- IRS forms
- Form 1098-Q
Form 1098-Q: Guide to Qualifying Longevity Annuity Contracts
Download Form 1098-QIf you have a qualifying longevity annuity contract (QLAC), you'll likely need to file Form 1098-Q. In this comprehensive guide, we'll cover everything you need to know about Form 1098-Q, including what it is, who needs to file it, what information is included, how to fill it out, when it's due, how to file it, the consequences of not filing, and how it affects your taxes. We'll also include some frequently asked questions to help clear up any confusion you might have.
What is Form 1098-Q?
Form 1098-Q is used by insurance companies to report information about qualifying longevity annuity contracts (QLACs), which are a type of annuity that provides income later in life. A QLAC is an annuity contract purchased with funds from a qualified retirement plan or IRA that provides a guaranteed stream of income payments starting on a specified date in the future. QLACs are unique in that they are exempt from required minimum distribution (RMD) rules until the date payments begin.
Who needs to file Form 1098-Q?
If you have a QLAC, your insurance company will need to file Form 1098-Q with the IRS and provide you with a copy for your records. You do not need to file Form 1098-Q with your tax return. Form 1098-Q filing requirements:
- Individuals or entities issuing contracts intended to be a QLAC that are purchased or held under certain plans, annuities, or accounts are required to file Form 1098-Q.
- Plans covered include those described in sections 401(a), 403(a), 403(b), and 408 (excluding Roth IRAs), as well as eligible governmental plans under section 457(b).
What information is included in Form 1098-Q?
Form 1098-Q (Rev. December 2019) includes the following information:
- The name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN) of the insurance company filing the form
- The name, address, and TIN of the owner of the QLAC
- The amount of the premium paid for the QLAC
- The date the QLAC was purchased
- The date payments are scheduled to begin
- The total value of the QLAC on December 31 of the prior year
When is Form 1098-Q due?
Form 1098-Q must be filed with the IRS by the last day of February 28 through the mail. If you are filing electronically, you have until March 31st to file the form. However, recipients' copy should be mailed by January 31.
How to fill out Form 1098-Q?
Your insurance company is responsible for filing Form 1098-Q with the IRS. The issuer must provide a copy of the form to the owner of the QLAC as well. The form must be filed with the IRS by February 28 of the year following the year in which the distribution was made.
Filing Form 1098-Q is a straightforward process. Here are the steps you need to follow:
Step 1: Obtain the Form
The first step is to obtain Form 1098-Q from the IRS. You can download the form from the IRS website or order a paper copy by calling the IRS at 1-800-TAX-FORM (1-800-829-3676). Operating Hours are 7 a.m. to 10 p.m., from Monday to Friday, your local time — except Alaska and Hawaii which are Pacific time.
Step 2: Fill Out the Form
Once you have the form, you need to fill it out. The form has four copies, one for the recipient, one for the IRS, one for the state tax department (if required), and one for your records. You'll need to fill out all four copies.
Copy A of the form is for information about the IRS center, including the name, address, and TIN (Taxpayer Identification Number).
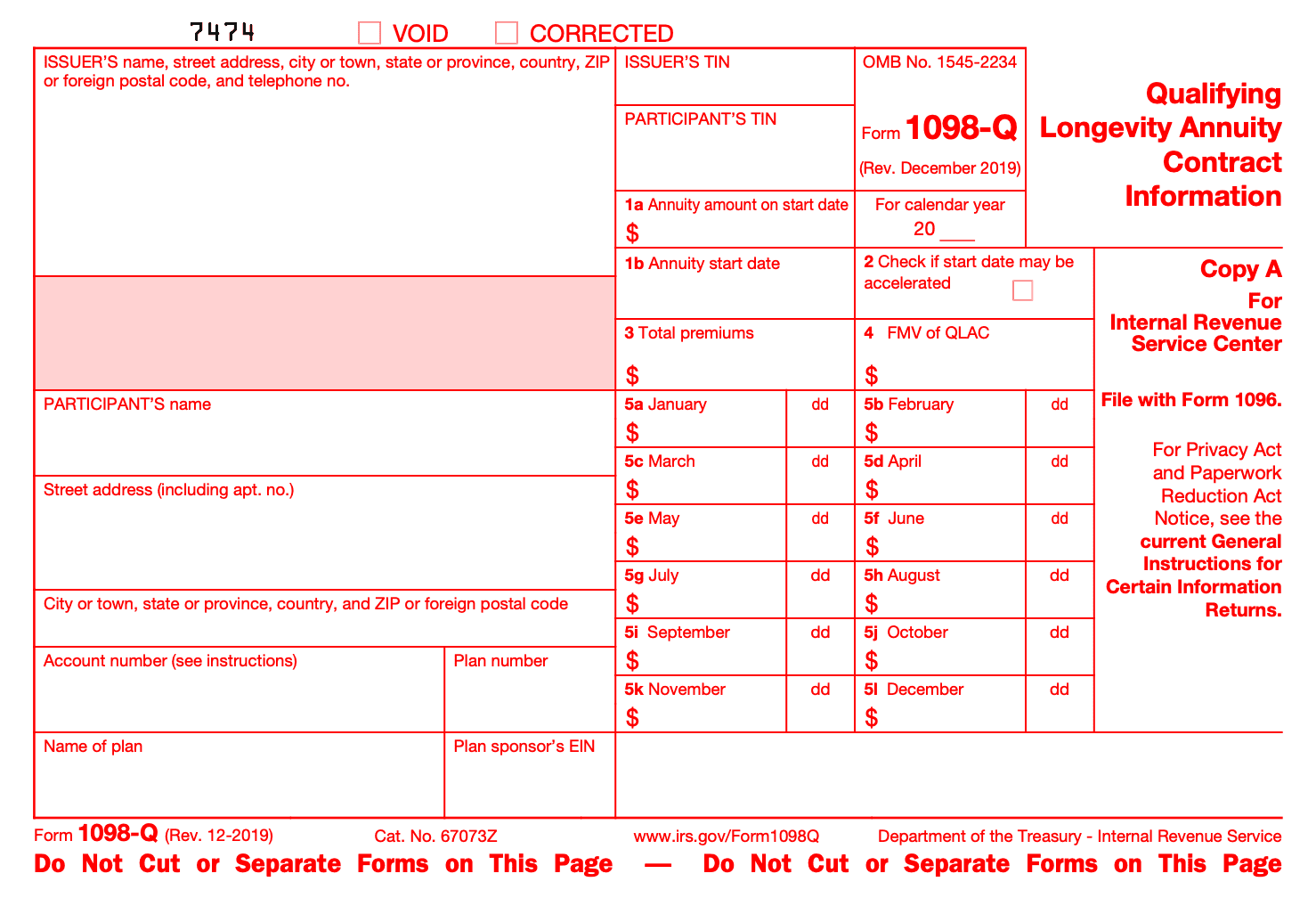
In Copy B and Copy C are for furnishing statements to recipients and for retaining in your own files. You'll need to provide information about the QLAC, including the name and TIN of the policyholder, the amount of premiums paid, and the amount of the QLAC contract.
Copy B
Copy C
Instructions for Participant by to fill the form:
- Box 1a: Annuitized amount on start date (if not started)
- Box 1b: Annuity start date (if not started), in format mm/dd/yyyy
- Box 2: Checkbox for possible accelerated start date
- Box 3: Cumulative premiums paid for contract, with limit of $135,000 for all QLACs since 2020. QLACs purchased under IRA or employer plans have a limit of 25% of account balance. Contact issuer if paid more.
- Box 4: Shows the fair market value (FMV) of QLAC as of December 31 of reporting year
- Boxes 5a through 5l: Displays the premium amounts and dates paid in the reporting year, with total payments and date of last payment for any month with multiple payments.
Step 3: Distribute the Form
After you've filled out the form, you need to distribute the copies to the appropriate parties. The recipient copy should be sent to the policyholder by January 31st of the year following the tax year. The IRS copy should be filed with the IRS by the last day of February (or March 31st if filing electronically). If you are required to file with the state, you'll need to file by the deadline specified by your state.
Step 4: Keep a Copy for Your Records
Be sure to keep a copy of the form for your records. You should keep a copy of the form along with any supporting documentation for at least 3-4 years from the date you filed the form. There are two options available for filing Form 1098-Q:
-
Option 1: File Form 1098-Q electronically
You can file Form 1098-Q electronically through the FIRE (Filing Information Returns Electronically) system. This option is available for those who have 250 or more forms to file. You can register for an account on the FIRE system and follow the instructions to file your Form 1098-Q electronically. This method is faster and more convenient than filing a paper return.
-
Option 2: Mail Form 1098-Q to the IRS
If you have fewer than 250 forms to file, you can mail Form 1098-Q to the IRS. The mailing address will depend on your location and whether or not you are including a payment with your return. You can find the appropriate address in the instructions for Form 1098-Q.
Check out the IRS specifications for premium and its limitations:
Limitations on Premiums — Plans:
Dollar Limitation:
The dollar limitation for all QLACs purchased under eligible plans is $135,000 as of 2020. The cumulative total premiums paid for all QLACs under these plans cannot exceed this limit.
Percentage Limitation:
- The maximum premium amount for a QLAC contract under an eligible employer plan or IRA is limited to 25% of the account balance.
- If the account balance is less than $540,000, the maximum premium amount is the lesser of $135,000 or the account balance multiplied by 0.25.
- If the account balance is $540,000 or more, the maximum premium amount is $135,000.
Limitations on Premiums — IRAs:
Dollar Limitation:
- For QLACs purchased under an IRA, the maximum premium that can be applied to the QLAC contract in a given year is the lesser of $135,000 or 25% of the individual's account balance.
- Exceeding this limit may result in additional tax liabilities.
Percentage Limitation:
The limit for QLACs purchased under an eligible employer plan or IRA is 25% of the account balance. Exceeding this limit may result in additional tax liabilities.
What are the consequences of not filing Form 1098-Q?
Issuers who fail to file Form 1098-Q with the IRS or provide a copy to the owner of the QLAC may be subject to penalties. The penalty for failure to file a correct information return is $280 per form, with a maximum penalty of $3,392,000 per year for large businesses.
The penalties for failing to file a correct Form 1098-Q are as follows:
- $50 per form if filed within 30 days of the due date, with a maximum penalty of $194,000 per year ($50 per form for up to 3,880 forms).
- $110 per form if filed more than 30 days after the due date but by August 1, with a maximum penalty of $556,500 per year ($110 per form for up to 5,050 forms).
- $280 per form if filed after August 1 or not filed at all, with a maximum penalty of $1,113,000 per year ($280 per form for up to 3,975 forms).
In addition to the penalties, the IRS may charge interest on any unpaid tax liabilities. Therefore, it is important to file Form 1098-Q accurately and on time to avoid any potential penalties and interest charges.
How does Form 1098-Q affect your taxes?
If you receive income from a qualifying longevity annuity contract (QLAC), you will need to report this income on your tax return. The income from a QLAC is not taxed until it is paid out to the annuitant. Therefore, you do not need to report the income until you begin receiving payments.
If the distribution is made after the owner reaches age 70½, it may be excluded from taxable income up to a certain amount, as long as the distribution is made in accordance with the requirements for QLACs.
The payments received from a QLAC are generally subject to federal income tax when they are received. However, a portion of the payments may be excluded from income if they are part of a return of premium. The exclusion is calculated using an IRS formula based on the premium paid for the QLAC, the owner's age, and the start date of the payments.
FAQs about Form 1098-Q
Q: What is a QLAC?
A: A QLAC is a qualifying longevity annuity contract, which is a type of annuity that provides income later in life, typically starting at age 85.
Q: Who can purchase a QLAC?
A: Individuals can purchase a QLAC with funds from their IRA or other qualified retirement plan.
Q: How much can be invested in a QLAC?
A: The maximum amount that can be invested in a QLAC is the lesser of $135,000 or 25% of the individual's total retirement account balances.
Q: Is there a penalty for taking a distribution from a QLAC before age 85?
A: Yes, there is a 25% penalty on the amount of the distribution if it is taken before age 85.
Q: What is the advantage of a QLAC?
A: A QLAC can provide income later in life when other sources of income may be running low, and it can help to protect against the risk of outliving one's retirement savings.
Q: How to report Form 1098-Q in Form 1040?
A: Form 1098-Q is an informational form and is generally not required to be reported on a tax return. There is no specific data entry screen for this form in Form 1040.
Q: What is the payer ID on 1099-Q?
A: Form 1099-Q is used to report distributions from Qualified Education Programs (QTPs) and the payer identification number (Payer ID) is the 9-digit number assigned by the IRS to the entity responsible for distributing the funds. The Payer ID is typically found in Box 7 of the Form 1099-Q.
Conclusion
Form 1098-Q is an important document for owners of QLACs and issuers of these annuity contracts. It provides information about the premiums paid into the QLAC and any distributions made from the contract. By understanding the requirements for filing Form 1098-Q and the tax implications of owning a QLAC, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement planning.


