- Glossary
- Discounted Cash Flow
Discounted Cash Flow
A valuation technique known as "discounted cash flow" (DCF) determines an investment's value based on its projected future cash flows. DCF analysis aims to assess the value of an investment today by using projections of how much money an investment will generate in the future.
It can help people who are attempting to choose between buying securities or a company. Discounted cash flow analysis is a tool that business owners and managers can use to guide their decisions on operational and capital budgets.
What Is The Discounted Cash Flow DCF Formula?
The discounted cash flow is calculated as the sum of the cash flow for each period divided by one plus the discount rate (WACC) raised to the power of the period number.
Here is the DCF formula:
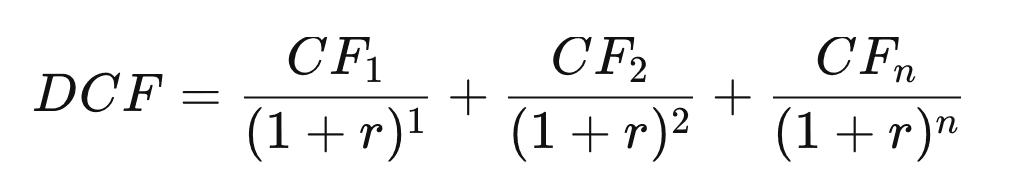
Where:
CF = Cash Flow in the Period
r = the interest rate or discount rate
n = the period number
Analyzing The Components Of The Formula
1. Cash Flow (CF)
The net cash payments an investor receives for owning a specific security during a specific time period are represented by cash flow (CF) (bonds, shares, etc.)
Unlevered free cash flow is commonly used as the CF when creating a financial model of a business. The CF would be interest and/or principal payments when pricing a bond.
2. Discount Rate (r)
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of a company is often used as the discount rate for business appraisal purposes (WACC). WACC is used by investors since it illustrates the required rate of return on their investment in the company.
The discount rate for a bond would be the same as the security's interest rate.
3. Period Number (n)
There is a time period associated with each cash flow. The most frequent time units are months, quarters, and years. The time periods could be comparable or completely different. If they are different, they are shown as a percentage of a year.
What Is The DCF Formula Used For?
The value of a company or investment is calculated using the DCF formula. It displays the price an investor would be prepared to pay for an investment given a required rate of return on investment (the discount rate).
Examples of Uses for the DCF Formula:
- To value an entire business
- To value a project or investment within a company
- To value a bond
- To value shares in a company
- To value an income-producing property
- To value the benefit of a cost-saving initiative at a company


