- IRS forms
- Form 1098-E
Form 1098-E: Filing Requirements & Mistakes to Avoid
Download Form 1098-EIntroduction:
If you are a student or have student loans, it's important to know about Form 1098-E. This form reports the amount of interest paid on qualified student loans during the tax year. The information on Form 1098-E is used by the IRS to determine if you qualify for certain education-related tax deductions.
In this blog, we'll discuss what Form 1098-E is, who needs to file it, how to file it, when to file it, common mistakes to avoid when filing, and what to do if you encounter an issue.
What is Form 1098-E?
Form 1098-E is a tax form used to report the amount of interest paid on qualified student loans during the tax year. This form is issued by the entity that services your student loan, such as a bank or financial institution.
Who needs to file Form 1098-E?
If you paid $600 or more in interest on a qualified student loan during the tax year, you will receive a Form 1098-E from the entity that services your loan. The entity that services your loan is required to file Form 1098-E with the IRS and provide a copy to you.
When to file Form 1098-E?
The entity that services your loan must provide you with a copy of Form 1098-E by January 31st of the following year. They must also file a copy with the IRS by February 28th, or March 31st if filed electronically.
Contents of Form 1098-E
Here's a breakdown of the information required for each copy of Form 1098-E:
Copy A:
- Student's name, address, and social security number (SSN)
- Lender's name, address, and identification number (TIN)
- Total interest received during the year
- Box 1: Student loan interest received by the lender
- Checkbox for loans made before September 1, 2004, where loan origination fees and/or capitalized interest are not reported in box 1
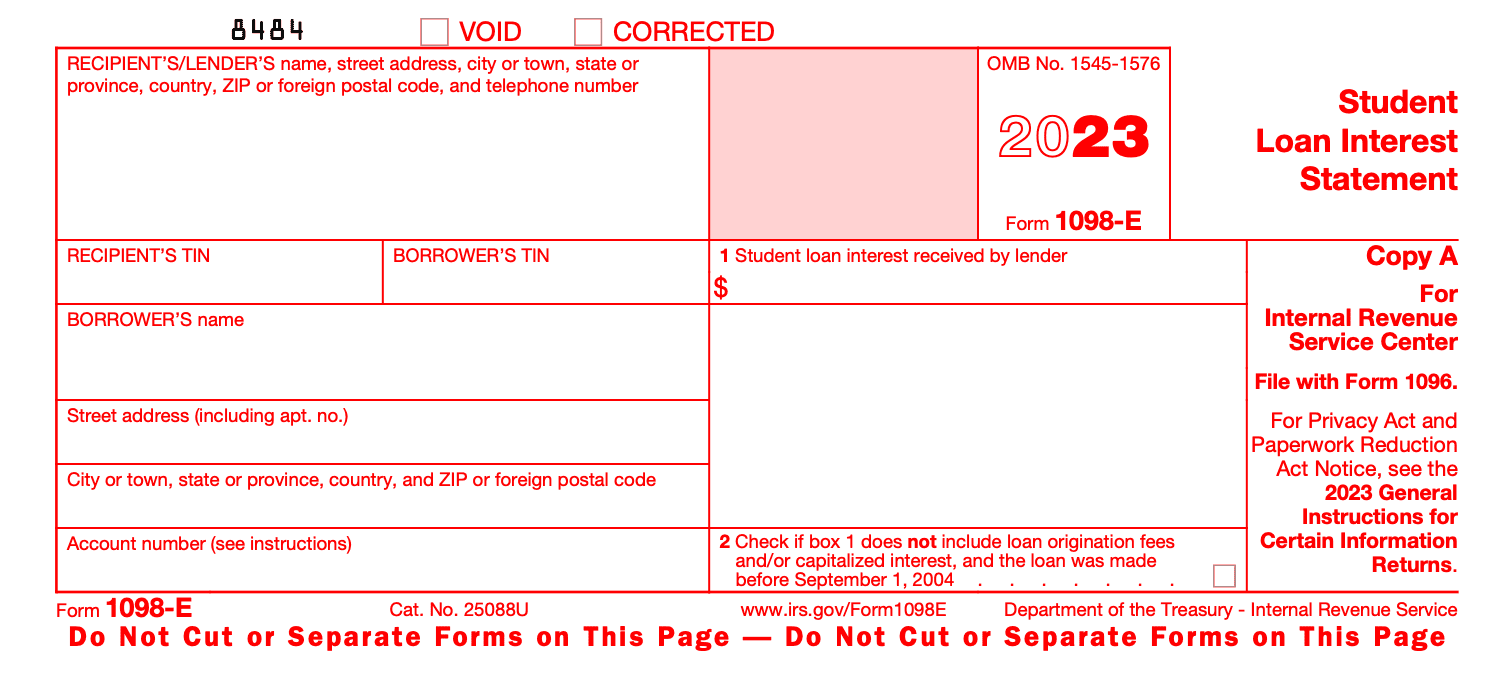
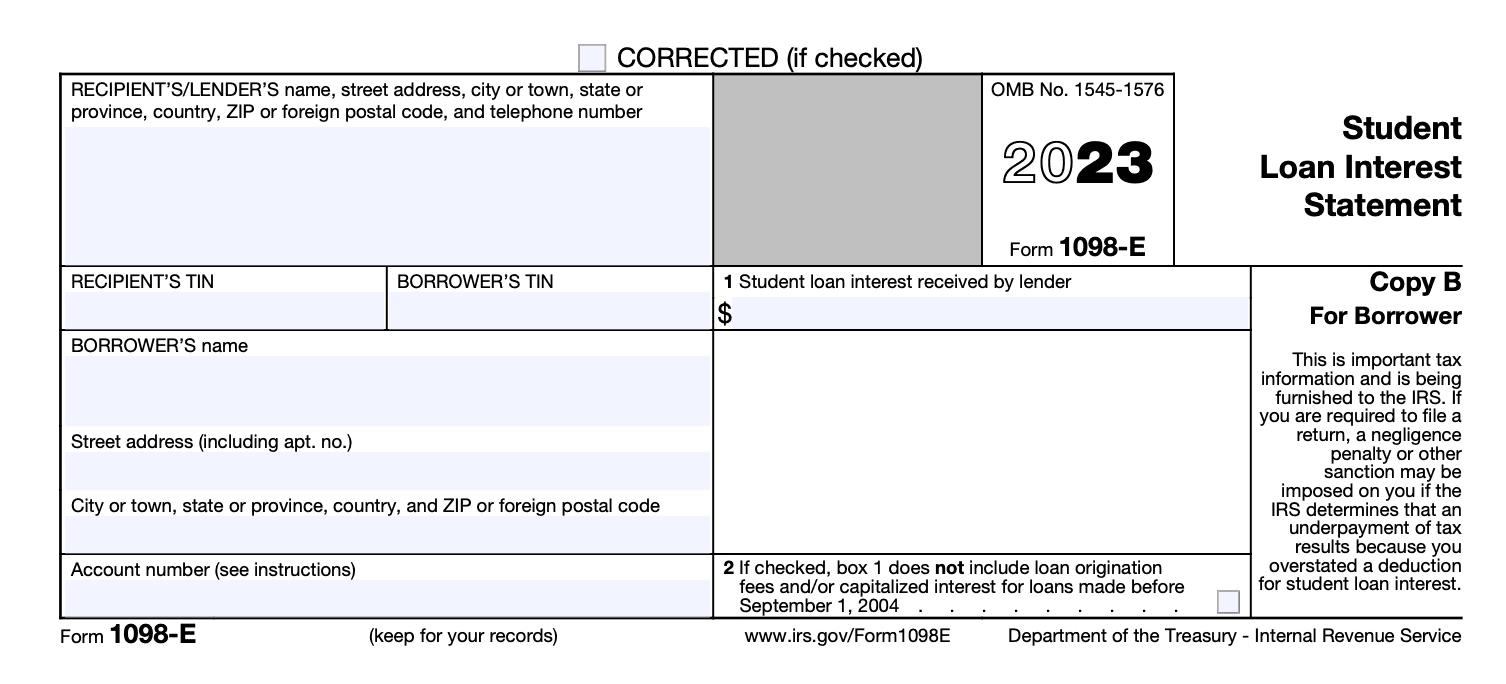
Copy B: Same information as Copy A, but for the borrower's records
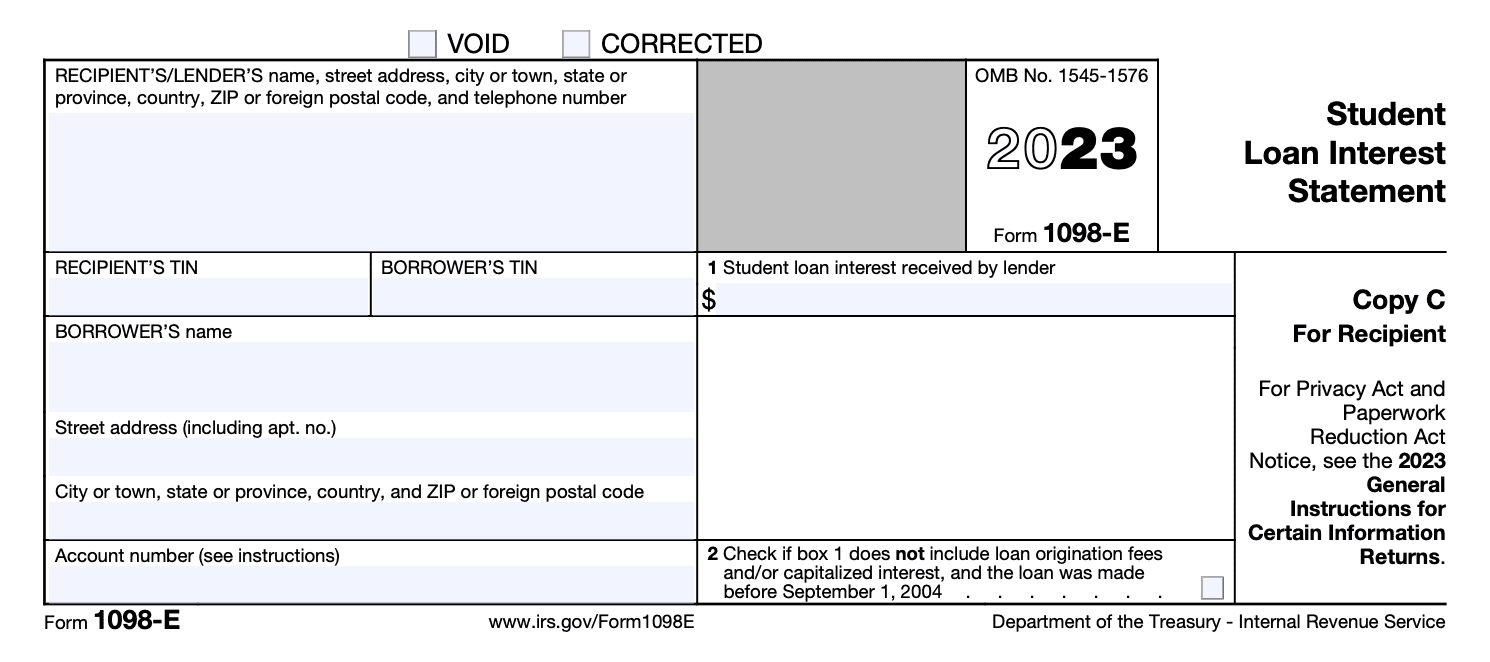
Copy C: Same information as Copy A, but for the filer's records
Steps on How to file Form 1098-E
As a borrower, you don't need to file Form 1098-E with the IRS. The entity that services your loan will handle this process for you. However, it's important to make sure that the information on Form 1098-E is accurate. If there are any errors, you should contact the entity that services your loan to have them corrected.
Key points to note about filing Form 1098-E:
- File Form 1098-E if you receive student loan interest of $600 or more from an individual during the year in the course of your trade or business.
- You may file a separate Form 1098-E for each student loan of the borrower or file one Form 1098-E for the interest from all student loans of the borrower.
- Financial institutions, governmental units (or any of its subsidiary agencies), educational institutions, or any other person who receives student loan interest of $600 or more from an individual during the course of your trade or business must file Form 1098-E.
- Only the first person to receive the interest payment must file Form 1098-E if more than one person has a connection with the loan.
- A student loan must be subsidized, guaranteed, financed, or otherwise treated as a student loan under a program of the federal, state, or local government, or of a postsecondary educational institution, or certified by the borrower as a student loan incurred solely to pay qualified higher education expenses to be reportable for 2023.
- Report interest paid on revolving accounts, such as credit card accounts, only if the borrower certifies that all the loan proceeds are solely used to pay qualified higher education expenses.
- Do not report interest on loans made under a qualified employer plan, as defined in section 72(p)(4), or under a contract purchased under a qualified employer plan within the meaning of section 72(p)(5).
- If you are required to file Form 1098-E, you must provide a statement or acceptable substitute, on paper or electronically, to the borrower.
- Educational institutions, insurers, and lenders may present the option to consent to receive Form 1098-E electronically.
- All filers of Form 1098-E may truncate a borrower’s TIN (social security number (SSN), individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN), adoption taxpayer identification number (ATIN), or employer identification number (EIN)) on payee statements.
- The account number is required if you have multiple accounts for a recipient for whom you are filing more than one Form 1098-E.
- Box 1 requires the interest you received on a student loan(s) during the calendar year.
- Check box 2 if loan origination fees and/or capitalized interest are not reported in box 1 for loans made before September 1, 2004.
How to Claim the Student Loan Interest Deduction?
To claim the student loan interest deduction, you need a 1098-E form showing $600 or more in interest payments to a lender within a year. But if you paid less or don't receive the form, you can request or download your loan servicer's payment history and interest statements. Keep copies of these records in case of an audit.
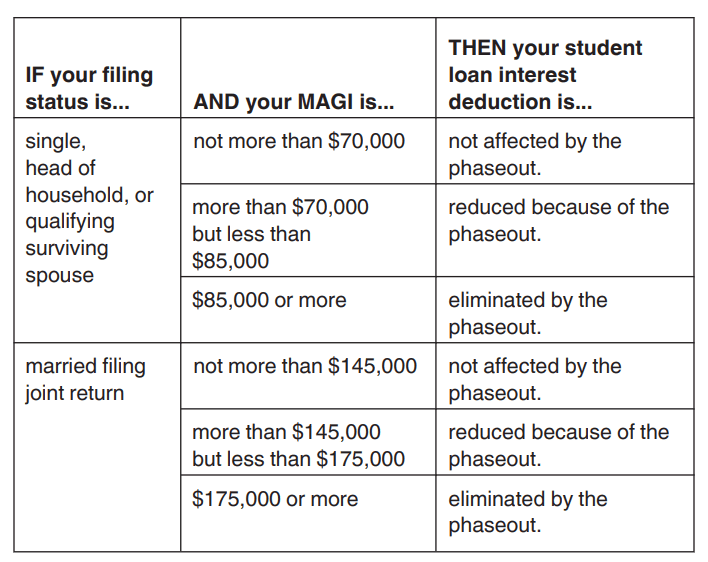
As long as you earned less than $85,000 as a single filer or $175,000 as a married joint filer and paid interest on a student loan during the year, you can claim the deduction on line 21 of Form 1040 without itemizing. You can deduct either the total interest you paid or up to $2,500, whichever is smaller. However, the deduction gradually phases out for single filers earning over $70,000 and joint filers earning over $145,000.
Who can Claim Student Loan Interest Deductions?
- Anyone who paid $600 or more in interest on their student loan debt to a lender within a calendar year.
- If you paid less than $600, you can still claim the deduction by requesting or downloading records of what you paid in interest and your payment history from your loan servicer.
- You can claim the deduction without needing to itemize on your Income Tax Return, or Form 1040.
- You can reduce your taxable income by either the total student loan interest you paid during the year or $2,500–whichever is smaller.
- The deduction phases out as your modified adjusted gross income rises. For single filers making more than $70,000 and joint filers making more than $145,000, the deduction begins to phase out.
- If your income falls in the phase-out range, you’ll need to calculate how much you can claim.
- To calculate the amount you can claim, subtract either $70,000 (or $145,000 for joint filers) from your annual income and then divide by $15,000 (or $30,000 for joint filers).
- Next, multiply the resulting sum by the amount of student loan interest you paid.
- Finally, subtract that figure from the total student interest you paid or $2,500 to get the amount you can actually claim on your return.
- For instance, a single filer earning $78,000 who paid $800 in student loan interest would only be able to deduct about $373 from their taxable income thanks to the phase-out reduction.
- If you use tax software to file your return, most will automatically complete this calculation, sparing you the math exercise, says Walker.
Note: (link: https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p970.pdf text: IRS publication 970) provides a full breakdown with examples of how to complete this calculation.
Common mistakes to avoid when filing
When you receive Form 1098-E, it's important to review the information carefully to ensure that it's accurate. Common mistakes to watch out for include:
- Incorrect loan balance: Make sure the loan balance reported on Form 1098-E is correct.
- Incorrect interest amount: Make sure the interest amount reported on Form 1098-E is correct.
- Multiple loans: If you have multiple student loans, make sure that the interest paid on each loan is accurately reported on Form 1098-E.
What to do if you encounter an issue?
If you discover an error on Form 1098-E, you should contact the entity that services your loan to have the error corrected. If you don't receive Form 1098-E, you should contact the entity that services your loan to request a copy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Form 1098-E is an important tax form that reports the amount of interest paid on qualified student loans during the tax year. If you paid $600 or more in interest on a qualified student loan, you will receive a Form 1098-E from the entity that services your loan. The entity that services your loan is required to file Form 1098-E with the IRS and provide a copy to you. It's important to review the information on Form 1098-E carefully to ensure that it's accurate. If you encounter an issue, you should contact the entity that services your loan to have it corrected.


