Net Income Formula: Calculate, Improve, and Maximize Profitability
Net income, known as the “bottom line,” measures a business’s profitability after all expenses are deducted from revenue. This key financial metric helps business owners make informed decisions, attract investors, and plan for sustainable growth. Calculating net income reveals true financial health, while strategies like increasing revenue, cutting costs, and optimizing taxes can help improve it. Mastering net income empowers businesses to strengthen profitability and drive future success.
Introduction
Calculating and understanding net income is essential for any business owner. Net income, often referred to as the “bottom line,” is a key indicator of profitability, showing how much profit remains after accounting for all expenses. Whether you’re running a small business or managing a growing enterprise, understanding how to calculate and interpret net income can guide financial decisions, optimize profitability, and support sustainable growth.
This guide will explain the net income formula, its components, its importance, and actionable strategies to improve net income.
What is Net Income?
Net income, also known as “net earnings” or “profit,” is the amount of money left after all expenses have been subtracted from total revenue. It’s a comprehensive measure of profitability as it includes all business expenses, from operating costs to taxes and non-operating expenses, giving a realistic view of financial health. In essence, net income helps answer, “Is my business profitable after covering all expenses?”
Why Net Income is Important for Financial Analysis
Tracking net income regularly provides insight into your business’s financial health. Here’s why net income is critical:
• Evaluates Profitability: Net income shows how much profit remains after covering all expenses.
• Attracts Investors and Lenders: Investors gauge profitability through net income to assess future growth potential. For lenders, net income reflects a business’s ability to meet debt obligations.
• Guides Decision-Making: Positive net income enables reinvestment, expansion, and strategic decisions. Negative net income might signal a need to cut costs.
• Supports Tax Planning: Calculating net income helps ensure compliance with tax laws, making it easier to plan for tax obligations and take advantage of deductions.
Net-Income Formula
The net income formula is straightforward:
Net Income = Total Revenue - Total Expenses
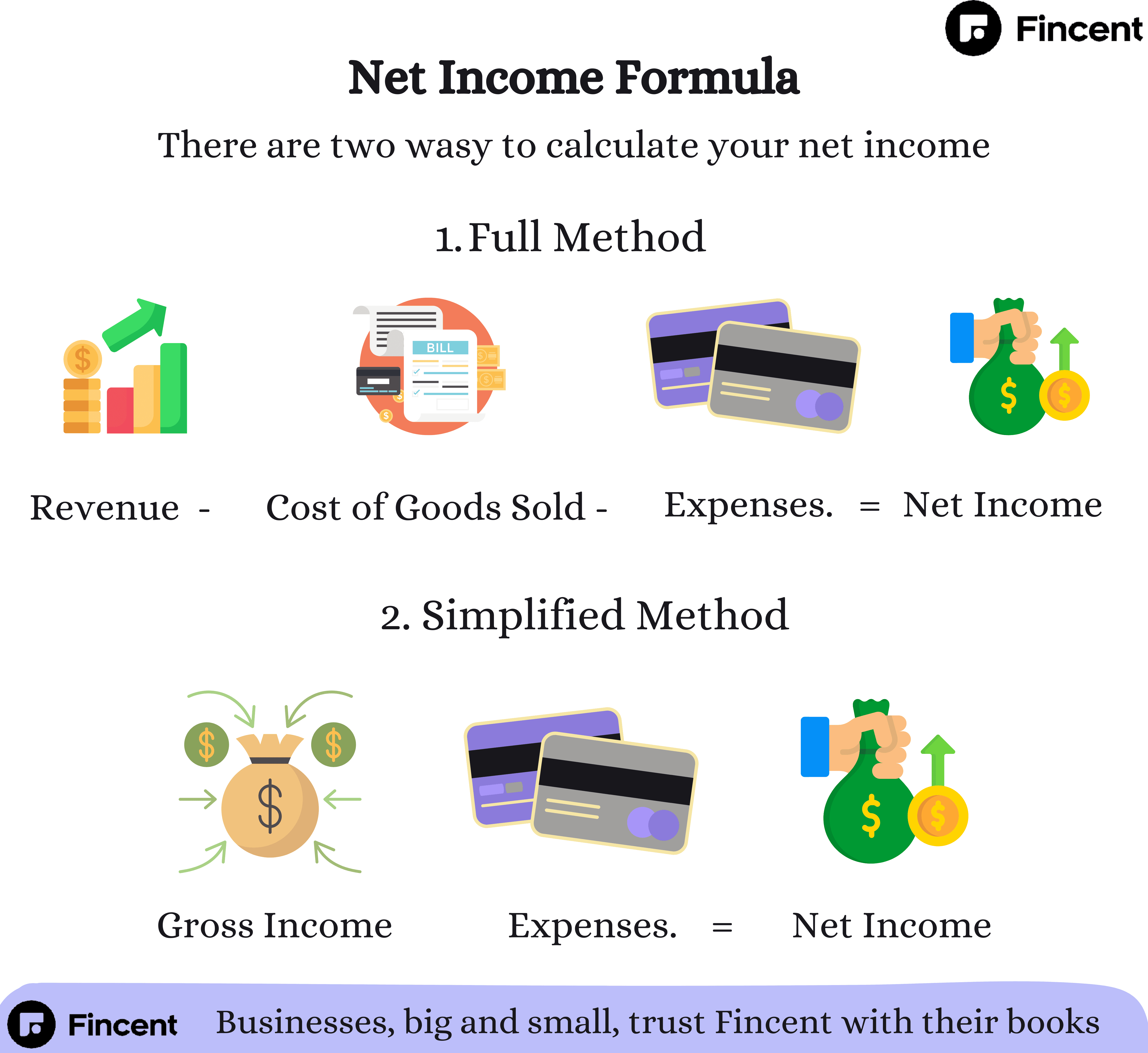
Where:
• Total Revenue is the total earnings from sales, services, or other business income.
• Total Expenses include all operating and non-operating costs, such as wages, rent, utilities, interest payments, and taxes.
Breaking Down the Net-Income Formula
1. Total Revenue
Total revenue is the sum of all income generated by the business, also known as gross income. Key sources include:
• Sales Revenue from products or services
• Investment Income from dividends or interest
• Other Income Streams like rental income or royalties
To calculate total revenue, add up all income sources within the reporting period.
2. Total Expenses
Expenses are the costs associated with running the business and are divided into two main categories:
• Operating Expenses: Daily business costs, such as wages, rent, and office supplies.
• Non-Operating Expenses: Expenses unrelated to core business activities, like interest on loans, taxes, or one-time costs (e.g., equipment).
By subtracting all expenses from revenue, you calculate net income.
Net-Income Formula: An Example Calculation
Let’s look at an example. Imagine your business earned $500,000 in revenue last year. After totaling up operating and non-operating expenses at $350,000, the net income calculation would be:
Net Income = $500,000 (Total Revenue) - $350,000 (Total Expenses) = $150,000
This means your business generated $150,000 in profit after covering all costs.
Net Income vs. Gross Income: Key Differences
It’s essential to distinguish between net income and gross income:
• Gross Income: The total revenue before any expenses are deducted. In equation form:
Gross Income = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
• Net Income: The profit remaining after all expenses (both operating and non-operating) are deducted from gross income.
For example, if your gross income is $500,000 and expenses are $350,000, your net income would be $150,000.
Operating Net Income and Its Formula
Operating income, also called EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes), is a profitability measure that excludes non-operating expenses to show profits solely from core operations. Here’s how to calculate it:
Operating Net Income = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses - Depreciation - Amortization
Operating net income is useful for comparing profitability across similar companies by focusing solely on core business operations.
Example of Operating Net Income Calculation
Returning to the previous example, if your net income for the quarter is $20,000 and you have an interest expense of $1,000, your operating net income would be:
Operating Net Income = $20,000 (Net Income) + $1,000 (Interest Expense) = $21,000
Using Net Income to Drive Business Decisions
Regularly calculating and analyzing net income helps you:
• Track Profitability Trends: Monitoring net income over time shows if your business is growing, stagnating, or declining.
• Inform Strategic Planning: Positive net income gives financial flexibility to invest in growth initiatives.
• Identify Problem Areas: Lower-than-expected net income may reveal inefficiencies or excessive costs, allowing adjustments to improve financial performance.
How to Improve Net Income
Improving net income can boost profitability and stability. Here are some strategies:
1. Increase Revenue
Consider methods such as:
• Expanding into New Markets: Exploring new customer segments.
• Upselling and Cross-Selling: Encouraging customers to buy additional or premium products.
• Introducing New Products or Services: Diversifying offerings to attract more customers.
2. Reduce Operating Costs
Cutting costs can improve profitability. Possible strategies include:
• Renegotiating Supplier Contracts: Seeking bulk discounts or better terms.
• Implementing Cost-Saving Technologies: Automating tasks to improve efficiency.
• Streamlining Operations: Eliminating unnecessary processes.
3. Optimize Tax Strategies
Effective tax planning reduces taxable income and boosts net income. Try:
• Leveraging Deductions: Working with a tax advisor to maximize allowable deductions.
• Using Tax-Deferred Accounts: Setting up accounts to lower taxable income.
• Timing Major Purchases: Aligning expenses with tax strategies to minimize taxes.
4. Review Pricing Strategies
Reevaluating your pricing model can increase revenue. Raising prices—if justifiable—can directly improve net income.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How is net income different from cash flow?
Net income reflects profits after expenses, while cash flow shows money entering and leaving the business. Net income includes non-cash expenses like depreciation, which don’t affect cash flow.
2. Why is net income called the “bottom line”?
Net income appears as the last line on an income statement, showing final profits after all expenses.
3. How often should I calculate net income?
Businesses typically calculate net income monthly, quarterly, and annually to track profitability.
4. Can I improve net income without increasing revenue?
Yes, by reducing expenses and optimizing tax strategies, it’s possible to increase net income without raising revenue.
5. What factors can cause fluctuations in net income?
Net income can fluctuate due to changes in revenue, rising operational costs, market conditions, tax adjustments, or shifts in non-operating expenses.
Conclusion
Net income is fundamental for understanding a business’s profitability and guiding key financial decisions. By mastering the net income formula, differentiating between gross and net income, and learning strategies to improve profitability, business owners can position themselves for sustainable growth and success.
Related articles
How to do bookkeeping for real estate business
Keeping track of real-estate investments/businesses’ financial health helps you be profitable, receive tax benefits, and make sound financial decisions in difficult times.
Read moreFounder’s Guide to Annual Financial Planning
Learn what financial planning is, why it matters, and its key components to help your business grow better.
Read more