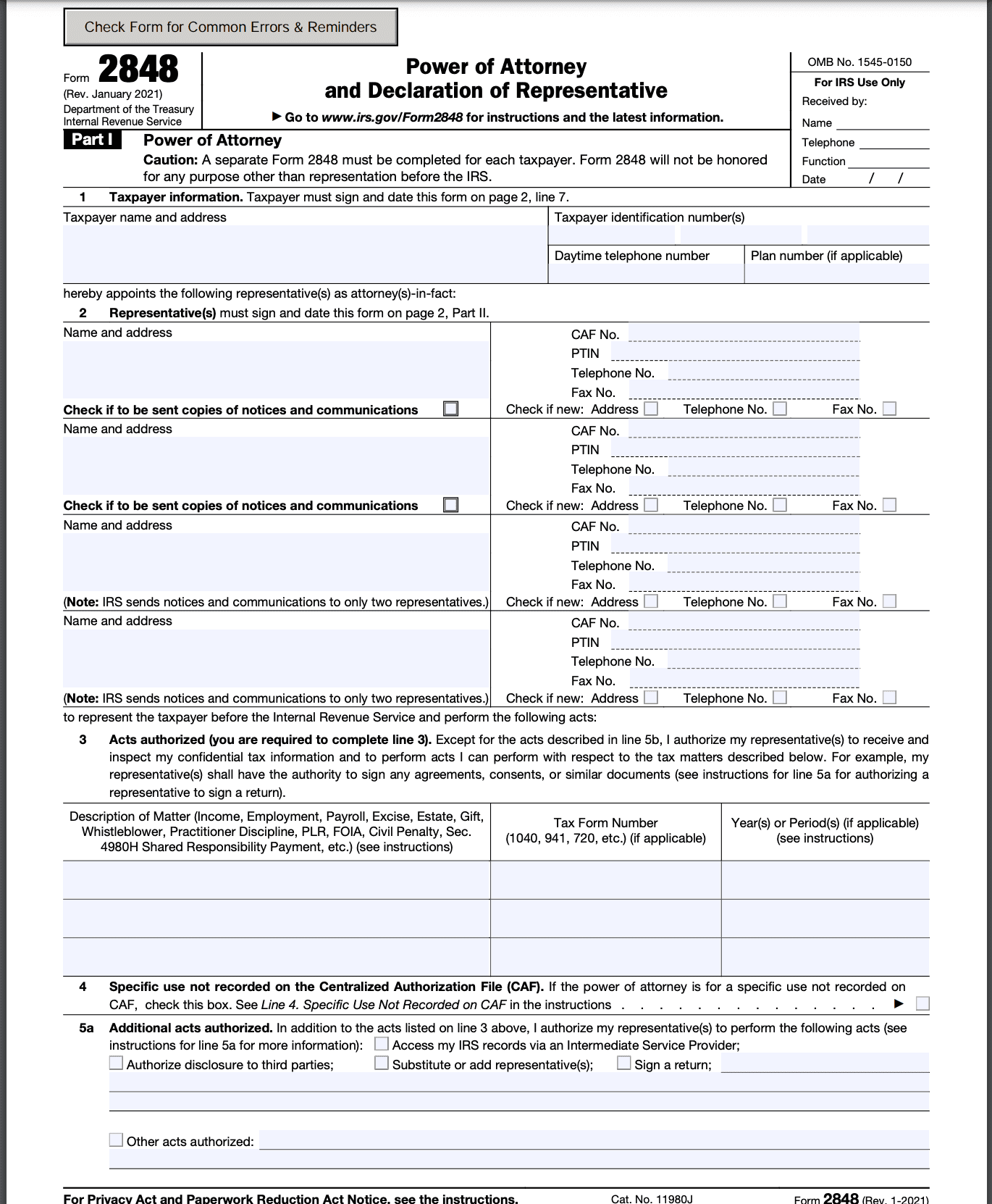

Step 3: Designate representative(s)
In Part II, enter the name, address, and phone number of the individual(s) you are authorizing as your representative(s). You can designate more than one representative by attaching a separate sheet with their information.

Step 4: Specify tax matters
Indicate the specific tax matters for which you are authorizing your representative(s) to act on your behalf in Part III. You can authorize them for a specific tax year or for all tax years. You can also limit their authority to certain tax forms, schedules, or matters.
Step 5: Signature and declaration
The taxpayer or authorized individual must sign and date the form in Part IV. If the taxpayer is a
business, the form should be signed by an authorized individual, such as an officer or a partner.
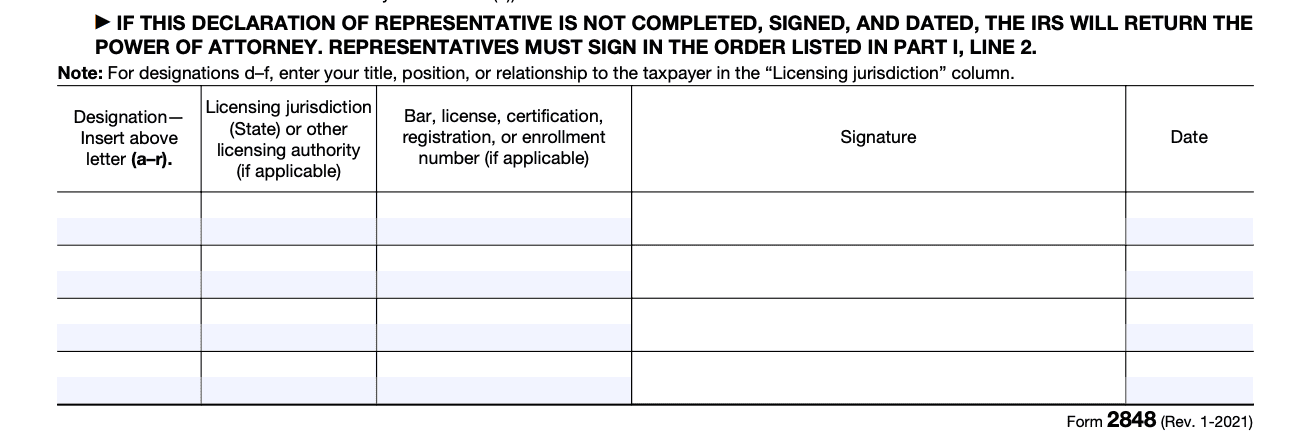
Step 6: Representative's declaration
If you have designated a representative, they must also sign and date the form in Part V, accepting the appointment and acknowledging the responsibilities that come with it.
Step 7: Attachments and mailing
If you have any additional information or attachments, such as a power of attorney document, include them with Form 2848. Make a copy of the completed form and attachments for your records, and then mail the original to the appropriate IRS office. The mailing address is provided in the form instructions.
Note: It's important to read the instructions for Form 2848 thoroughly before completing the form to ensure you provide all necessary information and follow any specific requirements or guidelines.
Remember that Form 2848 authorizes someone to represent you before the IRS, so choose your representative(s) carefully and only grant them the authority you are comfortable with.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 2848
When filing Form 2848, also known as Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative, there are several special considerations you should keep in mind to ensure accuracy and proper authorization. Here are some important points to consider:
Correctly identify the taxpayer and representative: Provide accurate and complete information for both the taxpayer (the person granting authority) and the representative (the person receiving authority). This includes names, addresses, and taxpayer identification numbers (such as Social Security numbers or employer identification numbers).
Specify the tax matters: Clearly state the specific tax matters for which the representative is authorized to act on behalf of the taxpayer. This may include income tax, estate tax, gift tax, or other types of taxes. Be specific about the tax forms, years, and periods covered.
Sign and date the form: Both the taxpayer and the representative must sign and date the Form 2848. If the taxpayer is a corporation or partnership, an authorized person must sign on behalf of the entity.
Limited or general authority: Determine whether the authority granted to the representative is limited or general. Limited authority restricts the representative's power to certain tax matters, while general authority grants broader powers. Specify the limitations or provide clear instructions if limited authority is intended.
Designation of multiple representatives: If the taxpayer wishes to designate multiple representatives, each representative's information should be provided on a separate Form 2848. Clearly indicate the scope of authority granted to each representative.
Keep copies of the form: It is essential to retain a copy of the completed and signed Form 2848 for your records. The IRS may request a copy for verification purposes.
Update or revoke the authorization: If there are any changes to the representative's information or if the taxpayer wishes to revoke the authorization, submit a new Form 2848 to the IRS. Make sure to clearly indicate that it is an update or a revocation.
Authorization for specific tax years: By default, Form 2848 authorizes the representative to act for all tax years, including future years. However, the taxpayer can limit the representation to specific years or periods if desired.
Third-party designee: The taxpayer has the option to designate a third-party designee who can discuss the Form 2848 with the IRS. This person may be contacted to clarify information on the form.
It's important to note that Form 2848 is a legal document, and errors or incomplete information could result in delays or complications.
Modes of Filing Form 2848: Offline/Online/E-Filing
Here's how you can file Form 2848 using different methods:
Offline filing
a. Download the form: Go to the official IRS website and search for "Form 2848." Download and print the form.
b. Complete the form: Fill out the form with accurate information. Include your name, address, taxpayer identification number (such as your Social Security Number or Employer Identification Number), and the representative's information.
c. Sign the form: Both you and your representative must sign and date the form.
d.** Submit the form**: Mail or fax the completed form to the appropriate IRS address or fax number provided in the instructions for Form 2848.
Online filing
a. Visit the IRS online services: Go to the official IRS website and navigate to the "Online Services" section.
b. **Create an account: **If you don't already have one, create an account with the IRS. You will need to provide personal information to verify your identity.
c.** Access the e-services application**: Once you have an account, log in and access the E-Services application. d. Complete Form 2848: Fill out the required fields and provide the representative's information.
e. Electronically sign: Use the electronic signature method provided by the IRS to sign the form.
f.** Submit the form**: After signing, submit the form electronically through the E-Services application.
E-filing
a. Use authorized e-file software: If you're using authorized tax preparation software to file your tax return, some software options may include the ability to electronically file Form 2848 along with your return.
b.** Follow software instructions**: Within the tax software, look for the option to file Form 2848 or grant power of attorney. Follow the instructions provided by the software to complete and submit the form electronically.
Remember to carefully review the instructions for Form 2848 to ensure you provide accurate information and meet all the requirements. It's also advisable to retain a copy of the completed form for your records, regardless of the filing method you choose.
Key Takeaways
- Form 2848, the Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative, is a vital tool that empowers individuals and businesses to effectively manage their tax obligations.
- By designating a representative, taxpayers can benefit from professional expertise, save time, and streamline their interactions with the IRS.
- Understanding the purpose and proper utilization of Form 2848 is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of tax management successfully.
- By completing and filing this form accurately, individuals and businesses can ensure efficient tax administration and compliance with IRS regulations, ultimately contributing to their financial well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Form 2848?
Form 2848 is a legal document that grants authority to a designated representative to act on behalf of an individual or business entity for tax-related matters with the IRS.
2. Who needs to file Form 2848?
Form 2848 is typically filed by individuals or businesses that want to authorize another person (such as an attorney, accountant, or tax professional) to represent them before the IRS.
3.** What information is required on Form 2848?**
Some of the information required on Form 2848 includes the taxpayer's name, tax identification number (e.g., Social Security Number or Employer Identification Number), representative's information, and a description of the specific tax matters or years for which the representative is authorized to act.
4. Can I authorize more than one representative on Form 2848?
Yes, you can authorize multiple representatives by listing their information in Part II of Form 2848. However, you must ensure that each representative is properly qualified and authorized to act on your behalf.
5. Do I need to sign and date Form 2848?
Yes, both the taxpayer and the authorized representative(s) must sign and date the form. If the taxpayer is a business entity, the form must be signed by an individual who has the authority to bind the entity.
6.** Can I revoke or modify Form 2848?**
Yes, you can revoke or modify Form 2848 by submitting a new Form 2848 with the updated information or by sending a written statement to the IRS indicating the changes. It's important to notify both the IRS and the representative(s) about any changes.
- How long does the authorization on Form 2848 last?
The authorization on Form 2848 remains in effect until it is revoked or automatically expires after a specific period. Generally, the authorization expires after three years from the date signed unless you specify an earlier expiration date or revoke it.
8. Can Form 2848 be used for state tax matters?
No, Form 2848 is specific to the IRS and federal tax matters. Each state may have its own power of attorney form for authorizing representation for state tax issues.
9. How should I submit Form 2848?
Form 2848 can be submitted by mail or fax to the appropriate IRS office. Alternately, you may be able to submit it electronically through the IRS e-services platform, depending on the availability and requirements.
10. Where can I find Form 2848?
Form 2848 can be downloaded from the IRS website (www.irs.gov) by searching for "Form 2848" in the forms and publications section. You can also obtain a copy from local IRS offices or request one by calling the IRS at their toll-free number.


