- IRS forms
- Form 1095-C
Form 1095-C: Employer-Provided Health Insurance Offer and Coverage
Download Form 1095-CIntroduction
Are you confused about how to file your taxes with Form 1095-C? Don't worry, you're not alone. Filing taxes can be a daunting task, especially when you're dealing with healthcare coverage. But with the right information and guidance, you can navigate the process with ease.
In this blog, we will provide a comprehensive guide on Form 1095-C and how to file your federal taxes using this form. We'll cover everything you need to know, including who needs to file, how to file, when to file, and common mistakes to avoid. Whether you're a first-time filer or a seasoned pro, this guide will help you maximize your tax benefits and avoid costly mistakes.
By the end of this blog, you'll have a clear understanding of how to use Form 1095-C to file your taxes and take advantage of the tax benefits provided by your employer's health coverage. So, let's dive in and unlock the benefits of Form 1095-C.
What is Form 1095-C?
Form 1095-C is a tax form used to report information about an employer's offer of health insurance coverage to their employees. It includes details such as the months of coverage, the employee's share of the premium, and any other relevant information. The form is filed with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) by employers who are subject to the Affordable Care Act's (ACA) employer-shared responsibility provisions.
Who Needs to File Form 1095-C?
Employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees are required to file Form 1095-C with the IRS. This includes both for-profit and non-profit organizations. The form is also provided to each employee who was eligible for employer-provided health insurance coverage during the year, regardless of whether they enrolled in the coverage or not.
Steps on How to File Form 1095-C
To file Form 1095-C, employers must follow these steps:
- Collect and verify the required information: Employers must collect and verify information about their employees, such as their names, social security numbers, and employment status, to ensure that the form is completed accurately.
- Complete Form 1095-C: Employers must fill out the form for each eligible employee, including details such as the months of coverage, the employee's share of the premium, and any other relevant information.
- File Form 1095-C with the IRS: Employers must file Form 1095-C with the IRS, along with Form 1094-C, which is a transmittal form that summarizes the information provided on all of the employer's Forms 1095-C.
- Provide a copy of Form 1095-C to employees: Employers must also provide a copy of Form 1095-C to each employee who was eligible for employer-provided health insurance coverage during the year, regardless of whether they enrolled in the coverage or not.
When to File Form 1095-C
Employers must file Form 1095-C with the IRS by the last day of February if filing by paper or March 31st if filing electronically. Employers must also provide a copy of the form to their employees by January 31st.
Specific Instruction for filing Form 1095-C
Part I - Employee:
Line 1: Provide the employee's full name, including their first name, middle initial, and last name.
Line 2: Enter the employee's Social Security number, including the dashes and all nine digits.
Lines 3-6: Enter the employee's full address, including their apartment number if applicable. A country code is not necessary for addresses within the United States.
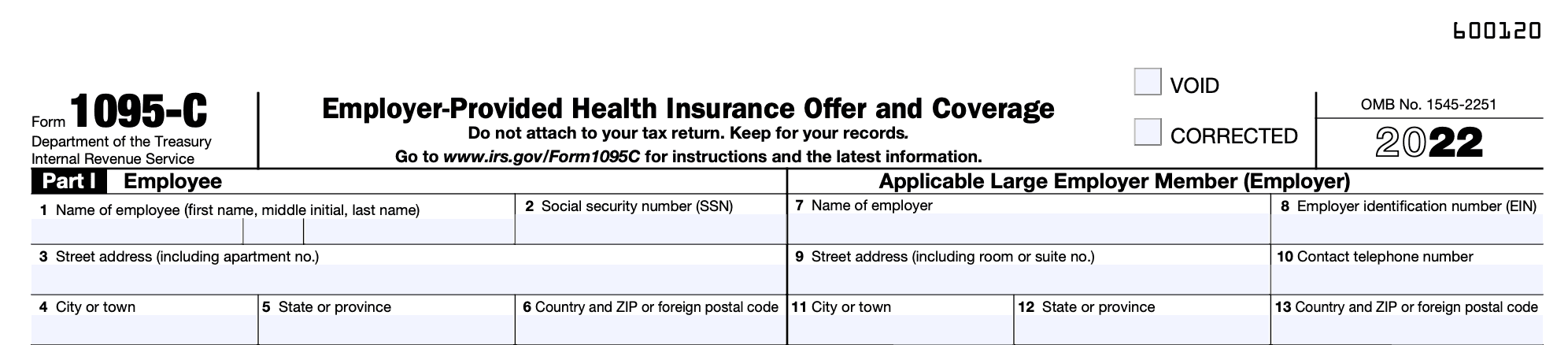
Applicable Large Employer Member (Employer):
Line 7: Enter the name of the Applicable Large Employer (ALE) Member.
Line 8: Enter the ALE Member's Employer Identification Number (EIN), which is a nine-digit number with a dash included. Do not use the Social Security number for this field. The ALE Member's name and EIN should match the information provided on lines 1 and 2 of Form 1094-C.
Note: When filing Form 1095-C, it is crucial to provide a valid EIN. Failure to do so will result in the non-processing of the form. If you do not have an EIN, you can apply for one online through the IRS website at IRS.gov/EIN.
Lines 9 and 11-13: Input the Applicable Large Employer (ALE) Member's full address, including their room or suite number if applicable. It should match the address listed on lines 3-6 of Form 1094-C.
Line 10: Provide the phone number of the person who recipients may call for any inquiries regarding the information provided on the form. This phone number may differ from the contact information listed on line 8 of Form 1094-C.
Part II - Employee Offer of Coverage
Part II of Form 1095-C is used to report whether an employer offered health insurance coverage to an employee and their dependents. Here's a breakdown of the different lines to be completed:
- Line 14: This line requires the employer to indicate whether or not they offered coverage to the employee and their dependents for each month of the year. If coverage was offered, the employer must move on to Lines 15-17 to provide more details.
- Line 15: This line requires the employer to indicate the type of coverage that was offered to the employee (such as self-only, spouse, dependents, or family coverage).
- Line 16: This line requires the employer to indicate the lowest-cost monthly premium for self-only coverage that was offered to the employee. This information is important because it's used to determine whether the coverage was considered affordable under the Affordable Care Act.
- Line 17: This line requires the employer to indicate whether or not the employee was enrolled in the coverage that was offered. If the employee was enrolled, the employer must provide the start and end dates of the coverage. If the employee was not enrolled, the employer must provide a code indicating why the employee declined the coverage.
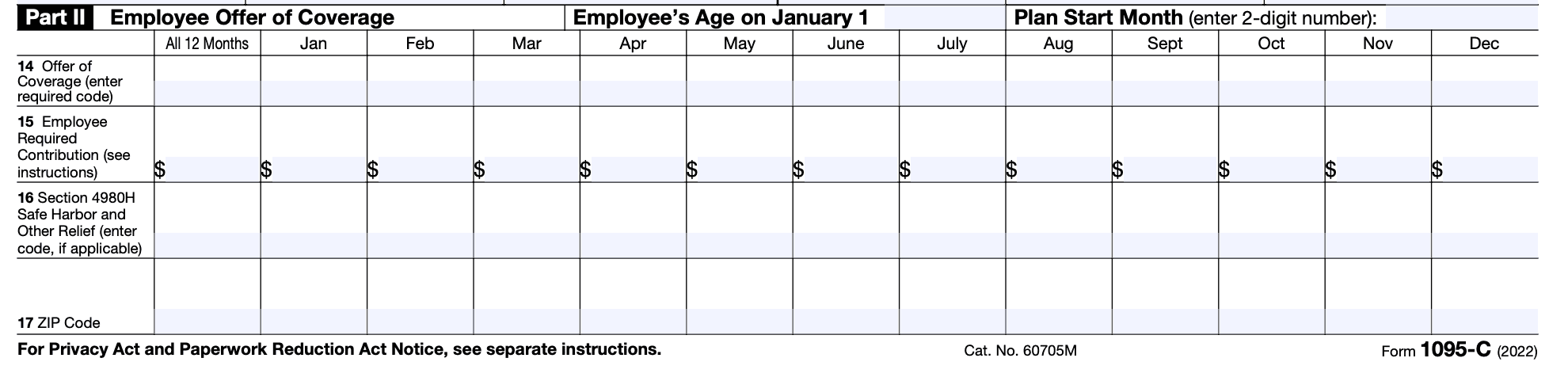
It's important to fill out Part II of the form accurately, as it helps the IRS determine if the employee is eligible for a premium tax credit when purchasing coverage through a Marketplace.
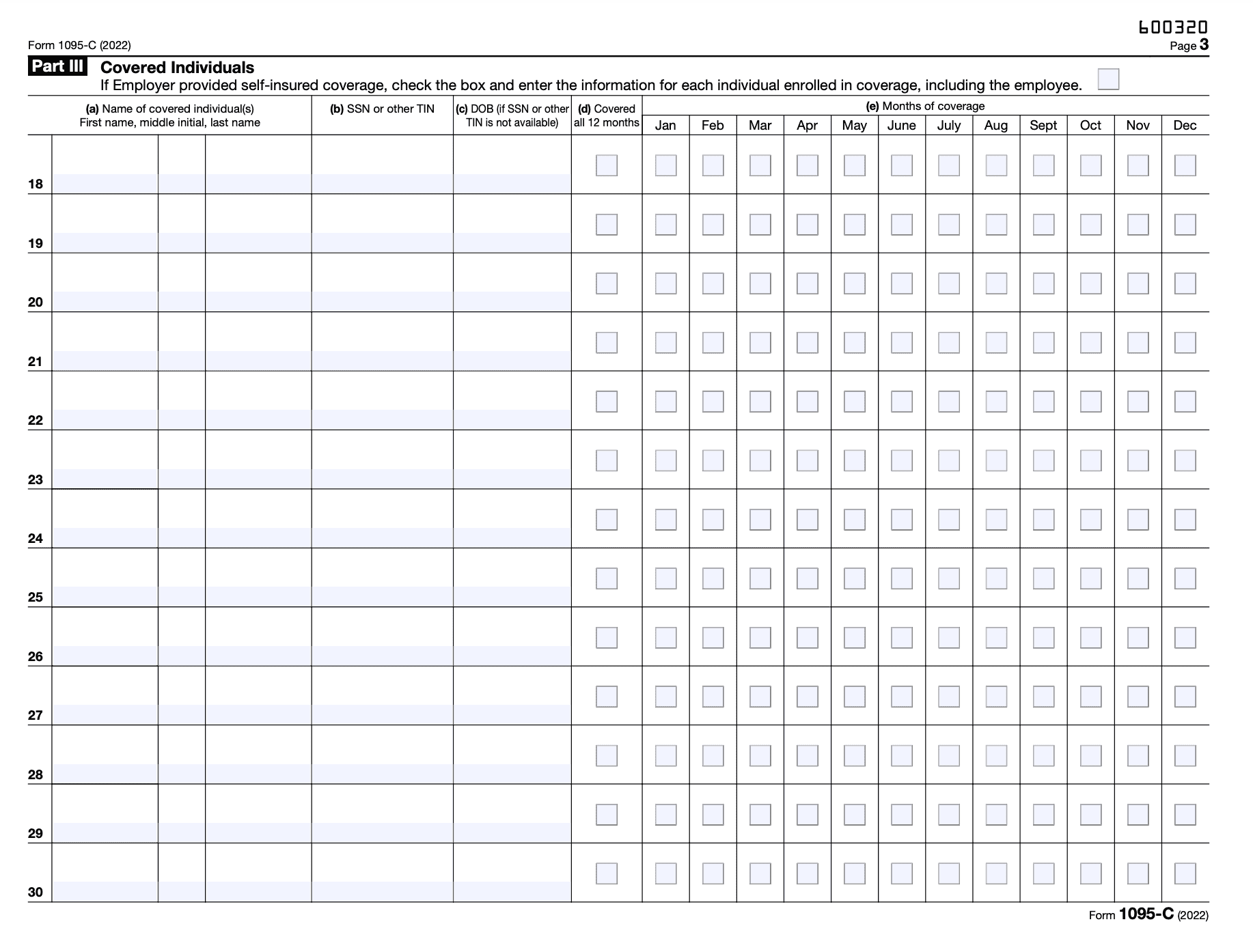
Part III—Covered Individuals
- Line 18: This line requires the employer to indicate whether or not the employee was covered under the employer-sponsored health insurance plan for each month of the year. If the employee was covered, the employer must move on to Lines 19-24 to provide more details.
- Lines 19-22: These lines require the employer to provide the name, SSN, and the months in which each covered individual (such as the employee's spouse or dependent children) was covered under the employer-sponsored health insurance plan.
- Line 23: This line requires the employer to indicate the type of coverage that was offered to each covered individual (such as self-only, spouse, dependents, or family coverage).
- Line 24: This line requires the employer to indicate the months in which the coverage was in effect for each covered individual.
- Lines 25-30: These lines require the employer to provide the name and SSN of each individual who was covered under the employer-sponsored health insurance plan for at least one day during the calendar year, but who was not an employee for any month of the year. This could include retirees or COBRA beneficiaries.
Important Information People Miss To Update
- Incorrect or incomplete personal information of the employee or ALE member, such as name, SSN or EIN, and address.
- Failure to report the offer of health coverage to employees for each month.
- Incorrect or incomplete information on line 16 regarding the employee's cost of coverage or the employer's contributions.
- Missing information on lines 14 and 15, which reports the months during which coverage was offered and whether it was provided to the employee's spouse and dependents.
- Failing to report changes in employment status or eligibility for health coverage during the year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing
Some common mistakes to avoid when filing Form 1095-C include:
- Failing to report all required information: Employers must ensure that all required information is reported accurately, including the months of coverage, the employee's share of the premium, and any other relevant information.
- Filing the wrong version of the form: Employers should ensure that they are using the correct version of the form for the year being reported.
- Failing to file on time: Employers must file Form 1095-C with the IRS and provide a copy to their employees by the respective deadlines.
What to Do if You Encounter an Issue
If you encounter an issue when filing Form 1095-C, you should contact the IRS for assistance. The IRS provides a range of resources, including phone support and online guidance, to help employers with their tax filing obligations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, filing Form 1095-C is an important part of the tax process for applicable large employers and their employees. By providing accurate information regarding employee health coverage, employers can help ensure that employees receive the necessary tax credits and avoid any potential penalties. Remember to carefully review and double-check all information before submitting the form, and don't hesitate to reach out to the IRS if you encounter any issues or have questions. By following these steps and taking the necessary precautions, you can ensure a smooth filing process and help ensure compliance with the Affordable Care Act.


